Jing Si Fa [2024] No.14
District Justice Bureau, Beijing Economic and Technological Development Zone Ping An Office, and all offices of the Municipal Bureau:
The benchmark of administrative discretion in Beijing judicial administrative system (administrative license, administrative inspection, administrative confirmation, administrative payment) (for Trial Implementation) has been considered and passed by the third director’s office meeting in 2024, and is hereby issued, please follow it.
Beijing Municipal Bureau of Justice
April 7, 2024
Benchmarks of administrative discretion in Beijing judicial administrative system (administrative licensing, administrative inspection, administrative confirmation and administrative payment) (for Trial Implementation)
First, the administrative licensing discretion benchmark
1. License for the establishment of law firm
1.1. Setting basis
Article 18 of the Lawyers Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) (revised in 2017).
1.2. Implementation subject
The district judicial bureau conducts the first trial and the municipal judicial bureau conducts the final trial.
1.3. Licensing conditions
Articles 14, 15, 16 and 17 of the Lawyers Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) (revised in 2017);
Articles 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16 and 17 of the Administrative Measures for Law Firms (revised in 2018);
Articles 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 19, 20, 21 and 22 of the Detailed Rules for the Administration of Beijing Law Firm (J.S.F. [2021] No.18).
1.4. Application materials
A. an application for the establishment of a law firm;
B. Notice of pre-approval of the name of the law firm;
C. Articles of association of the law firm;
D. proof of residence or letter of commitment;
E. asset certificate or letter of commitment;
F. A copy of the lawyer’s practice certificate of the founder;
G. Partnership agreement, person in charge of law firm (partnership office), etc.
1.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
1.6. Approval process
1.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or inconsistent with the statutory form, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within five days from the date of receiving the application materials. If the applicant makes corrections as required, it shall be accepted; Fails to inform, since the date of receipt of the application materials is accepted;
C. If the application matters obviously do not meet the statutory requirements or the applicant refuses to make corrections or cannot make corrections to the relevant materials, the application shall not be accepted, and the reasons shall be explained in writing to the applicant.
1.6.2. Review and decision
A. Issue examination opinions on whether the application for establishing a law firm meets the statutory conditions and whether the materials are true and complete. If the establishment is approved, the practice license of the law firm shall be issued. If the establishment is not approved, the reasons shall be explained in writing to the applicant.
B approvals and certificates: the decision on approving the establishment of a law firm and the practice license of the law firm (original and duplicate).
1.7. Charges
No charge.
1.8. Quantitative restrictions
No restrictions.
1.9. Annual inspection report
Article 59 of the Measures for the Administration of Law Firms.
2. Law firm change license
2.1. Setting basis
Article 21 of the Lawyers Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) (revised in 2017).
2.2. Implementation subject
The district judicial bureau conducts the first trial and the municipal judicial bureau conducts the final trial.
2.3. Licensing conditions
Article 21 of the Lawyers Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) (revised in 2017);
Articles 26, 28, 29 and 30 of the Administrative Measures for Law Firms (revised in 2018);
Articles 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38 and 43 of the Detailed Rules for the Implementation of the Measures for the Administration of Beijing Law Firm (J.S.F. [2021] No.18).
2.4 Application materials
2.4.1. Change the name
A. application for change of name of law firm;
B. Notice of pre-approval of the name of the law firm;
C practice license of law firm (original and duplicate).
2.4.2. Change of Articles of Association
A. application for change of articles of association;
B. the newly revised articles of association of the law firm;
2.4.3. Change the partnership agreement
A. application for change of partnership agreement;
B. the newly revised partnership agreement of law firms;
2.4.4. Person in charge of change
A. application for change of person in charge;
B. Practice license of law firm (original and duplicate).
2.4.5. Change the organizational form
A. Application for change of organizational form, changed articles of association and partnership agreement of the law firm (only the changed articles of association of the law firm is required to be submitted when applying for change to an individual law firm), and capital verification report or commitment letter of registered assets conforming to the changed organizational form;
B. Practice license of law firm (original and duplicate).
2.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
2.6. Approval process
2.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or inconsistent with the statutory form, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within five days from the date of receiving the application materials. If the applicant makes corrections as required, it shall be accepted; Fails to inform, since the date of receipt of the application materials is accepted;
C. If the application matters obviously do not meet the statutory requirements or the applicant refuses to make corrections or cannot make corrections to the relevant materials, the application shall not be accepted, and the reasons shall be explained in writing to the applicant.
2.6.2. Review and decision
A. Review the application materials after accepting them, and form review opinions. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, a decision shall be made to approve the change.
B. Approval and certificate: the decision on approving the change of the law firm and the practice license of the law firm (original and copy).
2.7. Charges
No charge.
2.8. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
2.9. Annual inspection report
Article 59 of the Measures for the Administration of Law Firms.
3. Law firms cancel their licenses.
3.1. Setting basis
Article 22 of the Lawyers Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) (revised in 2017).
3.2. Implementation subject
The district judicial bureau conducts the first trial and the municipal judicial bureau conducts the final trial.
3.3. Licensing conditions
Article 22 of the Lawyers Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) (revised in 2017);
Article 31 of the Administrative Measures for Law Firms (revised in 2018);
Article 46 of the Detailed Rules for the Implementation of the Administrative Measures of Beijing Law Firm (J.S.F. [2021] No.18).
3.4 Application materials
A. Application for cancellation of law firm
B. liquidation report
C. Press announcements
D practice license of law firm (original and duplicate).
3.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
3.6. Approval process
3.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or inconsistent with the statutory form, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within five days from the date of receiving the application materials. If the applicant makes corrections as required, it shall be accepted; Fails to inform, since the date of receipt of the application materials is accepted;
C. If the application matters obviously do not meet the statutory requirements or the applicant refuses to make corrections or cannot make corrections to the relevant materials, the application shall not be accepted, and the reasons shall be explained in writing to the applicant.
3.6.2. Review and decision
A. Review whether the application for the establishment of a law firm meets the statutory conditions and whether the materials are true and complete. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, a decision shall be made to approve the cancellation.
B. Approval: Decision on agreeing to cancel the law firm.
3.7. Charges
No charge.
3.8. Quantitative restrictions
No restrictions.
3.9. Annual inspection report
Not involved.
4. License for the establishment of branch offices of law firms
4.1. Setting basis
Article 19 of the Lawyers Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) (revised in 2017).
4.2. Implementation subject
The district judicial bureau conducts the first trial and the municipal judicial bureau conducts the final trial.
4.3. Licensing conditions
Article 19 of the Lawyers Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) (revised in 2017);
Articles 33, 34 and 35 of the Administrative Measures for Law Firms (revised in 2018);
Articles 50, 51 and 52 of the Detailed Rules for the Implementation of the Measures for the Administration of Beijing Law Firms (J.S.F. [2021] No.18).
4.4 Application materials
4.4.1. Beijing Branch of Law Firms from Other Provinces and Cities
A. Tips on the risk of handling the follow-up procedures of the newly established law firm Beijing Branch
B. Application for the establishment of Beijing Branch of a law firm from other provinces and cities
C. Measures for the administration of branch offices of law firms formulated by the General Office
D. Materials used for residence of Beijing Branch of law firms from other provinces and cities
E. Capital materials for the establishment of a branch of a provincial law firm in Beijing.
F. Letter of Commitment on the Application for the Establishment of Beijing Branch of Law Firms from Other Provinces and Cities
G power of attorney issued by the head office to the person in charge of the branch office
H. List of lawyers accredited by the Head Office in Beijing Branch
I. People’s Republic of China (PRC) lawyer’s practice certificate of lawyers accredited by the Head Office in Beijing Branch.
J. Resident ID card of the People’s Republic of China for lawyers sent by Beijing Branch of the Head Office
4.4.2. Beijing Law Firm City Branch
A. Tips on the risk of follow-up procedures for law firms to set up branches in the same city
B. Application for branch office in the same city
C measures for the administration of branch offices of law firms in the same city formulated by the general office
D. materials used in the residence of the same city branch
E. Capital materials for setting up branches in the same city branch
F power of attorney issued by the head office to the person in charge of the branch office
4.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
4.6. Approval process
4.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or inconsistent with the statutory form, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within five days from the date of receiving the application materials. If the applicant makes corrections as required, it shall be accepted; Fails to inform, since the date of receipt of the application materials is accepted;
C. If the application matters obviously do not meet the statutory requirements or the applicant refuses to make corrections or cannot make corrections to the relevant materials, the application shall not be accepted, and the reasons shall be explained in writing to the applicant.
4.6.2. Review and decision
A. Review whether the application for the establishment of a law firm meets the statutory conditions and whether the materials are true and complete. If the establishment is approved, the practice license of the law firm shall be issued. If the establishment is not approved, the reasons shall be explained in writing to the applicant.
B approvals and certificates: the decision on approving the Beijing branch of a foreign law firm and the decision on approving the same city branch; Practice license of law firm branch (original and copy).
4.7. Charges
No charge.
4.8. Quantitative restrictions
No restrictions.
4.9. Annual inspection report
Article 59 of the Measures for the Administration of Law Firms.
5. Change of license of branch office of law firm
5.1. Setting basis
Article 19 of the Lawyers Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) (revised in 2017).
5.2. Implementation subject
The district judicial bureau conducts the first trial and the municipal judicial bureau conducts the final trial.
5.3. Licensing conditions
Articles 19 and 21 of the Lawyers Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) (revised in 2017);
Article 38 of the Administrative Measures for Law Firms (revised in 2018);
Articles 55, 56 and 57 of the Detailed Rules for the Implementation of the Administrative Measures of Beijing Law Firm (J.S.F. [2021] No.18).
5.4. Application materials
5.4.1. Change the branch name
A. an application for changing the name of a branch of a law firm;
B. approve the decision of changing the name of the law firm;
C. Practice license of law firm branch (original and copy).
5.4.2. Change the person in charge of the branch.
Application for change of person in charge.
5.4.3. Change of branch management measures
A. application for change of management measures of branch offices of law firms;
B. Measures for the administration of branch offices of law firms;
C capital materials for the establishment of branches (if one of the reasons for changing the management measures of branches is the change of registered capital, it needs to be provided).
5.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
5.6. Approval process
5.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or inconsistent with the statutory form, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within five days from the date of receiving the application materials. If the applicant makes corrections as required, it shall be accepted; Fails to inform, since the date of receipt of the application materials is accepted;
C. If the application matters obviously do not meet the statutory requirements or the applicant refuses to make corrections or cannot make corrections to the relevant materials, the application shall not be accepted, and the reasons shall be explained in writing to the applicant.
5.6.2. Review and decision
A. Review the application materials after accepting them, and form review opinions. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, a decision shall be made to approve the change.
B. Approval and certificate: the decision on approving the change of the branch office of the law firm and the practice license of the branch office of the law firm (original and copy).
5.7. Charges
No charge.
5.8. Quantitative restrictions
No restrictions.
5.9. Annual inspection report
Not involved.
6. Cancellation of license of law firm branch
6.1. Setting basis
Article 22 of the Lawyers Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) (revised in 2017).
6.2. Implementation subject
The district judicial bureau conducts the first trial and the municipal judicial bureau conducts the final trial.
6.3. Licensing conditions
Article 22 of the Lawyers Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) (revised in 2017);
Article 39 of the Administrative Measures for Law Firms (revised in 2018);
Article 58 of the Detailed Rules for the Implementation of the Administrative Measures of Beijing Law Firm (J.S.F. [2021] No.18).
6.4 Application materials
A. application for cancellation of law firm;
B. liquidation report;
C. press announcements;
D practice license of law firm (original and duplicate).
6.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
6.6. Approval process
6.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or inconsistent with the statutory form, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within five days from the date of receiving the application materials. If the applicant makes corrections as required, it shall be accepted; Fails to inform, since the date of receipt of the application materials is accepted;
C. If the application matters obviously do not meet the statutory requirements or the applicant refuses to make corrections or cannot make corrections to the relevant materials, the application shall not be accepted, and the reasons shall be explained in writing to the applicant.
6.6.2. Review and decision
A. Review whether the application for the establishment of a law firm meets the statutory conditions and whether the materials are true and complete. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, a decision shall be made to approve the cancellation.
B. Approval: Decision on agreeing to cancel the branch office of the law firm.
6.7. Charges
No charge.
6.8. Quantitative restrictions
No restrictions.
6.9. Annual inspection report
Not involved.
7. Lawyer’s practice license
7.1. Setting basis
Article 6 of the Lawyers Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) (revised in 2017).
7.2. Implementation subject
The district judicial bureau conducts the first trial and the municipal judicial bureau conducts the final trial.
7.3. Licensing Conditions
Articles 5, 7 and 8 of the Lawyers Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) (revised in 2017);
"Decision of the State Council Municipality on Setting Administrative License for Administrative Examination and Approval Items that Need to Be Retained" (Order No.671st of the State Council), item 70 of the annex;
Articles 6, 7, 8 and 9 of the Administrative Measures for Lawyers’ Practice (revised in 2016);
Articles 2, 3, 6, 12 and 14 of the Measures for the Administration of Lawyers Profession in the Mainland by Residents of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region and the Macao Special Administrative Region who have obtained legal professional qualifications in the Mainland (revised in 2013);
Articles 2, 4 and 5 of the Measures for the Administration of Lawyers’ Profession by Taiwan Province Residents with National Legal Professional Qualifications in the Mainland (revised in 2017);
Articles 6, 7 and 8 of the Detailed Rules for the Implementation of the Measures for the Administration of Lawyers’ Practice in Beijing (J.S.F. [2021] No.66).
7.4 Application materials
A. lawyer’s practice application and letter of commitment;
B. legal professional qualification certificate or lawyer qualification certificate;
C. To apply for practicing as a lawyer for the first time, it shall submit the internship assessment materials issued by the Municipal Lawyers Association; To re-apply for practicing as a lawyer, it shall submit the materials that the applicant has passed the examination issued by the Municipal Lawyers Association;
D. identification of the applicant.
Note:
1. To apply for practicing as a part-time lawyer, in addition to the above materials, a commitment letter for practicing as a part-time lawyer and an opinion issued by the applicant’s unit agreeing to engage as a part-time lawyer shall also be submitted.
2. Residents of Hong Kong and Macao Special Administrative Regions who have obtained legal professional qualifications in the Mainland apply for practicing law in the Mainland. In addition to the above materials, they should also submit a copy of their identity certificates notarized by a notary public recognized in the Mainland and proof materials that they have not been subjected to criminal punishment, whether they are qualified as lawyers in Hong Kong, Macao, Taiwan Province or foreign countries and whether they are employed by Hong Kong, Macao, Taiwan Province or foreign law firms. Those who are Hong Kong legal practitioners and Macao lawyers with more than five years’ practice experience should also submit the certificate of the applicant’s practice experience and years in Hong Kong and Macao, which is issued by the Hong Kong Law Society, the Bar Association or the Macao Law Society and notarized by a notary public recognized by the mainland.
3. Taiwan Province residents who have obtained the national legal professional qualification to apply for practicing law in mainland China shall submit, in addition to the aforementioned materials, a letter of commitment for Taiwan Province residents to apply for practicing law in mainland China and a certificate notarized by a notary office in Taiwan Province that they have not been subjected to criminal punishment, whether they are qualified as lawyers in Taiwan Province, Hong Kong and Macao, and whether they are employed by a foreign law firm in Taiwan Province, Hong Kong and Macao.
7.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
7.6. Approval process
7.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or inconsistent with the statutory form, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within five days from the date of receiving the application materials. If the applicant makes corrections as required, it shall be accepted; Fails to inform, since the date of receipt of the application materials is accepted;
C. If the application matters obviously do not meet the statutory requirements or the applicant refuses to make corrections or cannot make corrections to the relevant materials, the application shall not be accepted, and the reasons shall be explained in writing to the applicant.
7.6.2. Review and decision
A issue review opinions on whether the applicant meets the statutory requirements and whether the submitted materials are true and complete. If the applicant is granted practice, a lawyer’s practice certificate shall be issued to the applicant. If the practice is not allowed, the reasons shall be explained in writing to the applicant.
B. Certificate: People’s Republic of China (PRC) lawyer’s practice certificate.
7.7. Charges
No charge.
7.8. Quantitative restrictions
No restrictions.
7.9. Annual inspection report
Not involved.
8. Lawyers change their licenses
8.1. Setting basis
Article 10 of the Lawyers Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) (revised in 2017).
8.2. Implementation subject
The district judicial bureau conducts the first trial and the municipal judicial bureau conducts the final trial.
8.3. Licensing Conditions
Articles 9 and 10 of the Lawyers Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) (revised in 2017);
Articles 20, 21, 22 and 23 of the Administrative Measures for Lawyers’ Practice (revised in 2016);
Articles 19, 20, 21, 23, 24 and 25 of the Detailed Rules for the Implementation of the Measures for the Administration of Lawyers’ Practice in Beijing (Jing Si Fa [2021] No.66).
8.4 Application materials
8.4.1. Lawyers change their practice institutions:
A. Personal letter of commitment for lawyers to change their institutions (if lawyers from other provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government apply to change their practice institutions, they shall also submit the acceptance notice of the applicant’s lawyer’s practice files and the examination materials for joining the Municipal Lawyers Association);
B. The labor contract and employment contract signed by the institution to be transferred to practice and the applicant (if applying for practicing as a part-time lawyer, a part-time lawyer’s commitment letter and the opinions of the unit where he works shall also be submitted).
8.4.2. Cancellation of lawyer’s practice certificate:
A. cancellation registration form stamped with the official seal of the law firm
B original lawyer’s practice certificate (if the original lawyer’s practice certificate is lost, the original statement of loss shall be submitted).
8.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
8.6. Approval process
8.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or inconsistent with the statutory form, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within five days from the date of receiving the application materials. If the applicant makes corrections as required, it shall be accepted; Fails to inform, since the date of receipt of the application materials is accepted;
C. If the application matters obviously do not meet the statutory requirements or the applicant refuses to make corrections or cannot make corrections to the relevant materials, the application shall not be accepted, and the reasons shall be explained in writing to the applicant.
8.6.2. Review and decision
A issue review opinions on whether the applicant meets the statutory requirements and whether the submitted materials are true and complete.
B. (Change) If the change is approved, the lawyer’s practice certificate shall be renewed for the applicant; If no change is made, the reasons shall be explained in writing to the applicant. (Cancellation) If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, a decision shall be made to approve the cancellation.
C. Approval or certificate: (change) People’s Republic of China (PRC) lawyer’s practice certificate; (Cancellation) Decision on Cancellation of Lawyer’s Practice Certificate.
8.7. Charges
No charge.
8.8. Quantitative restrictions
No restrictions.
8.9. Annual inspection report
Not involved.
9. Establishment of representative offices of Hong Kong and Macao law firms in the Mainland (including merger and division)
9.1. Setting basis
Article 34 of the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (the State Council Decree No.338);
Decision of the State Council on canceling and adjusting a number of administrative examination and approval items (Guo Fa [2014] No.27), item 6.
9.2. Implementation subject
Municipal justice bureau
9.3. Licensing Conditions
Articles 6, 7 and 8 of the Measures for the Administration of Representative Offices of Law Firms of Hong Kong and Macao Special Administrative Regions in the Mainland (revised in 2015).
9.4 Application materials
A. An application signed by the principal person in charge of the law firm for establishing a representative office and sending representatives. (The name of the representative office to be established shall be "Representative Office of XXX Law Firm (Chinese name of the law firm) in XXX (name of mainland city)")
B documents certifying that the law firm has been legally established in its special administrative region;
C the partnership agreement or articles of association of the law firm and the list of responsible persons and partners;
D the letter of authorization from the law firm to each proposed representative of the representative office, and the confirmation that the proposed chief representative is a partner of the law firm or a person with the same position;
E. The lawyer qualification of each proposed representative of the representative office and the certification documents that the proposed chief representative has been practicing outside the mainland for not less than 3 years and other proposed representatives have been practicing outside the mainland for not less than 2 years;
F certification documents issued by the lawyers association of the special administrative region where the law firm is located that all the proposed representatives of the representative office are members of the lawyers association in this region;
G. A certificate issued by the lawyer management agency of the special administrative region where the law firm is located that the law firm and the proposed representatives have not been subjected to criminal punishment and have not been punished for violating lawyers’ professional ethics and practice discipline.
9.5. Time limit for approval
The legal period is six months. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
9.6. Approval process
9.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete, the applicant shall be notified to supplement the materials within 15 days from the date of receiving the application materials. If the applicant completes the application materials within 3 months from the date of submitting the application materials for the first time, it shall be handled in accordance with the provisions of the preceding paragraph; If the applicant fails to complete the application materials within 3 months from the date of submitting the application materials for the first time, it shall make a decision of rejection and notify the applicant in writing within 15 days;
C. If the application matters obviously do not meet the statutory requirements or the applicant refuses to make corrections or cannot make corrections to the relevant materials, the application shall not be accepted, and the reasons shall be explained in writing to the applicant.
9.6.2. Review and decision
A. Review whether the applicant meets the statutory requirements and whether the submitted materials are true and complete. If the establishment is approved, a practice license shall be issued; If the license is not granted, the applicant shall be informed in writing of the reasons.
B certificate: the practice license (original and copy) of the mainland representative office of the law firm of Hong Kong and Macao Special Administrative Regions.
9.7. Charges
No charge.
9.8. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
9.9. Annual Review Report
Article 22 of the Measures for the Administration of Mainland Representative Offices of Law Firms of Hong Kong and Macao Special Administrative Regions.
10. Changes in the Mainland Representative Offices of Hong Kong and Macao Law Firms
10.1. Setting basis
Article 34 of the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (the State Council Decree No.338);
Decision of the State Council on canceling and adjusting a number of administrative examination and approval items (Guo Fa [2014] No.27), item 6.
10.2. Implementation subject
Municipal justice bureau
10.3. Licensing Conditions
Article 12 of the Measures for the Administration of Mainland Representative Offices of Law Firms of Hong Kong and Macao Special Administrative Regions.
10.4 Application materials
A. An application for name change of the representative offices of Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan law firms in the Mainland or China signed by the principal responsible persons of the law firms in Hong Kong and Macao Special Administrative Regions;
B notarized and certified documents that the name of the Hong Kong law firm has changed in this region.
10.5. Time limit for approval
The legal period is six months. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
10.6. Approval process
10.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete, the applicant shall be notified to supplement the materials within 15 days from the date of receiving the application materials. If the applicant completes the application materials within 3 months from the date of submitting the application materials for the first time, it shall be handled in accordance with the provisions of the preceding paragraph; If the applicant fails to complete the application materials within 3 months from the date of submitting the application materials for the first time, it shall make a decision of rejection and notify the applicant in writing within 15 days;
C. If the application matters obviously do not meet the statutory requirements or the applicant refuses to make corrections or cannot make corrections to the relevant materials, the application shall not be accepted, and the reasons shall be explained in writing to the applicant.
10.6.2. Review and decision
A. Review whether the applicant meets the statutory requirements and whether the submitted materials are true and complete. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, a decision shall be made to approve the change.
B certificate: the practice license (original and copy) of the mainland representative office of the law firm of Hong Kong and Macao Special Administrative Regions.
10.7. Charges
No charge.
10.8. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
10.9. Annual Report
Article 22 of the Measures for the Administration of Mainland Representative Offices of Law Firms of Hong Kong and Macao Special Administrative Regions.
11 cancellation of the representative offices of Hong Kong and Macao law firms in the Mainland
11.1. Setting basis
Article 34 of the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (the State Council Decree No.338);
Decision of the State Council on canceling and adjusting a number of administrative examination and approval items (Guo Fa [2014] No.27), item 6.
11.2. Implementation subject
Municipal justice bureau
11.3. Licensing conditions
Articles 13 and 14 of the Measures for the Administration of Mainland Representative Offices of Law Firms of Hong Kong and Macao Special Administrative Regions.
11.4 Application materials
Application for cancellation of the representative offices of Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan law firms in the Mainland or China signed by the principals of the law firms in Hong Kong and Macao Special Administrative Regions.
11.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
11.6. Approval process
11.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete, the applicant shall be notified to supplement the materials within 15 days from the date of receiving the application materials. If the applicant completes the application materials within 3 months from the date of submitting the application materials for the first time, it shall be handled in accordance with the provisions of the preceding paragraph; If the applicant fails to complete the application materials within 3 months from the date of submitting the application materials for the first time, it shall make a decision of rejection and notify the applicant in writing within 15 days;
C. If the application matters obviously do not meet the statutory requirements or the applicant refuses to make corrections or cannot make corrections to the relevant materials, the application shall not be accepted, and the reasons shall be explained in writing to the applicant.
11.6.2. Review and decision
A. Review whether the applicant meets the statutory requirements and whether the submitted materials are true and complete. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, a decision shall be made to approve the change.
B approval: the decision on agreeing to cancel the Beijing representative office of the law firm.
11.7. Charges
No charge.
11.8. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
11.9. Annual Report
Not involved.
12 Hong Kong and Macao law firms in the mainland representative offices stationed representatives (including the addition of new representatives)
12.1. Setting basis
Article 34 of the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (the State Council Decree No.338);
Decision of the State Council on canceling and adjusting a number of administrative examination and approval items (Guo Fa [2014] No.27), item 7.
12.2. Implementation subject
Municipal justice bureau
12.3. Licensing Conditions
Articles 6, 7, 8 and 12 of the Measures for the Administration of Representative Offices of Law Firms of Hong Kong and Macao Special Administrative Regions in the Mainland (revised in 2015).
12.4 Application materials
A. application for accredited representatives;
B the letter of authorization from the Hong Kong law firm to send the chief representative and representative to the representative office;
C confirmation that the proposed chief representative is a partner of the law firm (a person with the same position);
D. list of partners of the firm;
E. the documents of the lawyer’s qualification years;
F documents that the proposed representative of the representative office is a member of the domestic bar association;
G documents and translations issued on behalf of the judicial organs of the country of nationality (region) that the chief representative to be appointed and the representative have not been subjected to criminal punishment;
H a document issued by the lawyer management authority in the place where the representative practices that the proposed chief representative and representative have not been punished for violating lawyer’s professional ethics and practice discipline;
I. Representative’s practice risk insurance documents;
J a copy of the identity document (passport) of the proposed representative and its Chinese translation;
K. Application Form for Additional Representatives of Hong Kong and Macao Law Firms in Mainland Representative Offices.
12.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is six months. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
12.6. Approval process
12.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, or the applicant submits all the corrected application materials as required by the administrative organ, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or do not conform to the prescribed format and quantity, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within five days from the date of receiving the application materials, and the information shall be recorded; Fails to inform, since the date of receipt of the application materials is accepted.
12.6.2. Review and decision
A. If it meets the requirements after examination, a practicing certificate shall be issued to the licensed representative; If the license is not granted, the reasons shall be informed in writing.
B certificate: the practice certificate of the mainland representative office of Hong Kong and Macao Special Administrative Regions law firms.
12.7. Intermediary services
Paragraph 2 of Article 8 of the Measures for the Administration of Representative Offices of Law Firms in the Mainland of Hong Kong and Macao Special Administrative Regions (revised in 2015).
12.8. Charges
No charge.
12.9. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
12.10. Annual Review Report
Article 22 of the Measures for the Administration of Representative Offices of Law Firms in the Mainland of Hong Kong and Macao Special Administrative Regions (revised in 2015).
13. The representative offices of Hong Kong and Macao law firms in the Mainland will be reduced.
13.1. Setting basis
Article 34 of the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (the State Council Decree No.338);
Decision of the State Council on canceling and adjusting a number of administrative examination and approval items (Guo Fa [2014] No.27), item 7.
13.2. Implementation subject
Municipal justice bureau
13.3. Licensing Conditions
Article 12 of the Measures for the Administration of Representative Offices of Law Firms in the Mainland of Hong Kong and Macao Special Administrative Regions (revised in 2015).
13.4 Application materials
A. An application for reducing the number of representatives of the representative offices of Hong Kong and Macao law firms in Beijing (notarized);
B. representative card.
13.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is six months. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
13.6. Approval process
13.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, or the applicant submits all the corrected application materials as required by the administrative organ, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or do not conform to the prescribed format and quantity, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within five days from the date of receiving the application materials, and the information shall be recorded; Fails to inform, since the date of receipt of the application materials is accepted.
13.6.2. Review and decision
A. upon approval, withdraw the practicing certificate of the person who no longer serves as a representative.
B. approval: the decision to agree to reduce the representation of the law firm.
13.7. Intermediary services
Paragraph 2 of Article 8 of the Measures for the Administration of Representative Offices of Law Firms in the Mainland of Hong Kong and Macao Special Administrative Regions (revised in 2015).
13.8. Charges
No charge.
13.9. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
13.10. Annual Review Report
Not involved.
14 Hong Kong and Macao law firms and mainland law firms jointly apply for the first time.
14.1. Setting basis
Item 72 of the Annex of Decision of the State Council Municipality on Setting Administrative License for Administrative Examination and Approval Items Needed to Be Retained (revised in 2016) Catalogue of the State Council Municipality’s Decision on Setting Administrative License for Administrative Examination and Approval Items Needed to Be Retained.
14.2. Implementation subject
Municipal justice bureau
14.3. Licensing Conditions
Articles 5, 6 and 7 of the Measures for the Administration of Joint Venture between Law Firms of Hong Kong Special Administrative Region and Macao Special Administrative Region and Mainland Law Firms (revised in 2012).
14.4 Application materials
A. application for joint venture signed by both parties;
B. Joint venture agreement signed by both parties;
C photocopies of valid registration certificates of Hong Kong and Macao law firms approved to be established in Hong Kong and Macao, lists of sole proprietors or responsible persons and all partners, photocopies of practice licenses of representative offices in the Mainland and lists of representatives;
D certificates issued by relevant departments of the governments of Hong Kong and Macao Special Administrative Regions that the law firms of Hong Kong and Macao meet the standards of legal service providers of Hong Kong and Macao;
E a copy of the practice license of the mainland law firm, a list of responsible persons and all partners, and a certificate issued by the judicial administrative organ at the prefecture (city) level that the firm meets the conditions stipulated in Article 6 of the Measures for the Administration of Joint Ventures between Law Firms of Hong Kong Special Administrative Region and Macao Special Administrative Region and Mainland Law Firms;
F. If the representative offices of Hong Kong and Macao law firms in the Mainland are not located in the same province, autonomous region or municipality directly under the Central Government, the certificate issued by the provincial judicial administrative organ where the representative offices of Hong Kong and Macao law firms in the Mainland are located that the Hong Kong and Macao law firms meet the conditions specified in Item (6) of Article 5 of the Measures for the Administration of Joint Ventures between Law Firms in Hong Kong and Macao Special Administrative Regions;
G other materials required by the provincial judicial administrative organ.
14.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 30 natural days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
14.6. Approval process
14.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or inconsistent with the statutory form, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within five days from the date of receiving the application materials. If the applicant makes corrections as required, it shall be accepted; Fails to inform, since the date of receipt of the application materials is accepted;
C. If the application matters obviously do not meet the statutory requirements or the applicant refuses to make corrections or cannot make corrections to the relevant materials, the application shall not be accepted, and the reasons shall be explained in writing to the applicant.
14.6.2. Review and decision
A. For those who meet the requirements stipulated in these Measures, joint venture shall be granted and a joint venture license shall be issued; For those who do not meet the requirements of these measures, no joint venture is allowed, and the applicant shall be notified in writing.
B. Approval: Decision on approving the joint venture between Beijing Law Firm and Hong Kong (Macau) Law Firm.
14.7. Charges
No charge.
14.8. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
14.9. Annual Report
Article 22 of the Measures for the Administration of Joint Ventures between Law Firms of Hong Kong Special Administrative Region and Macao Special Administrative Region and Mainland Law Firms (revised in 2012).
15. Extension of the joint venture between Hong Kong and Macao law firms and mainland law firms.
15.1. Setting basis
Item 72 of the Annex of Decision of the State Council Municipality on Setting Administrative License for Administrative Examination and Approval Items Needed to Be Retained (revised in 2016) Catalogue of the State Council Municipality’s Decision on Setting Administrative License for Administrative Examination and Approval Items Needed to Be Retained.
15.2. Implementation subject
Municipal justice bureau
15.3. Licensing Conditions
Articles 5, 6, 7 and 10 of the Measures for the Administration of Joint Venture between Law Firms of Hong Kong Special Administrative Region and Macao Special Administrative Region and Mainland Law Firms (revised in 2012).
15.4 Application materials
A. application for joint venture signed by both parties;
B. Joint venture agreement signed by both parties;
C photocopies of valid registration certificates of Hong Kong and Macao law firms approved to be established in Hong Kong and Macao, lists of sole proprietors or responsible persons and all partners, photocopies of practice licenses of representative offices in the Mainland and lists of representatives;
D certificates issued by relevant departments of the governments of Hong Kong and Macao Special Administrative Regions that the law firms of Hong Kong and Macao meet the standards of legal service providers of Hong Kong and Macao;
E a copy of the practice license of the mainland law firm, a list of responsible persons and all partners, and a certificate issued by the judicial administrative organ at the prefecture (city) level that the firm meets the conditions stipulated in Article 6 of the Measures for the Administration of Joint Ventures between Law Firms of Hong Kong Special Administrative Region and Macao Special Administrative Region and Mainland Law Firms;
F. If the representative offices of Hong Kong and Macao law firms in the Mainland are not located in the same province, autonomous region or municipality directly under the Central Government, the certificate issued by the provincial judicial administrative organ where the representative offices of Hong Kong and Macao law firms in the Mainland are located that the Hong Kong and Macao law firms meet the conditions specified in Item (6) of Article 5 of the Measures for the Administration of Joint Ventures between Law Firms in Hong Kong and Macao Special Administrative Regions;
G other materials required by the provincial judicial administrative organ.
15.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 30 natural days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
15.6. Approval process
15.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or inconsistent with the statutory form, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within five days from the date of receiving the application materials. If the applicant makes corrections as required, it shall be accepted; Fails to inform, since the date of receipt of the application materials is accepted;
C. If the application matters obviously do not meet the statutory requirements or the applicant refuses to make corrections or cannot make corrections to the relevant materials, the application shall not be accepted, and the reasons shall be explained in writing to the applicant.
15.6.2. Review and decision
A. For those who meet the requirements stipulated in these Measures, joint venture shall be granted and a joint venture license shall be issued; For those who do not meet the requirements of these measures, no joint venture is allowed, and the applicant shall be notified in writing.
B. Approval: Decision on approving the joint venture between Beijing Law Firm and Hong Kong (Macau) Law Firm.
15.7. Charges
No charge.
15.8. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
15.9. Annual Report
Article 22 of the Measures for the Administration of Joint Ventures between Law Firms of Hong Kong Special Administrative Region and Macao Special Administrative Region and Mainland Law Firms (revised in 2012).
16 annual inspection of the joint venture between Hong Kong and Macao law firms and mainland law firms.
16.1. Setting basis
Item 72 of the Annex of Decision of the State Council Municipality on Setting Administrative License for Administrative Examination and Approval Items Needed to Be Retained (revised in 2016) Catalogue of the State Council Municipality’s Decision on Setting Administrative License for Administrative Examination and Approval Items Needed to Be Retained.
16.2. Implementation subject
Municipal justice bureau
16.3. Licensing Conditions
Article 22 of the Measures for the Administration of Joint Ventures between Law Firms of Hong Kong Special Administrative Region and Macao Special Administrative Region and Mainland Law Firms (revised in 2012).
16.4 Application materials
Report on joint venture.
16.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
16.6. Approval process
16.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or inconsistent with the statutory form, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within five days from the date of receiving the application materials. If the applicant makes corrections as required, it shall be accepted; Fails to inform, since the date of receipt of the application materials is accepted;
C. If the application matters obviously do not meet the statutory requirements or the applicant refuses to make corrections or cannot make corrections to the relevant materials, the application shall not be accepted, and the reasons shall be explained in writing to the applicant.
16.6.2. Review and decision
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the legal form, go through the registration formalities.
B registration form: the annual inspection registration record of the joint venture between Hong Kong and Macao law firms and mainland law firms.
16.7. Charges
No charge.
16.8. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
16.9. Annual Review Report
Article 22 of the Measures for the Administration of Joint Ventures between Law Firms of Hong Kong Special Administrative Region and Macao Special Administrative Region and Mainland Law Firms (revised in 2012).
17. Registration of representative offices and accredited representatives of Hong Kong and Macao law firms in the Mainland to carry out legal service activities.
17.1. Setting basis
Article 34 of the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (the State Council Decree No.338);
Decision of the State Council on canceling and adjusting a number of administrative examination and approval items (Guo Fa [2014] No.27), item 6.
17.2. Implementation subject
Municipal justice bureau
17.3. Licensing Conditions
Articles 9 and 10 of the Measures for the Administration of Mainland Representative Offices of Law Firms of Hong Kong and Macao Special Administrative Regions (revised in 2015).
17.4 Application materials
A. annual work report;
B. Financial statements audited by accounting firms;
C. Settlement of tax payment vouchers in China;
D. Changes of representatives in the representative office this year and the overall employment of mainland auxiliary personnel;
E. Residence of representatives of representative offices in China;
F materials that the chief representative and representative of the representative office have not received criminal punishment in the previous year and have not been punished for violating lawyers’ professional ethics and discipline;
G. Effective professional liability risk insurance documents of the representative office and its representatives;
H. Materials on the legal practice of the head office (department) in the country.
17.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
17.6. Approval process
17.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or inconsistent with the statutory form, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within five days from the date of receiving the application materials. If the applicant makes corrections as required, it shall be accepted; Fails to inform, since the date of receipt of the application materials is accepted;
C. If the application matters obviously do not meet the statutory requirements or the applicant refuses to make corrections or cannot make corrections to the relevant materials, the application shall not be accepted, and the reasons shall be explained in writing to the applicant.
17.6.2. Review and decision
A. if the application materials are complete and conform to the legal form, make it.
B registration form: the annual inspection registration record of the joint venture between Hong Kong and Macao law firms and mainland law firms.
17.7. Charges
No charge.
17.8. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
17.9. Annual Review Report
Article 22 of the Measures for the Administration of Representative Offices of Law Firms in the Mainland of Hong Kong and Macao Special Administrative Regions (revised in 2015).
18 foreign law firms apply for the establishment of representative offices in China (including the merger and division of representative offices)
18.1. Setting basis
Article 6 of the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (Order No.338th of the State Council).
18.2. Implementation subject
The first instance of the Municipal Bureau of Justice and the final instance of the Ministry of Justice
18.3. Licensing Conditions
Articles 7 and 8 of the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (Order No.338th of the State Council);
Articles 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 and 11 of the Regulations of the Ministry of Justice on Implementing the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (revised in 2004).
18.4 Application materials
18.4.1. Establishment, merger and division of representative offices
A. An application signed by the principal responsible person of the foreign law firm for establishing a representative office and sending a representative. The name of the representative office to be established shall be "Representative Office of ×× Law Firm (Chinese translation of the law firm) in ×× (city name of China)";
B documents certifying that the foreign law firm has been legally established in its own country;
C the partnership agreement or articles of association of the foreign law firm and the list of responsible persons and partners;
D the letter of authorization from the foreign law firm to each proposed representative of the representative office, and the confirmation that the proposed chief representative is a partner of the law firm or a person with the same position;
E. The lawyer qualification of each proposed representative of the representative office and the certification documents that the proposed chief representative has been practicing outside China for not less than 3 years and other proposed representatives have been practicing outside China for not less than 2 years;
F certification documents issued by the lawyers association of the country where the foreign law firm is located that the proposed representatives of the representative office are members of the domestic lawyers association;
G. A certificate issued by the lawyer management agency of the country where the foreign law firm is located that the law firm and the proposed representatives have not been subjected to criminal punishment and have not been punished for violating lawyers’ professional ethics and practice discipline.
18.4.2. Add representative office
In addition to the above materials, the following materials shall be submitted:
A. Basic information of established representative offices;
B a copy of the Practice License for Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (copy) of the established representative offices;
C certificates issued by the judicial departments (bureaus) of the provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government where the established representative offices are domiciled, that the recently established representative offices in China have been practicing continuously for three years, and certificates that the established representative offices and their representatives abide by the laws, regulations and rules of China, abide by lawyers’ professional ethics and practice discipline, and have not been investigated for various legal responsibilities stipulated in the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China.
18.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 9 months. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
18.6. Approval process
18.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, it shall be handled in accordance with Article 9 of the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China;
B. If the application materials are incomplete, the applicant shall be notified to supplement the materials within 15 days from the date of receiving the application materials. If the applicant completes the application materials within 3 months from the date of submitting the application materials for the first time, it shall be handled in accordance with Article 9 of the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China;
C. If the applicant fails to complete the application materials within 3 months from the date of submitting the application materials for the first time, it shall make a decision of rejection and notify the applicant in writing within 15 days.
18.6.2. Review and decision
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, the review opinions and documents shall be submitted to the Ministry of Justice for review. After examination and approval by the Ministry of Justice, if the establishment is permitted, a practice license shall be issued; If the license is not granted, the applicant shall be informed in writing of the reasons.
B certificate: practice license of representative office of foreign law firm in China (original and copy).
18.7. Charges
No charge.
18.8. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
18.9. Annual Report
Article 22 of the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (Order No.338th of the State Council).
19. A foreign law firm applies for changing the name of its representative office
19.1. Setting basis
Article 12 of the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (Order No.338th of the State Council).
19.2. Implementation subject
The first instance of the Municipal Bureau of Justice and the final instance of the Ministry of Justice
19.3. Licensing Conditions
Article 12 of the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (Order No.338th of the State Council);
Articles 19 and 20 of the Provisions of the Ministry of Justice on Implementing the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (revised in 2004).
19.4 Application materials
A an application for name change signed by the principal responsible person of a foreign law firm;
B notarized and certified documents that the foreign law firm has changed its name in its home country.
19.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
19.6. Approval process
19.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or inconsistent with the statutory form, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within five days from the date of receiving the application materials. If the applicant makes corrections as required, it shall be accepted; Fails to inform, since the date of receipt of the application materials is accepted;
C. If the application matters obviously do not meet the statutory requirements or the applicant refuses to make corrections or cannot make corrections to the relevant materials, the application shall not be accepted, and the reasons shall be explained in writing to the applicant.
19.6.2. Review and decision
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, the review opinions and documents shall be submitted to the Ministry of Justice for review. If the Ministry of Justice approves the change, it shall go through the change formalities with the approval notice.
B certificate: practice license of representative office of foreign law firm in China (original and copy).
19.7. Charges
No charge.
19.8. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
19.9. Annual Report
Article 22 of the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (Order No.338th of the State Council).
20. Foreign law firms apply to move their representative offices to other cities.
20.1. Setting basis
Article 6 of the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (Order No.338th of the State Council).
20.2. Implementation subject
The first instance of the Municipal Bureau of Justice and the final instance of the Ministry of Justice.
20.3. Licensing conditions
Provisions of the Ministry of Justice on Implementing the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (revised in 2004), Article 26, etc.
20.4 Application materials
A. an application signed by the head of a foreign law firm;
Note: those who move into this city shall go through the new establishment procedures after being approved by the Ministry of Justice; Those who move out of this city shall go through the cancellation procedures after approval by the Ministry of Justice.
20.5. Time limit for approval
After the approval of the Ministry of Justice, the legal time limit for moving into this city is 9 months; Move out of the city, after the approval of the Ministry of Justice, the statutory time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
20.6. Approval process
20.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or inconsistent with the statutory form, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within five days from the date of receiving the application materials. If the applicant makes corrections as required, it shall be accepted; Fails to inform, since the date of receipt of the application materials is accepted;
C. If the application matters obviously do not meet the statutory requirements or the applicant refuses to make corrections or cannot make corrections to the relevant materials, the application shall not be accepted, and the reasons shall be explained in writing to the applicant.
20.6.2. Review and decision
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, the review opinions and documents shall be submitted to the Ministry of Justice for review. Approved by the Ministry of Justice, the applicant holds a notice of approval and goes through the relevant cancellation and registration procedures in accordance with the regulations.
B. approval: notice of approval; Approval for establishment (moving into this city); Cancel the approval (move out of the city).
20.7. Charges
No charge.
20.8. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
20.9. Annual Review Report
Article 22 of the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (Order No.338th of the State Council).
21. Foreign law firms apply for cancellation of representative offices.
21.1. Setting basis
Article 14 of the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (Order No.338th of the State Council).
21.2. Implementation subject
The first instance of the Municipal Bureau of Justice and the final instance of the Ministry of Justice.
21.3. Licensing conditions
Article 14 of the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (Order No.338th of the State Council);
Provisions of the Ministry of Justice on Implementing the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (revised in 2004) Articles 21 and 22.
21.4 Application materials
An application signed by the principal responsible person of a foreign law firm.
21.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 60 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
21.6. Approval process
21.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or inconsistent with the statutory form, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within five days from the date of receiving the application materials. If the applicant makes corrections as required, it shall be accepted; Fails to inform, since the date of receipt of the application materials is accepted;
C. If the application matters obviously do not meet the statutory requirements or the applicant refuses to make corrections or cannot make corrections to the relevant materials, the application shall not be accepted, and the reasons shall be explained in writing to the applicant.
21.6.2. Review and decision
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, submit a written review opinion to the Ministry of Justice (report on agreeing to cancel the Beijing representative office of the law firm);
B after receiving the report, the Ministry of justice shall go through the approval procedures according to law.
21.7. Charges
No charge.
21.8. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
21.9. Annual Review Report
Not involved.
22 representative offices of foreign law firms in China (including adding new representatives)
22.1. Setting basis
Article 6 of the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (Order No.338th of the State Council).
22.2. Implementation subject
The first instance of the Municipal Bureau of Justice and the final instance of the Ministry of Justice.
22.3. Licensing conditions
Articles 7 and 8 of the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (Order No.338th of the State Council);
Provisions of the Ministry of Justice on Implementing the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (revised in 2004) Articles 5, 27 and 28.
22.4 Application materials
A. The application and translation of the chief representative and representative signed by the principal responsible person of the foreign law firm;
B the letter of authorization and translation of the chief representative and representative of the foreign law firm to the representative office;
C confirmation that the chief representative to be appointed is a partner of the law firm or a person in the same position, and the translation confirmation; List of partners of the firm and its translation;
D. The qualification documents of the proposed chief representative and lawyer of the representative office;
E documents and translations of the chief representative to be appointed who has been practicing outside China for not less than 3 years and other representatives to be appointed who have been practicing outside China for not less than 2 years;
F documents and translations issued by the lawyers association of the country where the law firm is located that the representative office is to be the chief representative and the representative is a member of the lawyers association of the country;
G. A certificate issued by the lawyer management agency of the country where the foreign law firm is located that the law firm and the proposed representatives have not been subjected to criminal punishment and have not been punished for violating lawyers’ professional ethics and practice discipline;
H practice risk insurance documents and translations of the proposed chief representative and representative;
I a copy of the identity document (passport) of the proposed representative and its Chinese translation;
J. application form for foreign law firms to send more representatives to representative offices in China.
22.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 9 months. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
22.6. Approval process
22.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete, the applicant shall be notified to supplement the materials within 15 days from the date of receiving the application materials. If the applicant completes the application materials within 3 months from the date of submitting the application materials for the first time, it shall be handled in accordance with Article 9 of the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China;
C. If the applicant fails to complete the application materials within 3 months from the date of submitting the application materials for the first time, it shall make a decision of rejection and notify the applicant in writing within 15 days.
22.6.2. Review and decision
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, the review opinions and documents shall be submitted to the Ministry of Justice for review.
B. The Ministry of Justice will issue a practicing certificate to the representative after examination.
C certificate: practice certificate of representative office of foreign law firm in China.
22.7. Charges
No charge.
22.8. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
22.9. Annual Review Report
Article 22 of the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (Order No.338th of the State Council).
23. The representative offices of foreign law firms in China will be reduced.
23.1. Setting basis
Article 12 of the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (Order No.338th of the State Council).
23.2. Implementation subject
Municipal justice bureau
23.3. Licensing conditions
Article 12 of the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (Order No.338th of the State Council).
23.4 Application materials
An application for reducing the number of representatives of foreign law firms in Beijing signed by the principal responsible person of the law firm.
23.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 130 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
23.6. Approval process
23.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or inconsistent with the statutory form, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within five days from the date of receiving the application materials. If the applicant makes corrections as required, it shall be accepted;
C. If the application matters obviously do not meet the statutory requirements or the applicant refuses to make corrections or cannot make corrections to the relevant materials, the application shall not be accepted, and the reasons shall be explained in writing to the applicant.
23.6.2. Review and decision
If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, the review opinions and documents shall be submitted to the Ministry of Justice for approval.
23.7. Charges
No charge.
23.8. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
23.9. Annual Review Report
Not involved.
24. Registration of representative offices and accredited representatives of foreign law firms in China to carry out legal service activities
24.1. Setting basis
Article 10 of the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (the State Council Decree No.338)
24.2. Implementation subject
Municipal justice bureau
24.3. Licensing conditions
Articles 10, 19 and 22 of the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (the State Council Decree No.338).
24.4 Application materials
A. annual work report;
B. Financial statements audited by accounting firms;
C. Settlement of tax payment vouchers in China;
D. Changes of representatives in the representative office this year and the overall employment of auxiliary personnel in China;
E. Residence of representatives of representative offices in China;
F materials that the representative of the representative office has not received criminal punishment in the previous year and has not been punished for violating the lawyer’s professional ethics and discipline;
G. Effective professional liability risk insurance documents of the representative office and its representatives for this year;
H. Materials on the legal practice of the head office (department) in the country.
24.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
24.6. Approval process
24.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or inconsistent with the statutory form, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within five days from the date of receiving the application materials. If the applicant makes corrections as required, it shall be accepted; Fails to inform, since the date of receipt of the application materials is accepted;
C. If the application matters obviously do not meet the statutory requirements or the applicant refuses to make corrections or cannot make corrections to the relevant materials, the application shall not be accepted, and the reasons shall be explained in writing to the applicant.
24.6.2. Review and decision
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the legal form, go through the registration formalities.
B registration form: the annual inspection and registration records of the representative offices of foreign law firms in China.
24.7. Charges
No charge.
24.8. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
24.9. Annual Review Report
Article 22 of the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China (Order No.338th of the State Council).
25. Registration of establishment of judicial authentication institutions and branches.
25.1. Setting basis
Articles 2, 3 and 6 of the Decision of the NPC Standing Committee on the Management of Judicial Expertise (revised in 2015);
Article 11 of the Measures for the Administration of Registration of Judicial Authentication Institutions (2005).
25.2. Implementation subject
The district judicial bureau conducts the first trial and the municipal judicial bureau conducts the final trial.
25.3. Licensing conditions
Articles 5 and 16 of the Decision of the NPC Standing Committee on the Management of Judicial Expertise (revised in 2015);
Measures for the Administration of the Registration of Judicial Authentication Institutions (2005) Articles 14, 15, 16 and 17.
25.4 Application materials
A. application form for registration of judicial authentication institutions;
B. the applicant’s business license;
C. domicile and financial information;
D. testing laboratory data;
E. instruments and equipment purchase vouchers;
F application form for the registration of judicial appraisers (there are more than three judicial appraisers in each judicial appraisal business);
G internal management system (including personnel, place, business, quality, finance, archives, training, etc.).
25.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
25.6. Approval process
25.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, or the applicant submits all the corrected application materials as required by the administrative organ, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or do not conform to the prescribed format and quantity, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within five days from the date of receiving the application materials, and the information shall be recorded; Fails to inform, since the date of receipt of the application materials is accepted.
25.6.2. Review and decision
A. The judicial administrative organ shall organize experts to review the instruments, equipment and testing laboratories necessary for the applicant to engage in judicial authentication business, and the review time shall not be included in the review time limit. If it meets the requirements after examination, the judicial administrative organ shall make a decision to approve the registration and issue a "judicial authentication license"; Do not meet the conditions, make a decision not to register, notify the applicant in writing and explain the reasons.
B. approvals and certificates: a decision on granting administrative license; People’s Republic of China (PRC) Judicial Appraisal License (original and duplicate).
25.7. Charges
No charge.
25.8. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
25.9. Annual Review Report
Not involved.
26. Change registration of judicial authentication institutions and branches
26.1. Setting basis
Articles 2, 3 and 6 of the Decision of the NPC Standing Committee on the Management of Judicial Expertise (revised in 2015);
Article 11 of the Measures for the Administration of Registration of Judicial Authentication Institutions (2005).
26.2. Implementation subject
The district judicial bureau conducts the first trial and the municipal judicial bureau conducts the final trial.
26.3. Licensing conditions
Articles 5 and 16 of the Decision of the NPC Standing Committee on the Management of Judicial Expertise (revised in 2015);
Article 24 of the Measures for the Administration of Registration of Judicial Authentication Institutions (2005).
26.4 Application materials
26.4.1. Application for increasing business scope
A. An application form for changing the business scope of a judicial authentication institution;
B. People’s Republic of China (PRC) judicial expertise license;
C. instruments and equipment purchase vouchers;
D. the certificate of qualification of the testing institution of the judicial appraiser or the application form for the registration of the judicial appraiser.
26.4.2. Application for reducing business scope
A. An application form for changing the business scope of a judicial authentication institution;
B. People’s Republic of China (PRC) forensic license.
26.4.3. Application for change of name
A. an application form for changing the name of a judicial authentication institution;
B. People’s Republic of China (PRC) judicial expertise license;
C letter of commitment to inform the business license of the sponsor or the business license of the judicial authentication institution after the name change.
26.4.4. Apply for change of legal representative and person in charge.
A. An application form for changing the legal representative/person in charge of the judicial authentication institution;
B. People’s Republic of China (PRC) judicial expertise license;
C. Resolution on the change of legal representative and person in charge of the institution;
D. Letter of commitment to inform the business license or the change of name of the judicial authentication institution.
26.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
26.6. Approval process
26.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, or the applicant submits all the corrected application materials as required by the administrative organ, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or do not conform to the prescribed format and quantity, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within five days from the date of receiving the application materials, and the information shall be recorded; Fails to inform, since the date of receipt of the application materials is accepted.
26.6.2. Review and decision
A. If it meets the requirements after examination, the judicial administrative organ shall make a decision to approve the change; If it is not changed, it shall notify the applicant in writing and explain the reasons.
B. approval: the decision to approve the change of administrative license.
26.7. Charges
No charge.
26.8. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
26.9. Annual Review Report
Not involved.
27. Continued registration of judicial authentication institutions and branches.
27.1. Setting basis
Articles 2, 3 and 6 of the Decision of the NPC Standing Committee on the Management of Judicial Expertise (revised in 2015);
Article 11 of the Measures for the Administration of Registration of Judicial Authentication Institutions (2005).
27.2. Implementation subject
The district judicial bureau conducts the first trial and the municipal judicial bureau conducts the final trial.
27.3. Licensing conditions
Articles 5 and 16 of the Decision of the NPC Standing Committee on the Management of Judicial Expertise (revised in 2015);
Article 26 of the Measures for the Administration of Registration of Judicial Authentication Institutions (2005).
27.4 Application materials
A. application form for registration of judicial authentication institutions;
B. materials on housing funds;
C. Purchase invoices for major equipment required by standards;
D. testing laboratory data;
E. the applicant’s business license;
F. instruments and equipment purchase vouchers;
G internal management system (including personnel, place, business, quality, finance, archives, training, etc.).
27.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
27.6. Approval process
27.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, or the applicant submits all the corrected application materials as required by the administrative organ, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or do not conform to the prescribed format and quantity, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within five days from the date of receiving the application materials, and the information shall be recorded; Fails to inform, since the date of receipt of the application materials is accepted.
27.6.2. Review and decision
A. The judicial administrative organ shall make a decision to approve the extension if it meets the requirements after examination; If not, notify the applicant in writing and explain the reasons.
B. approval: the decision to approve the extension of the administrative license.
27.7. Charges
No charge.
27.8. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
27.9. Annual Review Report
Not involved.
28. Cancellation of registration of judicial authentication institutions and branches.
28.1. Setting basis
Articles 2, 3 and 6 of the Decision of the NPC Standing Committee on the Management of Judicial Expertise (revised in 2015);
Article 11 of the Measures for the Administration of Registration of Judicial Authentication Institutions (2005).
28.2. Implementation subject
The district judicial bureau conducts the first trial and the municipal judicial bureau conducts the final trial.
28.3. Licensing conditions
Articles 5 and 16 of the Decision of the NPC Standing Committee on the Management of Judicial Expertise (revised in 2015);
Article 27 of the Measures for the Administration of Registration of Judicial Authentication Institutions (2005).
28.4 Application materials
A. application form for cancellation of registration of judicial authentication institutions;
B. People’s Republic of China (PRC) judicial expertise license;
C. practice certificate of judicial appraiser.
28.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
28.6. Approval process
28.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, or the applicant submits all the corrected application materials as required by the administrative organ, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or do not conform to the prescribed format and quantity, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within five days from the date of receiving the application materials, and the information shall be recorded; Fails to inform, since the date of receipt of the application materials is accepted.
28.6.2. Review and decision
A. If it meets the requirements after examination, the judicial administrative organ shall make a decision to cancel the license; If not, notify the applicant in writing and explain the reasons.
B. approval: written decision on cancellation of administrative license.
28.7. Charges
No charge.
28.8. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
28.9. Annual Review Report
Not involved.
29. Practice registration of judicial appraisers
29.1. Setting basis
Articles 2, 3 and 6 of the Decision of the NPC Standing Committee on the Management of Judicial Expertise (revised in 2015);
Article 10 of the Administrative Measures for the Registration of Judicial Appraisers (2005).
29.2. Implementation subject
The district judicial bureau conducts the first trial and the municipal judicial bureau conducts the final trial.
29.3. Licensing conditions
Articles 4 and 16 of the Decision of the NPC Standing Committee on the Management of Judicial Expertise (revised in 2015);
Articles 11, 12, 13 and 14 of the Administrative Measures for the Registration of Judicial Appraisers (2005).
29.4 Application materials
A. application form for registration of judicial appraisers;
B. Resident identity card of the People’s Republic of China;
C. diploma;
D. professional and technical title certificate;
E. Commitment letter of no criminal record;
F. agree to part-time materials;
G. description of physical health.
29.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
29.6. Approval process
29.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, or the applicant submits all the corrected application materials as required by the administrative organ, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or do not conform to the prescribed format and quantity, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within five days from the date of receiving the application materials, and the information shall be recorded; Fails to inform, since the date of receipt of the application materials is accepted.
29.6.2. Review and decision
A. If it meets the requirements after examination, the judicial administrative organ shall make a decision to approve the registration and issue the Practice Certificate of Judicial Appraiser; Do not meet the conditions, make a decision not to register, notify the judicial authentication institution in writing and explain the reasons.
B. approvals and certificates: a decision on granting administrative license; Practice certificate of judicial appraiser.
29.7. Charges
No charge.
29.8. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
29.9. Annual Review Report
Not involved.
30. Change of registration of judicial appraisers
30.1. Setting basis
Articles 2, 3 and 6 of the Decision of the NPC Standing Committee on the Management of Judicial Expertise (revised in 2015);
Article 10 of the Administrative Measures for the Registration of Judicial Appraisers (2005).
30.2. Implementation subject
The district judicial bureau conducts the first trial and the municipal judicial bureau conducts the final trial.
30.3. Licensing conditions
Articles 4 and 16 of the Decision of the NPC Standing Committee on the Management of Judicial Expertise (revised in 2015);
Article 18 of the Administrative Measures for the Registration of Judicial Appraisers (2005).
30.4 Application materials
30.4.1. Increase the category of practice.
A. application form for judicial appraisers to change their practice categories;
B. Practice certificate of judicial appraiser;
C. professional and technical title certificate.
30.4.2. Reduce the types of practice.
A. application form for judicial appraisers to change their practice categories;
B. Practice certificate of judicial appraiser.
30.4.3. Change of practice institution
A. An application form for judicial appraisers to change their practice institutions;
B. Practice certificate of judicial appraiser.
30.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
30.6. Approval process
30.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, or the applicant submits all the corrected application materials as required by the administrative organ, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or do not conform to the prescribed format and quantity, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within five days from the date of receiving the application materials, and the information shall be recorded; Fails to inform, since the date of receipt of the application materials is accepted.
30.6.2. Review and decision
A. The judicial administrative organ shall make a decision to approve the change if it meets the requirements after examination; If it does not change, it shall notify its judicial authentication institution in writing and explain the reasons.
B. approval: the decision to approve the change of administrative license.
30.7. Charges
No charge.
30.8. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
30.9. Annual report
Not involved.
31. Continued registration of judicial appraisers
31.1. Setting basis
Articles 2, 3 and 6 of the Decision of the NPC Standing Committee on the Management of Judicial Expertise (revised in 2015);
Article 10 of the Administrative Measures for the Registration of Judicial Appraisers (2005).
31.2. Implementation subject
The district judicial bureau conducts the first trial and the municipal judicial bureau conducts the final trial.
31.3. Licensing conditions
Articles 4 and 16 of the Decision of the NPC Standing Committee on the Management of Judicial Expertise (revised in 2015);
Article 19 of the Administrative Measures for the Registration of Judicial Appraisers (2005).
31.4 Application materials
A. application form for registration of judicial appraisers;
B. Resident identity card of the People’s Republic of China;
C. diploma;
D. professional and technical title certificate;
E. Commitment letter of no criminal record;
F. description of physical health.
31.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
31.6. Approval process
31.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, or the applicant submits all the corrected application materials as required by the administrative organ, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or do not conform to the prescribed format and quantity, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within five days from the date of receiving the application materials, and the information shall be recorded; Fails to inform, since the date of receipt of the application materials is accepted.
31.6.2. Review and decision
A. The judicial administrative organ shall make a decision to approve the extension if it meets the requirements after examination; If it is not extended, it shall notify its judicial authentication institution in writing and explain the reasons.
B. approval: the decision to approve the extension of the administrative license.
31.7. Charges
No charge.
31.8. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
31.9. Annual review report
Not involved.
32. Cancellation of registration of judicial appraisers
32.1. Setting basis
Articles 2, 3 and 6 of the Decision of the NPC Standing Committee on the Management of Judicial Expertise (revised in 2015);
Article 10 of the Administrative Measures for the Registration of Judicial Appraisers (2005).
32.2. Implementation subject
The district judicial bureau conducts the first trial and the municipal judicial bureau conducts the final trial.
32.3. Licensing conditions
Articles 4 and 16 of the Decision of the NPC Standing Committee on the Management of Judicial Expertise (revised in 2015);
Article 20 of the Administrative Measures for the Registration of Judicial Appraisers (2005).
32.4 Application materials
A. application form for cancellation of judicial appraiser;
B. Practice certificate of judicial appraiser.
32.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
32.6. Approval process
32.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, or the applicant submits all the corrected application materials as required by the administrative organ, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or do not conform to the prescribed format and quantity, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within five days from the date of receiving the application materials, and the information shall be recorded; Fails to inform, since the date of receipt of the application materials is accepted.
32.6.2. Review and decision
A. The judicial administrative organ shall make a cancellation decision if it meets the requirements after examination; If it is not cancelled, it shall notify its judicial authentication institution in writing and explain the reasons.
B. approval: written decision on cancellation of administrative license.
32.7. Charges
No charge.
32.8. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
32.9. Annual report
Not involved.
33. Notary’s practice license
33.1. Setting basis
Article 21 of the Notary Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) (revised in 2017)
33.2. Implementation subject
Municipal Bureau of Justice and Ministry of Justice
33.3. Licensing conditions
Articles 18, 19 and 20 of the Notary Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) (revised in 2017);
Articles 7, 8, 9, 10 and 11 of the Measures for the Administration of Notary Practice (2006).
33.4 Application materials
33.4.1. Notaries generally serve.
A. recommendation letter from notary public;
B. Resident identity card of the People’s Republic of China; The corresponding experience description;
C. legal professional qualification certificate;
D. applicant’s internship appraisal;
E. the examination opinions of the local judicial administrative organ on the applicant;
F. labor contract;
G. commitment letter of no criminal record;
H. information on the relationship between personnel files.
33.4.2. Examination and post examination of notaries
A. the identity card of the people’s Republic of China;
B. Materials engaged in law teaching and research with senior titles;
C. diploma;
D. Ten years’ experience and job materials in trial, procuratorial work, legal work and legal service;
E. materials that the applicant has left the original post;
F the examination opinions of the local judicial administrative organ on the applicant;
G. labor contract;
H. Commitment letter of no criminal record;
I. information on the relationship between personnel files.
33.4.3. Notaries change their practice institutions
A. materials approved by the notary office;
B. opinions of the local judicial administrative organ;
C. Resident identity card of the People’s Republic of China;
D. labor contract;
E. Commitment letter of no criminal record;
F. Information on the relationship between personnel files.
33.4.4. Notary removed from office
A. recommendation letter from notary public;
B. Resident identity card of the People’s Republic of China;
C. Notary’s application for dismissal.
33.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 20 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
33.6. Approval process
33.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, or the applicant submits all the corrected application materials according to the requirements of this administrative organ, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or do not conform to the prescribed format and quantity, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected on the spot or within 5 days from the date of receiving the application materials, and the information shall be recorded; Fails to inform, since the date of receipt of the application materials is accepted;
C. If it does not meet the requirements, inform it within 5 working days and return the materials.
33.6.2 Review and decision
A. For those who meet the prescribed conditions and the notary staffing plan, make an audit opinion on agreeing to the applicant to serve as a notary, fill in the notary post application form, and report it to the Ministry of Justice for appointment;
B. Approval and certificate: forwarding the notice of the Ministry of Justice on the appointment of notaries; Notary’s practice certificate.
33.7. Charges
No charge.
33.8. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
33.9. Annual review report
Article 24 of the Measures for the Administration of Notary Practice (2006).
34. Identification of legal professional qualifications
34.1. Setting basis
Article 66 of the Judges Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) (revised in 2019);
Article 67 of the Procurator Law of the People’s Republic of China (revised in 2019);
Paragraph 2 of Article 25 of the Civil Service Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) (revised in 2018);
Item 1, Paragraph 2, Article 13 of the Arbitration Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) (revised in 2017);
Item 4 of Article 18 of the Notary Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) (revised in 2017);
Paragraph 2 of Article 6 of People’s Republic of China (PRC) Administrative Reconsideration Law (revised in 2023);
Paragraph 2 of Article 58 of the Administrative Punishment Law of the People’s Republic of China (revised in 2021).
34.2. Implementation subject
Municipal Bureau of Justice and Ministry of Justice
34.3. Licensing conditions
Article 18 of the Measures for the Implementation of the National Unified Legal Professional Qualification Examination (2018) and Article 7 of the Measures for the Administration of Legal Professional Qualification (2020).
34.4 Application materials
A. resident identity card;
B. Graduation certificate, degree certificate or original diploma and degree certificate;
C. application form for legal professional qualification of national unified legal professional qualification examination;
D. Other materials required by the announcement of the Ministry of Justice.
34.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 20 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
34.6. Approval process
34.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, or if the applicant submits all the corrected application materials according to the requirements of the accepting organ, it shall accept and issue an application acceptance form for legal professional qualification to the applicant;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or inconsistent with the statutory form, inform the applicant of all the materials and contents that need to be supplemented on the spot or within five working days;
C. If the application conditions for legal professional qualification are not met, a notice of rejection shall be issued and the reasons shall be explained.
34.6.2. Review and decision
A. Review and verify the application materials of persons applying for granting legal professional qualifications, submit a written verification report on granting or not granting legal professional qualifications, and report it to the Ministry of Justice for examination and confirmation.
B certificate: legal professional qualification certificate (original and copy).
34.7. Charges
No charge.
34.8. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
34.9. Annual report
Not involved.
35. Registration of the establishment of the Arbitration Commission
35.1. Setting basis
Article 10 of the Arbitration Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) (as amended in 2017);
Article 3 of the Interim Measures for the Registration of the Arbitration Commission (No.44 [1995] of the State Council).
35.2. Implementation subject
Municipal justice bureau
35.3. Licensing conditions
Articles 11, 12 and 13 of the Arbitration Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) (revised in 2017);
Article 3 of the Interim Measures for the Registration of the Arbitration Commission (No.44 [1995] of the State Council).
35.4 Application materials
A. application for the establishment of an arbitration commission;
B documents of the people’s government of the city where the arbitration commission is established;
C. articles of association of the arbitration commission;
D. necessary proof of funds;
E. proof of the domicile of the arbitration commission;
F. A copy of the letter of appointment of the members of the Arbitration Commission;
G. roster of arbitrators to be appointed.
35.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 10 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
35.6. Approval process
35.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, or the applicant submits all the corrected application materials according to the requirements of this administrative organ, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or do not conform to the prescribed format and quantity, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected, and the information shall be recorded;
C. if it does not meet the requirements, inform the reasons in writing.
35.6.2. Review and decision
A an arbitration commission that meets the conditions for establishment shall be established and registered, and a registration certificate shall be issued; Those who meet the conditions for establishment, but the documents provided do not meet the conditions, shall be registered after requesting correction; Those who do not conform to the provisions of the first paragraph of Article 3 of these Measures shall not be registered.
B certificate: People’s Republic of China (PRC) arbitration Commission registration certificate (original and copy).
35.7. Charges
No charge.
35.8. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
35.9. Annual review report
Not involved.
36. The Arbitration Commission cancelled its registration.
36.1. Setting basis
Article 6 of the Interim Measures for the Registration of the Arbitration Commission (No.44 [1995] of the State Council).
36.2. Implementation subject
Municipal justice bureau
36.3. Licensing conditions
Article 6 of the Interim Measures for the Registration of the Arbitration Commission (No.44 [1995] of the State Council).
36.4 Application materials
A. application for cancellation of registration;
B the people’s government of the city where the arbitration commission was established agrees to cancel the documents of the arbitration commission;
C. liquidation report confirmed by relevant authorities;
D. registration certificate of the arbitration commission.
36.5. Time limit for approval
The legal time limit is 10 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
36.6. Approval process
36.6.1. Acceptance
A. If the application materials are complete and conform to the statutory form, or the applicant submits all the corrected application materials as required by the administrative organ, it shall be accepted;
B. If the application materials are incomplete or do not conform to the prescribed format and quantity, the applicant shall be informed of all the contents that need to be corrected, and the information shall be recorded.
36.6.2. Review and decision
The registration authority shall, within 10 days from the date of receiving the required documents and certificates, cancel the registration of the arbitration commission that meets the termination conditions and recover the registration certificate of the arbitration commission.
36.7. Charges
No charge.
36.8. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
36.9. Annual review report
Not involved.
Note: The revocation and withdrawal of the above-mentioned administrative license shall be implemented in accordance with the Administrative License Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) and the relevant regulations of the Ministry of Justice and this Municipality.
Two, the administrative inspection discretion benchmark
1. Administrative inspection of domestic law firms (branches)
1.1. Inspection object
Domestic law firms and branches
1.2. Inspection method
On-site inspection, license inspection, on-site inquiry, information access, off-site inspection, and other means.
1.3. Inspection frequency
In principle, according to the annual law enforcement inspection plan (website publicity).
1.4. Check the content
1.4.1. Operating qualifications of domestic law firms
1.4.1.1. Is the publicity and custody of the original and duplicate practice licenses of domestic law firms and branches standardized?
A. The original of the public practice license (on-site inspection) is hung in the obvious position of the office of the law firm and branch;
B. In the process of supervision and inspection by judicial administrative organs, law firms and branches can produce the original copy of their practice licenses (on-site inspection);
C. The names actually used by law firms and branches are consistent with the names stated in the original and duplicate of the practice license; Where the registered items of the law firm are changed, the registered items of the branch offices have also been changed accordingly; If the law firm is closed, its practice certificate is revoked or terminated for other reasons, its branch office shall terminate at the same time and go through the cancellation procedures with the judicial administrative organ that made the original license (on-site inspection of web pages, agreements, brochures and practice license information comparison);
D. The information of the actual person in charge of the law firm and branch office is consistent with the registration information of the copy of the practice license, and the lawyer’s practice certificate of the person in charge has not been cancelled or revoked (on-site inspection, off-site verification through the management information system of the judicial administrative organ);
E. The original and duplicate copies of the practice licenses of law firms and branch offices are not obviously damaged or defiled, and the information stated is not marked by any artificial alteration (on-site inspection);
F the inspected law firm and branch are in normal practice; If the practice certificate has been revoked or the practice is stopped, the original and duplicate of the practice license have been returned to the judicial administrative organ (checked off-site by the management information system of the judicial administrative organ).
1.4.1.2. Has the practice license passed the annual inspection and assessment by the judicial administrative organ and been stamped with a special seal?
A law firms and branches have submitted annual inspection application materials to the judicial administrative organs before March 31st of that year, and accepted the annual inspection (off-site, checked by the management information system of the judicial administrative organs);
B copies of practice licenses of law firms and branch offices have been stamped with the special seal of "annual inspection and assessment of law firms" and have recorded the results of annual inspection and assessment, assessment institutions, assessment validity period and other records (on-site inspection);
C. The examination results, examination institutions, validity period and other records of the endorsement of the copy of the practice license of the law firm and branch office have not been altered, and are consistent with the information saved in the management system of the judicial administrative organ (on-site inspection).
1.4.1.3. Is the actual place of practice consistent with the place of registration and legal procedures have been obtained?
A. If a law firm or branch rents an office residence, it shall sign a residence lease agreement with the property owner, and the lease agreement is true and effective, and the deadline of the lease agreement is later than the deadline of the annual inspection validity period (on-site inspection of the house lease agreement);
B. If a law firm uses its own office residence, it shall have a residence real estate registration certificate, which is consistent with the copy of the real estate registration certificate submitted when handling the practice license (on-site inspection of the house real estate registration certificate).
1.4.1.4. Does the practice place meet the purpose of practice and whether the practice environment is suitable for lawyers to practice?
A the practice places of law firms and branches are only used for the purpose of handling legal services, not for other production and business activities, and are not mixed with other companies, enterprises or institutions (on-site inspection);
B. Signboards should be hung at the door or entrance of the office, indicating the standardized name and house number of the law firm (on-site inspection);
C. The office space shall be provided with reasonable functional partitions, including offices, conference rooms (reception rooms), accounting rooms, archives rooms, etc. The office area shall be clean and tidy, with complete functional settings and orderly items (on-site inspection);
D. A publicity column should be posted in an obvious position of the law firm, which includes the following contents: information of practicing lawyers with photos, charging standards for lawyer services, service commitments, complaint supervision telephone numbers, etc. (on-site inspection);
E. The filing room of law firm is equipped with special filing cabinets and fire-proof, insect-proof and moisture-proof facilities, and the room is kept clean, tidy and ventilated. The case file and related materials are stored in the archives room of the law firm (on-site inspection);
F the reception room should be equipped with necessary items such as seats, drinking fountains, paper cups, pens and pens (on-site inspection);
G. Law firms should be equipped with necessary office equipment (on-site inspection) including office telephones, photocopiers, fax machines and printers.
1.4.1.5. Whether the articles of association of this firm are formulated, and whether the contents specified in the articles of association are sound and perfect.
A. The law firm can produce the original articles of association on site and the text of the articles of association is the version of the judicial administrative organ of the last change times (on-site inspection, off-site verification through the management information system of the judicial administrative organ);
B. The actual partner and person in charge of the law firm are consistent with the articles of association, and there is no case that changes should be made but the procedures for changes have not been fulfilled (on-site inspection, off-site verification through the management information system of the judicial administrative organ);
C the articles of association of the law firm include the following contents (on-site inspection):
1) The name and domicile of the law firm;
2) the purpose of the law firm;
3) the organizational form of the law firm;
4) The amount and source of the assets to be established;
5) The responsibilities of the person in charge of the law firm and the procedures for its creation and change;
6) Law firm’s decision-making, establishment and responsibilities of management institutions;
7) The rights and obligations of our lawyers;
8) The main management systems of the law firm concerning practice, fees, finance and distribution;
9) Reasons, procedures and liquidation methods for the dissolution of the law firm;
10) Procedures for interpretation and amendment of the articles of association of the law firm;
11) The establishment form, position, function, responsibility and authority of the party organization of the law firm, the working mechanism of participating in the decision-making and management of the firm, and the safeguard measures for party building work;
12) Where a partnership law firm is established, the articles of association shall also specify the names of the partners, the amount and mode of contribution.
13) Other matters that need to be specified.
D the contents of the articles of association of the law firm are not in conflict with relevant laws, regulations and rules; The articles of association of the law firm shall come into effect (on-site inspection) from the date when the judicial administrative organ makes a decision to approve the establishment or change of the law firm.
1.4.1.6. Does the founder meet the corresponding qualifications and quantity?
A. The founder of a law firm should be a lawyer who has certain practice experience and can practice full-time, and has not received administrative punishment for stopping practice within three years before the application for establishment (on-site inspection, off-site verification through the management information system of the judicial administrative organ);
B. A general partnership law firm shall have three or more partners as founders, and the founders shall be lawyers with more than three years’ practice experience and full-time practice (on-site inspection, off-site verification through the management information system of judicial administrative organs);
C. A special general partnership law firm has more than 20 partners as founders, and the founders should be lawyers with more than three years’ practice experience and full-time practice (on-site inspection, off-site verification through the management information system of judicial administrative organs);
D the founder of a personal law firm shall be a lawyer with more than five years’ practice experience and full-time practice (on-site inspection, off-site verification through the management information system of the judicial administrative organ).
1.4.1.7. Whether the general partnership law firm and the special general partnership law firm have made a written partnership agreement, and whether the contents specified in the partnership agreement are sound and perfect.
A. The law firm can present the original partnership agreement on the spot and the text of the agreement is the version of the judicial administrative organ at the time of the last change (on-site inspection, off-site verification through the management information system of the judicial administrative organ);
B. The actual partners of the law firm are consistent with the partners in the agreement, and there is no case that the change procedures should be changed but not fulfilled (on-site inspection, off-site verification through the management information system of the judicial administrative organ);
C the partnership agreement shall contain the following contents (on-site inspection):
1) Partners, including name, residence, ID number, lawyer’s practice experience, etc.
2) The amount and mode of contribution of partners; Rights and obligations of partners;
3) The responsibilities of the person in charge of the partnership law firm and the procedures for its creation and change;
4) Responsibilities and rules of procedure of the partners’ meeting;
5) Partner’s income distribution and debt bearing mode;
6) Conditions and procedures for partners to join, quit and be removed from the partnership;
7) The methods and procedures for resolving disputes between partners, and the liabilities for violating the partnership agreement;
8) Procedures for interpretation and modification of the partnership agreement;
9) Other matters that need to be specified.
D the contents of the partnership agreement shall not conflict with relevant laws, regulations and rules. The partnership agreement shall be signed by all partners through consultation, and shall come into effect (on-site inspection) from the date when the judicial administrative organ makes a decision to approve the establishment or change of the law firm.
1.4.1.8. Number of full-time lawyers
A. As the founder, the general partnership law firm has not less than three partners, all of whom are consistent with the founders in the Articles of Association, and no one has been revoked from practicing qualification; The number of other full-time lawyers shall be subject to the actual registered number of law firms (on-site inspection of articles of association, roster and practice certificate, off-site verification through the management information system of judicial administrative organs);
B the special general partnership law firm shall have at least 20 partners as the founders, all of whom are in line with the founders in the Articles of Association, and no one has been disqualified; The number of other full-time lawyers shall be subject to the actual registered number of law firms (on-site inspection of articles of association, roster and practice certificate, off-site verification through the management information system of judicial administrative organs);
C the law firm funded by the state shall have at least two lawyers who meet the requirements of the Lawyers Law and can practice full-time (on-site inspection of articles of association, roster and practice certificate, off-site verification through the management information system of judicial administrative organs);
D the law firm is divided into three or more full-time lawyers stationed by the law firm (on-site inspection of articles of association, roster and practice certificate, off-site verification through the management information system of judicial administrative organs);
E. All full-time lawyers have signed labor contracts with this law firm and paid social security in this law firm, and there are no "registered" lawyers (on-site inspection of full-time lawyers’ labor contracts and social security payment records in the past three months).
1.4.1.9. Full-time lawyer qualification
A. Holding the Lawyer’s Practice Certificate issued by Beijing Municipal Bureau of Justice (on-site inspection); 2. The lawyer’s practice category is full-time lawyer (on-site inspection);
B the registered information of the lawyer’s actual practice law firm and lawyer’s practice certificate is consistent (on-site inspection);
C. In the corresponding column of lawyer’s practice certificate, the annual inspection and assessment results are competent and have been stamped with the special seal of "annual examination and filing of lawyers", and within the validity period of the annual inspection and assessment (on-site inspection, off-site verification through the management information system of judicial administrative organs);
D. After the full-time lawyer is given the administrative punishment of stopping practicing or revoking his practice license, he immediately stops handling the unfinished entrustment, and reports it to the law firm in time, and the law firm informs the client (on-site inspection of the personnel who have stopped practicing or revoked their practice license, and the law firm’s notification record);
E. Full-time lawyers do not practice during the period when they stop practicing, or continue to practice after their practice licenses are revoked (on-site inspection of entrustment contracts and files, on-site inquiry to clients of related cases, off-site verification through the management information system of judicial administrative organs).
1.4.1.10. Part-time lawyer qualification
A holding a part-time lawyer’s practice certificate issued by Beijing Municipal Bureau of Justice (on-site inspection);
B. Lawyers are part-time lawyers and I am a person engaged in legal education and research in institutions of higher learning and scientific research (on-site inspection of practice certificates and work units);
C. The actual practice law firm is consistent with the registration information of lawyer’s practice certificate, and there is no practice in more than two law firms (on-site inspection, off-site verification through the management information system of judicial administrative organs);
D. In the corresponding column of lawyer’s practice certificate, the annual inspection and assessment results are competent and have been stamped with the special seal of "lawyer’s annual assessment for the record", and within the validity period of the annual inspection and assessment (on-site inspection, off-site verification through the management information system of judicial administrative organs);
E. After a part-time lawyer is punished by administrative punishment of stopping practicing or revoking his practice license, he immediately stops handling the unfinished entrustment, and promptly reports it to the law firm, which will inform the client (on-site inspection of the personnel who have stopped practicing or revoked their practice license, and the law firm’s notification record);
F. Part-time lawyers do not practice during the period when they stop practicing, or continue to practice after their practice licenses are revoked (on-site inspection of entrustment contracts and files, on-site inquiry to clients of related cases, off-site verification through the management information system of judicial administrative organs).
1.4.1.11. Interns.
A. The interns hold the Internship Certificate for Applying for Lawyer Practitioners issued by the Lawyers Association (on-site inspection);
B. When accepting interns, the law firm or branch has no following circumstances (the person in charge of the law firm and the interns are asked on the spot, and checked off-site by the management system of the judicial administrative organ):
1) There is no internship guidance lawyer who meets the prescribed conditions;
2) Being subject to the following administrative punishment or industrial punishment due to suspension of business for rectification, and less than one year has passed since the date of punishment or punishment;
3) Being subject to administrative punishment of suspension of business for rectification, and the penalty period has not expired or has not exceeded three years after the expiration;
4) Being disciplined by the industry that prohibits accepting interns’ internships, and the disciplinary period has not expired.
C. Practice guidance lawyers in law firms or branches should have more than five years’ practice experience, love the career of lawyers, faithfully perform their duties as lawyers, have high professional ethics, high professional quality and rich practical experience, have not received administrative punishment or industrial punishment within three years, and each practice guidance lawyer should guide no more than two interns at the same time (on-site inspection of the number of interns, off-site verification of practice information through the management system of judicial administrative organs);
D. Law firms, branch offices and internship guidance lawyers have no following acts of instigating or indulging interns (spot-checking the assignment form of law firms or branch offices, spot-checking the files of internship guidance lawyers, spot-checking the clients by telephone, and spot-checking the business cards of interns):
1) Undertaking lawyer business alone;
2) Sign the agency agreement or legal consultant agreement in the name of lawyer and issue legal documents to the outside world;
3) Expressing opinions on defense or agency in the name of a lawyer in a court or arbitration tribunal;
4) Negotiating and contracting business in the name of a lawyer;
5) Printing business cards and other relevant materials in the name of lawyers;
6) Other activities that should be conducted in the name of lawyers according to law.
1.4.1.12. Information of auxiliary personnel
A. The law firm has signed labor contracts with all the hired auxiliary personnel and paid social security for them (on-site inspection of the auxiliary personnel’s labor contracts and social security payment records in the past three months);
B. Law firms and branch offices strictly supervise and manage the practice behavior of auxiliary personnel, and there is no any of the following behaviors (spot check on the assignment form of law firms or branch offices, spot check on lawyers’ files, spot check on clients by telephone, and spot check on the business cards of auxiliary personnel):
1) Making business cards and signs for the auxiliary staff with such names as "lawyer", "partner", "partner", "director" and "deputy director" which are inconsistent with the identity of the auxiliary staff;
2) In the special documents such as the letter of introduction and assignment issued by the law firm, the identity of the auxiliary personnel is not clearly indicated, and there is information that confuses the auxiliary personnel and lawyers;
3) Assign auxiliary personnel to engage in legal services alone;
4) Assigning auxiliary personnel is prohibited by other laws, regulations and rules.
C. A paralegal shall, in strict accordance with national laws, regulations and industry norms, assist lawyers in sorting out and drafting relevant documents and materials, investigating and collecting evidence, and, when appointed by a law firm and authorized by the parties concerned, assist lawyers in receiving and serving relevant litigation documents and handling other auxiliary legal affairs assigned by the law firm or lawyers, but shall not do any of the following acts (spot-check the work records of paralegal, spot-check the lawyer’s file, ask the client by telephone on the spot, and check the business cards of the assistants on the spot):
1) Printing business cards, signs or publicity as a lawyer;
2) Independently undertake legal service entrustment or sign and serve legal documents;
3) Charge the client privately.
1.4.2. Establishment and implementation of rules and regulations of domestic law firms
1.4.2.1. Is it standard to establish and implement financial management system?
A. A financial management system has been established and separate account books (on-site inspection) have been established for the legal services of law firms and branches;
B the accountants and cashiers of the law firm shall obtain corresponding qualifications, and the accountants and cashiers shall serve for different personnel (on-site inspection of personnel qualification certificates and signature of receipts and payments of financial bills);
C. Financial seals, bills, and counters keys for temporary cash storage shall be kept by special personnel in a unified way, and the security doors, safes, computers, ticket printers and other equipment and facilities in the financial room shall meet the requirements of basic specifications (on-site inspection);
D. In the separately established account books, the income and expenditure of all lawyers’ legal service fees have been accounted for one by one according to accounting standards, and there are no errors or omissions in the income and expenditure records. The lawyer’s legal service fees collected in the account should be accounted for separately and used for special purposes according to the entrustment agreement, and there is no cross-use or mixed use of fees under multiple entrustment agreements. Charges for lawyers’ legal services were collected from the unified account, but not from other accounts (some agreements were randomly selected from the entrustment agreements signed in the past three months, and the charging bills and accounting books were checked on the spot);
E. Strictly follow the requirements of financial management system and charging standard, standardize the use of bills, and issue bills according to the charging amount after the client pays the fees according to law, and there is no situation that bills are falsely written to the client or the objects of bills issued are inconsistent with the client (some agreements are randomly selected from the entrustment agreements signed in the last three months on site, and the charging bills are inspected on site);
F. There is no case of charging extra fees to the client beyond the agreement (some agreements are randomly selected from the entrustment agreements signed in the last three months on site, and the client is asked for inspection on site);
G. Standardize the production of financial statements, and submit them at the specified time (check the financial statements and reporting on site).
1.4.2.2. Do you pay taxes according to law?
A. The law firm can pay taxes according to law, and within the validity period of the annual inspection of the practice license, the law firm has no record of administrative punishment by the tax authorities (on-site inspection of tax payment vouchers or tax payment records, on-site inspection of the credit records of the law firm);
B. If a law firm withholds and pays personal income tax, it can withhold and pay according to the lawyer’s actual income according to law, and there is no record of administrative punishment imposed by the tax authorities for underpaying or underpaying personal income tax (on-site inspection of tax payment vouchers or tax payment records, on-site inspection of the credit records of lawyers and law firms).
1.4.2.3. Is it standardized to establish and implement the charge management system?
A. The legal services provided by the law firm have been clearly marked according to the provisions of the state and this Municipality, and the law firm’s website and office site have publicized the charging management measures and charging price standards as required (the charging price standards should include the names of charging items, corresponding price standards, calculation methods and other contents). (Check the publicity on site and check the charging method on site);
B. The law firm shall uniformly accept the entrustment and sign a written entrustment contract or charging contract with the client (on-site inspection of the entrustment contract or charging contract in the last three months);
C. The law firm has established a system of charge management and financial management, and strictly implemented it (text of on-site inspection system);
D. The law firm can issue legal bills for lawyers’ legal service fees to clients, and submit valid vouchers for fees paid on behalf of them or travel expenses for handling cases (on-site inspection of the bills and vouchers for fees);
E. Law firms and lawyers have not charged any fees to those who receive legal aid (taking legal aid cases on the spot and asking the recipients by telephone).
1.4.2.4. Is it standardized to establish and implement the system of asking for instructions, collective research, supervision and guidance for major and difficult cases?
A. The law firm has established a collective discussion and reporting system for major and difficult cases (text of on-site inspection system);
B. Whether the collective discussion and reporting system for major and difficult cases is complete includes the following contents (text of on-site inspection system):
1) the scope of major and difficult cases;
2) the mechanism of collective discussion and report;
3) the procedure of collective discussion;
4) Application and archiving of collective discussion conclusions;
5) Violation of internal treatment provisions of the system.
C records of the implementation of the collective discussion and reporting system for all major and difficult cases (on-site inspection records).
1.4.2.5. Is the conflict of interest review system established and implemented?
A the law firm has established a conflict of interest review system (text of on-site inspection system);
B. Whether the conflict of interest review system is complete includes the following contents (on-site inspection system text):
1) the scope of the review;
2) Review organization or management mechanism;
3) Prevention and control measures entrusted by conflict of interest;
4) Principles, procedures and methods for handling conflicts of interest;
5) Violation of the internal handling provisions of conflict of interest agents;
C records of the implementation of the conflict of interest review system of the law firm (on-site inspection).
1.4.3. Business Behavior of Domestic Law Firms
1.4.3.1. Do you accept cases with conflicts of interest in violation of regulations?
A. Law firms or branches strictly implement the conflict of interest review system, without any of the following circumstances:
1) Assign lawyers of the firm or branches to act as plaintiffs and defendants’ agents in the same litigation case, or defendants’ defenders and victims’ agents in the same criminal case (on-site inspection of entrustment agreements signed in recent three months);
2) Failing to review the conflict of interest of the entrusted matters according to the regulations, and appointing lawyers to act as agents or provide relevant legal services for the parties involved in non-litigation legal affairs with conflicts of interest at the same time or successively (on-site inspection of the entrustment agreement signed in the last three months);
3) Appoint the lawyer of our firm as an agent, defender or provide relevant legal services (ask the attorney on the spot) knowing that the lawyer and his close relatives have conflicts of interest with the entrusted matters;
4) conniving at or letting lawyers of the firm or its branches commit the following acts (checked by the management information system of the judicial administrative organ):
(1) Acting as an agent or providing relevant legal services for parties with conflicts of interest in the same civil litigation, administrative litigation or non-litigation legal affairs;
(2) Acting as a defender or agent for both the defendant and the victim in the same criminal case, or acting as a defender for two or more criminal suspects and defendants at the same time;
(3) providing legal services to the parties who have conflicts of interest with the consulting unit during his tenure as a legal adviser;
(4) A lawyer who has served as a judge or prosecutor, undertaking cases handled by the original court or procuratorate as an agent or defender;
(5) A lawyer who has served as an arbitrator or is still serving as an arbitrator, acting as an agent to undertake the case handled by the arbitration institution where he previously served or now serves;
B. In a law firm or branch, if there is a lawyer who has served as a member of the Standing Committee of the people’s congresses at all levels, he has stopped assigning him to engage in litigation agency or defense business (on-site inquiry and verification of the entrustment agreement) during his tenure.
1.4.3.2. Is it necessary to change the name, person in charge, articles of association, partnership agreement, domicile, partners and other major matters in violation of legal procedures?
A. To handle the change of the name, person-in-charge, articles of association, partnership agreement, domicile, partners and organizational form of the law firm for approval or filing according to the prescribed procedures;
1) If the name, person in charge, articles of association and partnership agreement of a law firm are changed, it shall be reported to the judicial administrative organ at the district level for review and approved by the Beijing Municipal Bureau of Justice in accordance with the procedures for establishing a law firm, and the actual name, person in charge, articles of association and partnership agreement after the change are consistent with the decision of the Beijing Municipal Bureau of Justice to approve the change (refer to the decision of approving the change issued by the Beijing Municipal Bureau of Justice on the spot);
2) If the domicile and partners of the law firm change, it shall be reported to the Beijing Municipal Bureau of Justice for filing within 15 days from the date of change (on-site inspection of the filing certification materials of the law firm, off-site verification by the management system of the judicial administrative organ);
3) If a law firm changes its organizational form, it shall handle the business connection, personnel arrangement, asset disposal, debt commitment and other matters according to law, and make corresponding amendments to the articles of association and partnership agreement before submitting an application for changing its name, person in charge, articles of association and partnership agreement to the judicial administrative organ (on-site inspection of relevant materials and vouchers for handling the above matters and the revised articles of association and partnership agreement);
B develop partners according to the prescribed conditions and procedures, and handle the withdrawal, delisting or selection of the person in charge of the law firm;
1) The new partner shall be a full-time practicing lawyer with more than three years’ practice experience, and there is no case where he has been punished for stopping practicing for more than six months and the punishment period has not exceeded three years (checking the practice information, inquiring about the public information of administrative punishment or checking the punishment through the management system of judicial administrative organs off-site);
2) If a partner withdraws from the partnership or is removed from the partnership, the law firm shall handle related property income, debt commitment and other affairs in accordance with the law, the articles of association of the firm and the partnership agreement (on-site inspection of relevant materials and vouchers for handling the above affairs);
3) The person in charge of the partnership law firm shall be elected by all the partners of the firm; The person in charge of a law firm funded by the state shall be elected by the lawyers of the firm and approved by the judicial administrative organ at the district level where it is located; The founder of an individual law firm is the person in charge of the firm. The person in charge of a law firm shall be submitted to the Beijing Municipal Bureau of Justice for approval when applying for the establishment permit (on-site verification of the identity of the person in charge of the law firm and inspection of relevant materials for selecting the person in charge).
C handle the division, merger, branch establishment, termination, liquidation and cancellation of the law firm according to the prescribed procedures;
1) If a law firm needs to change or cancel the original law firm and set up a new law firm due to division or merger, it shall, after handling the business connection, personnel arrangement, asset disposal, debt commitment and other matters of the relevant law firm, submit application materials such as separation agreement or merger agreement to the judicial administrative organ to handle the division and merger (on-site inspection of relevant materials and vouchers for handling the above matters);
2) When applying for the establishment of a branch office, a law firm shall submit the following materials to the judicial administrative organ:
(1) an application for establishing a branch office;
(2) the basic information of the firm, and the certificate issued by the licensing authority established by the firm that meets the conditions stipulated in Article 19 of the Lawyers Law and Article 33 of the Measures for the Administration of Law Firms;
(3) a copy of the practicing license of the firm, the articles of association and the partnership agreement of the firm;
(4) the list, resumes, identity certificates and copies of lawyers’ practice certificates of lawyers who intend to practice in the branch;
(5) the candidate and basic information of the person-in-charge of the branch to be appointed, and the certificate issued by the practice licensing authority for the candidate that meets the conditions specified in Item 5 of Paragraph 1 of Article 34 of the Measures for the Administration of Law Firms;
⑥ Name of the branch, proof of residence and proof of assets of the branch;
⑦ Measures for the administration of branches formulated by this Exchange. When applying for the establishment of a branch office, the applicant shall truthfully fill in the Registration Form for the Establishment of a Branch Office of a Law Firm (checked off-site by the administrative examination and approval management system of the judicial administrative organ);
3) After the cause of termination occurs, the law firm shall announce to the public, conduct liquidation in accordance with relevant regulations, and handle matters such as asset division and debt settlement according to law. A law firm shall submit an application for cancellation, a liquidation report, the practice license of the firm and other relevant materials to the judicial administrative organ at the local district level within 15 days after the liquidation, which will issue a review opinion and report all the cancellation application materials to the Beijing Municipal Bureau of Justice for review and cancellation procedures. If a law firm refuses to perform the obligation of announcement and liquidation, the judicial administrative organ at the district level can directly report to the Beijing Municipal Bureau of Justice for cancellation after making an announcement to the public. (Off-site inquiry of the law firm’s announcement through the website and verification of the relevant cancellation application materials submitted by the law firm to the judicial administrative organ).
1.4.3.3. Do you engage in business activities other than legal services?
A. The actual business scope of a law firm or branch is consistent with the business scope published in the law firm’s practice certificate or branch’s practice certificate issued by the judicial administrative organ, and there is no case of setting up an enterprise in the form of sole proprietorship, joint venture with others or entrusted shareholding, and appointing a lawyer to serve as the legal representative or general manager of the enterprise (on-site inspection, on-site questioning of the person in charge of the law firm and lawyers, off-site inspection of the annual assessment materials submitted by the law firm to the judicial administrative organ in the previous year);
B. The business scope of lawyer affairs or branches does not involve intermediary services unrelated to legal services such as engineering management services, enterprise management services, science and technology intermediary services, accounting evaluation, industrial and commercial tax agency consulting, patent and trademark agency, business information consulting, real estate intermediary services, financial and insurance securities intermediary services, professional marriage introduction services, culture, education and sports intermediary services, advertising consulting, planning, design and communication, etc. Or engage in other business activities for the purpose of profit (on-site inspection, on-site inquiry of the person in charge of the law firm and lawyers, off-site inspection of the annual assessment materials submitted by the law firm to the judicial administrative organ in the previous year).
1.4.3.4. Do you engage in business by slandering other law firms and lawyers or paying referral fees?
A. When a law firm or branch undertakes legal services through legal and proper channels, there are no following circumstances:
1) Contract business by misleading, luring, threatening or making false promises (spot check the case file, and check the relevant information with the parties by telephone call back);
2) Undertaking business by paying referral fees, giving kickbacks, promising to provide benefits, etc. (asking the person in charge of the law firm and relevant personnel on the spot);
3) Undertaking business by means of untrue and inappropriate publicity to the firm and lawyers or defaming the reputation of other lawyers and law firms (on-site inquiry of the website of law firms and relevant publicity materials);
4) Set up an office and reception room outside the residence of the firm to undertake business (ask the person in charge of the firm and relevant personnel on site).
B. Our lawyers did not commit the above-mentioned acts, or although they did, they were not caused by the connivance or laissez-faire of the law firm. After discovery, the law firm can take timely measures to correct the illegal acts and actively eliminate the harmful consequences (ask the person in charge of the law firm and the lawyers who committed the above-mentioned acts on the spot).
1.4.3.5. Whether to refuse to fulfill the obligation of legal aid?
A. The law firm cannot accept the legal aid cases assigned by the legal aid agencies for justified reasons, and makes a written explanation to the legal aid agencies that assigned the legal aid cases (ask the person in charge of the law firm on the spot, and consult the copy or photocopy of the explanatory materials issued by the law firm to the legal aid agencies);
B. After the law firm accepts the assignment, it arranges its lawyers to undertake legal aid cases in time according to the regulations, and there is no case of refusing to provide conditions and convenience for the handling of legal aid cases (spot check of legal aid files):
1) The law firm shall, within 2 working days from the date of receiving the notice of assignment, go through the formalities of accepting the assignment of cases and arrange for its lawyers to undertake legal aid cases;
2) The law firm shall inform the recipient of the name and contact information of the legal aid personnel within 5 working days from the date of assigning the legal aid personnel, and sign an agency agreement or defense agreement with the recipient or his legal representative or close relatives, except that it cannot be signed on time due to the reasons of the recipient.
C. There are no cases in which our lawyers refuse to accept legal aid cases assigned by law firms or legal aid agencies without justifiable reasons, or slack off or terminate their legal aid duties without authorization after accepting the assignment; Or although the situation exists, it does not belong to the connivance or laissez-faire of the law firm, and the law firm can take timely measures after discovering it.
Measures to correct illegal acts and actively eliminate harmful consequences (ask the person in charge of the law firm and the lawyers who have the above acts on the spot).
1.4.3.6. Does he provide false materials to the judicial administrative department or commit other fraudulent acts?
A. The law firm can actively cooperate with the supervision and inspection work of the judicial administrative organs, without intentionally concealing the real situation, refusing to provide relevant materials or providing false and false materials, or concealing, destroying or forging evidence materials (on-site inspection);
B. The law firm did not provide false, false or forged materials or engage in other fraudulent acts during the annual inspection and assessment, practice evaluation and evaluation of excellence (on-site verification of the true situation of relevant materials submitted by the law firm, and on-site inquiry of the person in charge of the law firm and relevant personnel);
C. The law firm has not provided false, false or forged certification materials to the judicial administrative organ or engaged in other fraudulent acts in the process of handling major changes, branch establishment, division, merger or termination, liquidation and cancellation (on-site verification of the truth of relevant materials submitted by the law firm, and on-site inquiry of the person in charge of the law firm and relevant personnel).
1.4.3.7, did you neglect the management of our lawyers, causing serious consequences?
A. The internal management system of the law firm is sound, the daily management is standardized and orderly, and the law firm operates normally (on-site verification of the actual operating conditions of the law firm and inspection of various internal management systems of the law firm);
B. Effectively supervise lawyers’ practice activities, without conniving, protecting or shielding our lawyers from engaging in illegal and disciplinary activities, resulting in serious consequences (ask the person in charge of the law firm and relevant personnel on the spot);
C. The lawyer did not continue to practice during the period when he was sentenced to suspend business for rectification or during the period when he was sentenced to stop practicing; Or although the above situation exists, it is not caused by the connivance or laissez-faire of the law firm. After discovering the situation, the law firm can take timely measures to correct the illegal behavior and actively eliminate the harmful consequences (ask the person in charge of the law firm and relevant personnel on the spot);
D the law firm accepts the annual inspection and assessment according to the regulations, and the annual inspection and assessment is rated as "qualified" (on-site inspection of the annual inspection and assessment results recorded in the copy of the practice certificate of the law firm in the past three years);
E. The law firm shall establish a labor contract system according to regulations, and handle social insurance such as unemployment, pension and medical care for lawyers and auxiliary personnel (on-site inspection of labor contracts and social insurance payment vouchers, etc.).
2. Administrative inspection of domestic lawyers
2.1. Inspection object
Domestic lawyers
2.2. Inspection method
On-site inspection, license inspection, on-site inquiry, information access, off-site inspection, and other means.
2.3. Inspection frequency
In principle, according to the annual law enforcement inspection plan (website publicity).
2.4. Inspection contents and standards
2.4.1. Qualification of domestic lawyers
2.4.1.1. Have you obtained a lawyer’s practice certificate?
2.4.1.2. Has the lawyer passed the annual examination and put on record by the judicial administrative organ and stamped the special seal on the practice certificate?
2.4.1.3. Is the registration information of lawyer’s practice institution and practice certificate consistent?
2.4.1.4. Is the lawyer’s practice certificate altered, altered, mortgaged, lent, leased or intentionally damaged?
2.4.2. Practice behavior of domestic lawyers
2.4.2.1. Do you practice in other law firms or social legal service institutions at the same time?
2.4.2.2. Whether to undertake business in the name of the lawyer of the law firm to be changed before being approved to change the practice institution, or whether to undertake business in the name of the lawyer of the original law firm after the change.
2.4.2.3. Do you undertake business by misleading, luring, threatening or making false promises?
2.4.2.4. Do you undertake business by paying referral fees, giving kickbacks, and promising to provide benefits?
2.4.2.5. Do you undertake business by making untrue and inappropriate publicity to yourself and your law firm or defaming the reputation of other lawyers and law firms?
2.4.2.6. Is there an office or reception room outside the residence of the law firm to undertake business?
2.4.2.7. Do you act as an agent or provide relevant legal services for parties with conflicts of interest in the same civil litigation, administrative litigation or non-litigation legal affairs?
2.4.2.8. Do you act as a defender or agent for both the defendant and the victim in the same criminal case, or act as a defender for more than two criminal suspects and defendants at the same time?
2.4.2.9. Did you provide legal services to the parties who have conflicts of interest with the legal advisory unit during his tenure as a legal adviser?
2.4.2.10. Have you ever served as a judge or prosecutor, and have you ever undertaken the cases handled by the former court or procuratorate as an agent or defender?
2.4.2.11. If he has served as an arbitrator or is still serving as an arbitrator, will he act as an agent to handle the cases handled by the arbitration institution where he previously served or now serves?
2.4.2.12. Did a former judge or prosecutor serve as an agent ad litem or defender or participate in litigation legal affairs undertaken by his law firm in other ways within two years after leaving the people’s court or people’s procuratorate?
2.4.2.13. Did he violate the uniform provisions on accepting entrustment or accept entrustment privately to undertake legal affairs during the period when he was sentenced to stop practicing?
2.4.2.14. Is it illegal to collect, use or encroach on lawyers’ service fees and lawyers’ travel expenses for handling cases in different places?
2.4.2.15. Do you ask the client for other fees, finance or other benefits in addition to the unified fees charged by the law firm?
2.4.2.16. Whether to ask the legal aid recipients for fees or accept financial or other benefits from the recipients?
2.4.2.17. Does he refuse to accept defense or agency after accepting the entrustment, and does not appear in court on time to participate in litigation or arbitration, except for the following legitimate reasons:
2.4.2.18. The entrusted matters are illegal, or the client engages in illegal activities by using the legal services provided by lawyers;
2.4.2.19. The client intentionally conceals important facts related to the case or provides false or forged evidence materials;
2.4.2.20. The client fails to perform the obligations stipulated in the entrustment contract;
2.4.2.21. The lawyer suffers from serious illness or is subject to administrative punishment above the suspension of practice;
2.4.2.22. Other persons who can refuse to defend or represent according to law.
2.4.2.23. Meeting with judges, prosecutors, arbitrators or other relevant staff members in non-working hours and non-working places for the purpose of influencing the outcome of handling cases during the period of undertaking agency and defense business;
2.4.2.24. Taking advantage of his special relationship with judges, prosecutors, arbitrators or other relevant staff members to influence the handling of cases according to law;
2.4.2.25. The handling of a case according to law is affected by distorting, untrue or misleading propaganda or slandering the reputation of the case-handling organ and staff and the other party.
2.4.2.26. Bribery by giving gifts, money or securities to judges, prosecutors, arbitrators and other staff members handling cases or their close relatives when they hold weddings, funerals and celebrations.
2.4.2.27 bribed judges, prosecutors, arbitrators and other staff members by means of renovating houses, reimbursing personal expenses, and subsidizing tourism and entertainment.
2.4.2.28. Bribing judges, prosecutors, arbitrators and other staff members by providing means of transportation, communication tools, housing or other articles.
2.4.2.29. For the purpose of influencing the outcome of handling a case, he directly pays bribes to judges, prosecutors, arbitrators and other staff members, introduces bribes or instigates or induces parties to pay bribes.
2.4.2.30. Did you conceal the real situation from the judicial administrative organs during the inspection and supervision, refused to provide or provide false or false materials, or concealed, destroyed or forged evidence materials?
2.4.2.31. Did you provide false, false or forged materials or engage in other fraudulent acts in the annual assessment, practice evaluation and evaluation of lawyers’ practice?
2.4.2.32. Did you provide false, false or forged materials when applying for changing the practice institution, going through the formalities of termination and cancellation of practice?
2.4.2.33 intentionally submits false evidence to a judicial organ, an administrative organ or an arbitration institution, or instigates, threatens or induces others to provide false evidence.
2.4.2.34. Instructing or helping clients or others to forge, conceal or destroy evidence, instructing or helping criminal suspects and defendants to collude in confession, threatening or inducing witnesses not to testify or commit perjury.
2.4.2.35. Obstructing the other party and its agents and defenders from obtaining evidence legally, or preventing others from providing evidence to the case handling organ or the other party.
2.4.2.36. Making or instructing clients to make statements that disturb the normal conduct of litigation and arbitration activities in a court or arbitration tribunal.
2.4.2.37. Preventing the client or other participants in the litigation from appearing in court, which makes the litigation and arbitration activities unable to proceed normally.
2.4.2.38. Inciting and abetting others to disturb the order of courts and arbitration tribunals.
2.4.2.39 refuses to defend himself in court, refuses to sign judicial documents or refuses to sign opinions on relevant litigation documents without justifiable reasons.
2.4.2.40. Inciting or instigating the parties to express their demands by illegal means such as illegal assembly, procession and demonstration, gathering people to disturb the order of public places and traffic, containing or attacking state organs, obstructing state organs and their staff from performing their duties according to law, and resisting law enforcement activities or the execution of judgments.
2.4.2.41. Using the media or other means to incite and abet the parties to interfere with the normal conduct of litigation, arbitration and administrative law enforcement activities by disturbing public order and endangering public security.
2.4.2.42. During the period of undertaking agency and defense business, he published and disseminated remarks that endangered national security, maliciously slandered judges, prosecutors, arbitrators, the other party and the third party, and seriously disturbed the court order.
2.4.2.43. During his practice, he published, produced and disseminated remarks, information, audio-visual products or supported, participated in or implemented activities aimed at endangering national security.
2.4.2.44. Violating the confidentiality obligations, intentionally or negligently revealing state secrets known in practice.
2.4.2.45. Do you use inducement, deception, coercion, extortion and other means to obtain the financial and rights disputes between the parties and others?
2.4.2.46. Does he instruct or induce the parties to transfer, sell or lease the finance and rights to others, and gain benefits from it?
2.4.2.47. Whether to provide the other party or the third party with information or evidential materials that are unfavorable to the client?
2.4.2.48. Does he collude with the other party or a third party in bad faith or cooperate in secret, thus preventing the client from exercising his rights legally?
2.4.2.49. Whether to accept the financial or other benefits of the other party, deliberately delay, slack off or fail to perform the duties of agency and defense according to law, thus causing adverse effects and losses to the handling of the client and entrusted matters.
2.4.2.50. Did you refuse to accept legal aid cases assigned by law firms or legal aid agencies without justifiable reasons?
2.4.2.51. Does he slack off or stop performing his legal aid duties without authorization after accepting the assignment?
2.4.2.52. Is it not timely to inform the recipients of the progress of legal aid?
2.4.2.53. Does the person who engages in legal services in the name of a lawyer obtain a lawyer’s practice certificate?
2.4.2.54. Is there any criminal punishment for intentional crime?
2.4.2.55. Is there any situation that should be given a warning punishment within one year after being given a warning punishment for violating the provisions of the Lawyers Law?
2.4.2.56. Is there any circumstance that should be punished for stopping practicing within two years after the expiration of the punishment for stopping practicing due to violation of the provisions of the Lawyers Law?
3. Administrative inspection of the legal service activities of the representative offices of Hong Kong and Macao law firms in the Mainland.
3.1. Inspection object
Representative offices of Hong Kong and Macao law firms in the Mainland
3.2. Inspection method
On-site inspection, license inspection, on-site inquiry, information access, off-site inspection, and other means.
3.3. Inspection frequency
In principle, according to the annual law enforcement inspection plan (website publicity).
3.4. Inspection contents and standards
3.4.1. Operating qualifications of representative offices of Hong Kong and Macao law firms in the Mainland
3.4.1.1. Has the representative office obtained a practice license?
A. It has obtained the practice license certificate of the representative offices of Hong Kong and Macao law firms in the Mainland issued by the Ministry of Justice (on-site inspection);
B. Hanging the original practicing license in the office of the representative office (on-site inspection);
C being able to produce a copy of the practice license during the supervision and inspection by the judicial administrative organ (on-site inspection)
D the information stated in the original and duplicate of the practice license of the representative office has not been altered (on-site inspection);
E. The name actually used by the representative office is consistent with the name stated in the original and duplicate of the practice license (on-the-spot inspection of web pages, agreements and brochures is compared with the practice license information);
F the information of the chief representative of the representative office is consistent with the registered information of the representative office (on-site inspection of the passport and residence permit information of the chief representative and comparison with the registered information); 7. The actual office address of the representative office is consistent with the domicile stated in the copy of the practice license (on-site inspection);
G. The representatives and employees of the representative office are consistent with the copy of the practice license (on-site inspection of the information of representatives and employees, off-site verification through the management information system of the judicial administrative organ);
H the special seal for annual inspection stamped in the copy of the practice license is true and effective (on-site inspection).
3.4.1.2. Has the representative office passed the annual inspection by the judicial administrative organ and stamped a special seal on the practice certificate?
A. The representative office shall submit a copy of the practice license and representative’s practice certificate and the inspection materials of the previous year to the Beijing Municipal Bureau of Justice before March 31st each year, and accept the annual inspection (off-site verification by the management information system of the judicial administrative organ);
B the representative office has passed the annual inspection and assessment, and the copy of the practice license has been stamped with the special seal for annual inspection and assessment (on-site inspection);
C. The validity period of the endorsement of the copy of the practice license has not been altered or expired, and it is consistent with the information saved in the management system of the judicial administrative organ (on-site inspection).
3.4.1.3. Has the representative office been dissolved or cancelled or revoked?
A the practice status of the representative office in the management system of the judicial administrative organ is normal (checked off-site by the lawyer management system);
B the representative office has no record of applying for cancellation or dissolution in the management system of judicial administrative organs (checked off-site by the lawyer management system);
C the representative office has no record of having its practice license revoked by the judicial administrative organ (checked off-site by the lawyer management system);
D the representative office has not been sealed up or banned by other administrative organs or judicial organs (on-site inquiry and on-site inspection).
3.4.1.4. Does the representative office apply for cancellation?
A. The judicial administrative organ has not received the application materials of Hong Kong and Macao law firms to cancel their representative offices in the Mainland (checked off-site through the lawyer management system);
B. The establishment materials issued by Hong Kong and Macao law firms are legal, authentic and valid when the representative office handles the licensing and annual inspection and assessment (checked off-site by the lawyer management system).
3.4.1.5. Is the representative’s qualification legal and valid, and is the actual information consistent with the registration?
A. If the representative offices increase or decrease their representatives, they have gone through the licensing procedures in accordance with the Administrative Measures of Hong Kong and Macao Special Administrative Regions on the Representative Offices in the Mainland, and the representative information of the representative offices is consistent with the registered information of the management system of the judicial administrative organs, and there is no information discrepancy (checked off-site through the lawyer management system);
B the representative of the representative office has not been punished by the judicial administrative organ to suspend business within a time limit or revoke the practice certificate, but still continues to practice (checked off-site by the lawyer management system);
C the representative of the representative office has not been disqualified by the Hong Kong and Macao law firm to which he belongs (on-site inquiry and on-site verification of the representative qualification certificate).
3.4.1.6. Does the representative have any situation that has not passed the annual inspection and assessment?
A. The representative of the representative office has passed the annual inspection, and the practice certificate of the representative has been stamped with the special seal for annual inspection, and there is no case of not accepting or failing the annual inspection (on-site inspection, off-site verification through the lawyer management system);
B after the representative of the representative office has passed the annual inspection, there is no case that the appointment of Hong Kong and Macao law firms is terminated within the validity period of the annual inspection (on-site inquiry, on-site verification of the appointment documents of Hong Kong and Macao law firms);
C. After the chief representative of the representative office passed the annual inspection, there was no case that the partner was dismissed by the Hong Kong and Macao law firm or held the same position as the partner within the validity period of the annual inspection (on-site inquiry, on-site verification of the appointment documents of the Hong Kong and Macao law firm);
D after the representative of the representative office has passed the annual inspection, there is no case of engaging in unapproved legal services within the validity period of the annual inspection (some agreements are randomly selected from the agreements in the past year for verification);
E. The representative office does not use any personnel other than the representative to engage in legal services (some agreements are randomly selected from the agreements in the past year for verification and on-site inquiry).
3.4.2. Business Behavior of Representative Offices of Hong Kong and Macao Law Firms in the Mainland
3.4.2.1. Does the representative office have any acts that endanger national security, public safety or social management order?
A. The representative office and its representatives shall abide by the relevant laws and regulations of People’s Republic of China (PRC), and have no acts endangering national security in their practice activities (on-site inspection, on-site questioning of the person in charge and representatives of the representative office):
B. The representative office and its representatives shall abide by the relevant laws and regulations of People’s Republic of China (PRC), and have no behaviors endangering public safety in their practice activities (on-site inspection, on-site questioning of the responsible persons and representatives of the representative office).
C representative offices and their representatives shall abide by the relevant laws and regulations of People’s Republic of China (PRC), and have no behaviors that endanger the social management order in their practice activities (on-site inspection, on-site questioning of the responsible persons and representatives of representative offices).
3.4.2.2. Does the representative office illegally engage in legal service activities or other profit-making activities in violation of regulations?
The representative office and its representatives have not engaged in other legal service activities or other profit-making activities other than the following acts (some agreements were randomly checked on the spot from the agreements in the past year):
A. To provide clients with legal advice on international treaties and practices in Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, Macao Special Administrative Region and other countries outside China where lawyers of the law firm have been allowed to practice law;
B to accept the entrustment of the parties or mainland law firms to handle legal affairs in areas where lawyers of the law firms have been allowed to practice law;
C to entrust mainland law firms to handle legal affairs in China on behalf of the parties in the Hong Kong and Macao Special Administrative Regions;
D. To maintain a long-term entrusted relationship with mainland law firms by concluding contracts to handle legal affairs;
E. providing information on the impact of the mainland’s legal environment;
F according to the agreement reached with the mainland law firm, the representative office may directly request the lawyers of the entrusted mainland law firm.
3.4.2.3. Does the representative office employ mainland lawyers or auxiliary staff to engage in legal services?
A. The representative office does not employ mainland lawyers (on-site inspection of the identity information of employees, off-site verification through the lawyer management system);
B. The actual employment of auxiliary personnel by the representative office is consistent with the information provided when handling the annual inspection of the representative office with the judicial administrative organ, and the auxiliary personnel employed are not engaged in legal service activities (on-site inspection of the identity information of auxiliary personnel, off-site comparison with the information provided during the annual inspection);
C. Without the presence of the representative of the representative office, the auxiliary personnel did not provide legal services to the clients alone (randomly asking the clients on the spot).
3.4.2.4. Does the representative office provide legal services? The fees charged have not been settled in the Mainland.
A. By comparing financial vouchers and tax payment vouchers, it is found whether the representative office has not settled in the Mainland;
B the legal services handled by the representative offices are settled in the mainland according to the agreement (the corresponding financial receipts and payments vouchers and tax payment vouchers are randomly selected on the spot).
3.4.2.5. Does the representative office fail to submit the annual inspection materials on time to accept the annual inspection, or fail to pass the annual inspection?
A. The representative offices of Hong Kong and Macao law firms in the Mainland shall submit copies of their practice licenses and representative practice certificates as well as the inspection materials of the previous year before March 31st each year, and accept the annual inspection (checked off-site through the lawyer management system);
B. If the representative office has passed the annual inspection, the copy of the practice license of the representative office has been stamped with the special seal for annual inspection, and there is no case of not accepting or failing the annual inspection (on-site inspection, off-site verification through the lawyer management system); 3. After the representative office has passed the annual inspection, there is no application for cancellation by Hong Kong and Macao law firms within the validity period of the annual inspection (on-site inquiry, off-site verification through the lawyer management system);
C after the representative office has passed the annual inspection, there is no case that the representative office should go through the change registration in accordance with the law but fails to do so in time within the validity period of the annual inspection (on-site inspection of the name, domicile, representative and scope of legal services).
3.4.2.6. Does the representative of the representative office hold or concurrently hold the position of representative in more than two representative offices at the same time?
A. The information contained in the power of attorney issued by the representative office and its affiliated Hong Kong and Macao law firm is consistent (on-site inspection of the power of attorney, on-site inquiry of the representative);
B the representative of a representative office has not been exposed by the media, complained or reported by the relevant departments, or transferred the case clues to the judicial administrative organ (off-site inspection of relevant websites, verification through the lawyer management system).
3.4.2.7. Does the representative office disclose the business secrets or personal privacy of the parties?
A the representative office has a management system (on-site inspection system text) to prevent the disclosure of business secrets or personal privacy of the parties;
B. There are no commercial secrets or personal privacy of the parties involved in the publicity web pages and publicity materials of the representative offices (on-site inspection of web pages and publicity materials);
C. In the legal service activities, the representatives and auxiliary personnel of the representative office did not spread business secrets or personal privacy to the society or to people other than the parties through the Internet, WeChat, SMS, etc. (on-site inquiry);
D. The representative office has not been exposed by the media, complained or reported by the relevant departments because of leaking business secrets or personal privacy, or transferred case clues to the judicial administrative organs (off-site inspection of relevant websites, verification through the lawyer management system).
3.4.2.8. Does the representative office take advantage of the convenience of legal services to accept property or other benefits from the parties?
A the representative office has a system for regulating the management of legal service agreements and fees (text of on-site inspection system);
B there is no act of signing a yin-yang agreement in the representative office. Yin-yang agreement: the legal service agreement provided by the representative office in the process of supervision and inspection by the judicial administrative organ is inconsistent with the legal service agreement actually signed with the parties (some agreements are randomly selected from the agreements in the past year to ask the parties);
C. In the process of providing legal services, there is no act of taking advantage of legal services to accept property or other benefits from the parties other than those stipulated in the agreement (randomly select some agreements from the agreements in the past year to ask the parties).
3.4.2.9. If the representative office is cancelled, will the property be transferred outside the mainland before the debt is paid off?
A. If the representative office is cancelled, it shall be liquidated according to law (on-site inspection);
B before or during the debt settlement, there is no case of transferring the property outside the mainland (on-site inspection, on-site inquiry to the person in charge of the representative office).
3.4.2.10. Does the representative office whose practice license has been revoked continue to engage in legal service activities in the Mainland?
A. After the practice license of the representative office is revoked, the original and duplicate of the practice license certificate have been returned to the judicial administrative organ (the practice license confiscated by the judicial administrative organ is checked and checked off-site through the lawyer management system);
B. After the practice license of the representative office is revoked, it will no longer continue to sign legal service agreements in the name of the representative office, and its representatives will no longer engage in legal service activities (on-site inquiry of the person in charge of the representative office, off-site inquiry of online public opinion).
4. Administrative inspection of the legal service activities of the representatives of Hong Kong and Macao law firms in the Mainland.
4.1. Inspection object
Representatives of representative offices of Hong Kong and Macao law firms in the Mainland
4.2. Inspection method
On-site inspection, license inspection, on-site inquiry, information access, off-site inspection, and other means.
4.3. Inspection frequency
In principle, according to the annual law enforcement inspection plan (website publicity).
4.4. Inspection contents and standards
4.4.1. Professional qualifications of representatives of representative offices of Hong Kong and Macao law firms in the Mainland
4.4.1.1. Has the representative obtained a practice certificate?
4.4.1.2. Have you passed the annual inspection by the judicial administrative organ and stamped the special seal on the practice certificate?
4.4.1.3. Is the practice institution consistent with the certificate records?
4.4.2. Practice Behavior of Representatives of Mainland Representative Offices of Hong Kong and Macao Law Firms
4.4.2.1. Is it illegal to engage in legal service activities or other profit-making activities?
4.4.2.2. Whether to disclose the business secrets or personal privacy of the parties concerned?
4.4.2.3. Does he act as or concurrently act as a representative in more than two representative offices?
4.4.2.4. Do you take advantage of the convenience of legal services to accept property or other benefits from the parties concerned?
Are lawyers, other organizations and individuals from 4.4.2.5, Hongkong and Macao law firms engaged in legal service activities in the Mainland without authorization?
4.4.2.6. Does the representative whose practice license has been revoked continue to engage in legal service activities in the Mainland?
5. Administrative inspection of the legal service activities of the representative offices of foreign law firms in China.
5.1. Inspection object
Representative offices of foreign law firms in China
5.2. Inspection method
On-site inspection, license inspection, on-site inquiry, information access, off-site inspection, and other means.
5.3. Inspection frequency
In principle, according to the annual law enforcement inspection plan (website publicity).
5.4. Inspection contents and standards
5.4.1. Qualification of representative offices of foreign law firms in China
5.4.1.1. Has the representative office obtained a practice license?
A. It has obtained the practice license certificate of representative offices of foreign law firms in China issued by the Ministry of Justice (on-site inspection);
B. Hanging the original practicing license in the office of the representative office (on-site inspection);
C being able to produce a copy of the practice license during the supervision and inspection by the judicial administrative organ (on-site inspection)
D the information stated in the original and duplicate of the practice license of the representative office has not been altered (on-site inspection);
E. The name actually used by the representative office is consistent with the name stated in the original and duplicate of the practice license (on-the-spot inspection of web pages, agreements and brochures is compared with the practice license information);
F the information of the chief representative of the representative office is consistent with the registered information of the representative office (on-site inspection of the passport and residence permit information of the chief representative and comparison with the registered information);
G. The actual office address of the representative office is consistent with the domicile stated in the copy of the practice license (on-site inspection);
H the representatives and employees of the representative office are recorded in the same way as the copy of the practice license (on-site inspection of the information of representatives and employees, off-site verification through the management information system of the judicial administrative organ);
I. The special seal for annual inspection stamped in the copy of the practice license is true and effective (on-site inspection).
5.4.1.2. Has the representative office passed the annual inspection by the judicial administrative organ and stamped a special seal on the practice certificate?
A. The representative office shall submit a copy of the practice license and representative’s practice certificate and the inspection materials of the previous year to the Beijing Municipal Bureau of Justice before March 31st each year, and accept the annual inspection (off-site verification by the management information system of the judicial administrative organ);
B the representative office has passed the annual inspection and assessment, and the copy of the practice license has been stamped with the special seal for annual inspection and assessment (on-site inspection);
C. The validity period of the endorsement of the copy of the practice license has not been altered or expired, and it is consistent with the information saved in the management system of the judicial administrative organ (on-site inspection).
5.4.1.3. Has the representative office been dissolved or cancelled or revoked?
A the practice status of the representative office in the management system of the judicial administrative organ is normal (checked off-site by the lawyer management system);
B the representative office has no record of applying for cancellation or dissolution in the management system of judicial administrative organs (checked off-site by the lawyer management system);
C the representative office has no record of having its practice license revoked by the judicial administrative organ (checked off-site by the lawyer management system);
D the representative office has not been sealed up or banned by other administrative organs or judicial organs (on-site inquiry and on-site inspection).
5.4.1.4. Does the representative office apply for cancellation?
A. The judicial administrative organ has not received the application materials for cancellation of foreign law firms in China (checked off-site through the lawyer management system);
B. The establishment materials issued by foreign law firms are legal, authentic and valid when the representative office handles the licensing and annual inspection and assessment (checked off-site through the lawyer management system).
5.4.1.5. Is the practice qualification of the representative office legal and valid, and is the actual information consistent with the registration?
A. If the representative offices increase or decrease their representatives, they have gone through the licensing procedures in accordance with the Regulations on the Administration of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China and the Measures for the Administration of Representative Offices in the Mainland. The representative information of the representative offices is consistent with the registered information of the judicial administrative organ management system, and there is no information discrepancy (checked by the lawyer management system off-site);
B the representative of the representative office has not been punished by the judicial administrative organ to suspend business within a time limit or revoke the practice certificate, but still continues to practice (checked off-site by the lawyer management system);
C the representative of the representative office is not disqualified by the foreign law firm to which it belongs (on-site inquiry, on-site verification of representative qualification certificate).
5.4.1.6. Does the representative of the representative office have not passed the annual inspection and assessment?
A. The representative of the representative office has passed the annual inspection, and the practice certificate of the representative has been stamped with the special seal for annual inspection, and there is no case of not accepting or failing the annual inspection (on-site inspection, off-site verification through the lawyer management system);
B. After the representative of the representative office has passed the annual inspection, it has not been dismissed by the foreign law firm within the validity period of the annual inspection (on-site inquiry and on-site verification of the appointment documents of the foreign law firm);
C after the chief representative of the representative office has passed the annual inspection, there is no case that the partner is dismissed by the foreign law firm or holds the same position as the partner within the validity period of the annual inspection (on-site inquiry and on-site verification of the appointment documents of the foreign law firm);
D after the representative of the representative office has passed the annual inspection, there is no case of engaging in unapproved legal services within the validity period of the annual inspection (some agreements are randomly selected from the agreements in the past year for verification);
E. The representative office does not use any personnel other than the representative to engage in legal services (some agreements are randomly selected from the agreements in the past year for verification and on-site inquiry).
5.4.2. Business Behavior of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China
5.4.2.1. Does the representative office have any acts that endanger national security, public safety or social management order?
A. The representative office and its representatives shall abide by the relevant laws and regulations of People’s Republic of China (PRC), and have no acts endangering national security in their practice activities (on-site inspection, on-site questioning of the person in charge and representatives of the representative office):
B. The representative office and its representatives shall abide by the relevant laws and regulations of People’s Republic of China (PRC), and have no behaviors endangering public safety in their practice activities (on-site inspection, on-site questioning of the responsible persons and representatives of the representative office).
C representative offices and their representatives shall abide by the relevant laws and regulations of People’s Republic of China (PRC), and have no behaviors that endanger the social management order in their practice activities (on-site inspection, on-site questioning of the responsible persons and representatives of representative offices).
5.4.2.2. Does the representative office illegally engage in legal service activities or other profit-making activities in violation of regulations?
The representative office and its representatives have not engaged in other legal service activities or other profit-making activities other than the following acts (some agreements were randomly checked on the spot from the agreements in the past year):
A. To provide the clients with legal advice on international treaties and practices in countries where the lawyers of the law firm have been allowed to practice as lawyers and other countries outside China;
B accept the entrustment of the parties or China law firm to handle legal affairs in the country where the lawyers of the law firm have been allowed to practice law;
C. On behalf of foreign parties, entrust China Law Firm to handle legal affairs in China;
D. Maintain a long-term entrusted relationship with China Law Firm to handle legal affairs through concluding contracts;
E. Providing information on the impact of the legal environment in China;
F. According to the agreement reached with China Law Firm, the representative office may directly request the lawyer of China Law Firm.
5.4.2.3. Does the representative office employ a practicing lawyer in China, or employ auxiliary personnel to engage in legal services?
A. The representative office has no employment of practicing lawyers in China (on-site inspection of the identity information of employees, off-site verification through the lawyer management system);
B. The actual employment of auxiliary personnel by the representative office is consistent with the information provided when handling the annual inspection of the representative office with the judicial administrative organ, and the auxiliary personnel employed are not engaged in legal service activities (on-site inspection of the identity information of auxiliary personnel, off-site comparison with the information provided during the annual inspection);
C. Without the presence of the representative of the representative office, the auxiliary personnel did not provide legal services to the clients alone (randomly asking the clients on the spot).
5.4.2.4. The fees charged by the representative office for providing legal services have not been settled in China.
A. By comparing financial vouchers and tax payment vouchers, it is found whether the representative office has not settled in the Mainland. ;
B. The legal services handled by the representative offices are settled in China according to the agreement (the corresponding financial receipts and payments vouchers and tax payment vouchers are randomly selected on site).
5.4.2.5. Does the representative office fail to submit the annual inspection materials on time to accept the annual inspection, or fail to pass the annual inspection?
A. The representative offices of foreign law firms in China shall submit copies of their practice licenses and representative practice certificates as well as the inspection materials of the previous year before March 31st each year, and accept the annual inspection (checked off-site through the lawyer management system);
B. If the representative office has passed the annual inspection, the copy of the practice license of the representative office has been stamped with the special seal for annual inspection, and there is no case of not accepting or failing the annual inspection (on-site inspection, off-site verification through the lawyer management system);
C after the representative office has passed the annual inspection, it has not been applied for cancellation by a foreign law firm within the validity period of the annual inspection (on-site inquiry, off-site verification through the lawyer management system);
D after the representative office has passed the annual inspection, there is no case that the representative office should go through the change registration in accordance with the law but fails to do so in time within the validity period of the annual inspection (on-site inspection of the name, domicile, representative and scope of legal services).
5.4.2.6. Does the representative of the representative office hold or concurrently hold the position of representative in more than two representative offices at the same time?
A the information contained in the power of attorney issued by the representative office and the foreign law firm to which the representative belongs is consistent (on-site inspection of the power of attorney, on-site inquiry of the representative);
B the representative of a representative office has not been exposed by the media, complained or reported by the relevant departments, or transferred the case clues to the judicial administrative organ (off-site inspection of relevant websites, verification through the lawyer management system).
5.4.2.7. Does the representative office disclose the business secrets or personal privacy of the parties?
A the representative office has a management system (on-site inspection system text) to prevent the disclosure of business secrets or personal privacy of the parties;
B. There are no commercial secrets or personal privacy of the parties involved in the publicity web pages and publicity materials of the representative offices (on-site inspection of web pages and publicity materials);
C. In the legal service activities, the representatives and auxiliary personnel of the representative office did not spread business secrets or personal privacy to the society or to people other than the parties through the Internet, WeChat, SMS, etc. (on-site inquiry);
D. The representative office has not been exposed by the media, complained or reported by the relevant departments because of leaking business secrets or personal privacy, or transferred case clues to the judicial administrative organs (off-site inspection of relevant websites, verification through the lawyer management system).
5.4.2.8. Does the representative office take advantage of the convenience of legal services to accept property or other benefits from the parties?
A the representative office has a system for regulating the management of legal service agreements and fees (text of on-site inspection system);
B there is no act of signing a yin-yang agreement in the representative office. Yin-yang agreement: the legal service agreement provided by the representative office in the process of supervision and inspection by the judicial administrative organ is inconsistent with the legal service agreement actually signed with the parties (some agreements are randomly selected from the agreements in the past year to ask the parties);
C. In the process of providing legal services, there is no act of taking advantage of legal services to accept property or other benefits from the parties other than those stipulated in the agreement (randomly select some agreements from the agreements in the past year to ask the parties).
5.4.2.9. If the representative office is cancelled, will the property be transferred outside China/Mainland before the debt is paid off?
A. If the representative office is cancelled, it shall be liquidated according to law (on-site inspection);
B there is no case of transferring the property outside China before or during the debt settlement (on-site inspection, on-site inquiry to the person in charge of the representative office).
5.4.2.10. Does the representative office whose practice license has been revoked continue to engage in legal service activities in China?
A. After the practice license of the representative office is revoked, the original and duplicate of the practice license certificate have been returned to the judicial administrative organ (the practice license confiscated by the judicial administrative organ is checked and checked off-site through the lawyer management system);
B. After the practice license of the representative office is revoked, it will no longer continue to sign legal service agreements in the name of the representative office, and its representatives will no longer engage in legal service activities (on-site inquiry of the person in charge of the representative office, off-site inquiry of online public opinion).
6. Administrative inspection of legal service activities of representatives of representative offices of foreign law firms in China.
6.1. Inspection object
Representatives of representative offices of foreign law firms in China
6.2. Inspection method
On-site inspection, license inspection, on-site inquiry, information access, off-site inspection, and other means.
6.3. Inspection frequency
In principle, according to the annual law enforcement inspection plan (website publicity).
6.4. Inspection contents and standards
6.4.1. Qualification of representatives of representative offices of foreign law firms in China
6.4.1.1. Has the representative of the representative office obtained the practice certificate?
6.4.1.2. Have you passed the annual inspection by the judicial administrative organ and stamped the special seal on the practice certificate?
6.4.1.3. Is the representative office’s representative practice institution consistent with the certificate record?
6.4.2. Practice Behavior of Representatives of Representative Offices of Foreign Law Firms in China
6.4.2.1. Does the representative of the representative office illegally engage in legal service activities or other profit-making activities in violation of regulations?
6.4.2.2. Is he a representative in two or more representative offices at the same time?
6.4.2.3. Whether to disclose the business secrets or personal privacy of the parties concerned?
6.4.2.4. Do you take advantage of the convenience of legal services to accept financial or other benefits from the parties?
6.4.2.5. Do foreign law firms, foreign lawyers and other foreign organizations and individuals engage in legal service activities in China without authorization?
6.4.2.6. Does the representative whose practice license has been revoked continue to engage in legal service activities in China?
7. Administrative inspection of grass-roots legal service offices
7.1. Inspection object
Grassroots law service office
7.2. Inspection method
On-site inspection, license inspection, on-site inquiry, information access, off-site inspection, and other means.
7.3. Inspection frequency
In principle, according to the annual law enforcement inspection plan (website publicity).
7.4. Inspection contents and standards
7.4.1. Operating qualification of grass-roots legal service offices
7.4.1.1. Has the grassroots legal service office obtained the Practice Certificate of Grassroots Legal Service Office?
7.4.1.2. Is the Practice Certificate of Grassroots Legal Service Office publicized in the practice place?
7.4.1.3. Is the practice place of grassroots legal service office consistent with the certificate registration information?
7.4.1.4. Does the practice place meet the purpose of practice?
7.4.1.5. Are the rules and regulations of grassroots legal service offices sound?
Articles of association, practice management system, financial management system, distribution system, business training system, complaint investigation system, personnel reward and punishment system, financial and fee management system, and file management system of grassroots legal service offices.
7.4.1.6. Does the number of employees in grassroots legal service offices meet the requirements?
7.4.1.7. Do grassroots legal service workers have professional qualifications?
7.4.2. Operation Behavior of Grassroots Legal Service Offices
7.4.2.1. Does the grassroots legal service office go beyond the business scope and litigation agency practice area?
7.4.2.2. Does the grass-roots legal service office violate the regulations by not accepting entrustment and collecting service fees in the name of the grass-roots legal service office, and not issuing valid charging vouchers to the clients?
7.4.2.3. Does the grass-roots legal service office compete for business by improper means such as belittling others, raising itself, making false promises and paying referral fees?
7.4.2.4. Does the grassroots legal service office practice in the name of a law firm?
7.4.2.5. Is the grass-roots legal service office forging, altering, mortgaging, leasing or lending its practice certificate?
7.4.2.6. Does the grassroots legal service office change its name, legal representative or responsible person, partner, domicile and articles of association in violation of regulations?
7.4.2.7. Does the grassroots legal service office fail to accept the annual assessment as required, or practise fraud in the annual assessment?
7.4.2.8. Does the grass-roots legal service office privately divide, misappropriate or otherwise illegally dispose of its assets in violation of financial management regulations?
7.4.2.9. Does the grassroots legal service office employ people who are not allowed to practice as grassroots legal service workers to undertake business in the name of grassroots legal service workers?
7.4.2.10. Does the grass-roots legal service office indulge or cover up the illegal and disciplinary acts of the grass-roots legal service workers in this office?
7.4.2.11. Is the internal management of grass-roots legal service office chaotic and unable to carry out business normally?
8 administrative inspection of the practice of grassroots legal service workers
8.1. Inspection object
Grassroots legal service workers
8.2. Inspection method
On-site inspection, license inspection, on-site inquiry, information access, off-site inspection, and other means.
8.3. Inspection frequency
In principle, according to the annual law enforcement inspection plan (website publicity).
8.4. Inspection contents and standards
8.4.1. Qualification of grassroots legal service workers
8.4.1.1. Have grassroots legal service workers obtained the Practice Certificate of Grassroots Legal Service Workers?
8.4.1.2. Is the registration information of the practice institution of grassroots legal service workers consistent with the Practice Certificate of Grassroots Legal Service Workers?
8.4.1.3. Is the Practice Certificate of Grassroots Legal Service Workers forged, altered, mortgaged, lent or leased?
8.4.2. Practice Behavior of Grassroots Legal Service Workers
8.4.2.1, a grass-roots legal service worker who used to be a judge, is he an agent ad litem in the original court?
8.4.2.2. Do grassroots legal service workers practice in the name of lawyers?
8.4.2.3. Do grassroots legal service workers practice in grassroots legal service offices and law firms or notaries at the same time, or practice in more than two grassroots legal service offices at the same time?
8.4.2.4. Do grassroots legal service workers know that the client’s request is illegal and fraudulent, and they still provide assistance to them?
8.4.2.5. Are grassroots legal service workers representing both parties or interested third parties in the same lawsuit, arbitration or administrative ruling?
8.4.2.6. Do grassroots legal service workers accept the entrustment to undertake legal affairs privately, or charge fees privately, or ask clients for extra remuneration?
8.4.2.7. Do grassroots legal service workers seek business by improper means such as belittling others, raising themselves, making false promises or paying referral fees?
8.4.2.8. Do grassroots legal service workers exceed the agency authority or abuse the agency authority in agency activities, infringing on the legitimate interests of the principal?
8.4.2.9. Do grassroots legal service workers fail to abide by the entrustment contract concluded with the parties, refuse or neglect to perform their legal service obligations, and damage the legitimate rights and interests of the clients?
8.4.2.10. Do grassroots legal service workers suppress, insult or retaliate against the parties in their professional activities such as mediation, agency and legal counsel, causing adverse effects?
8.4.2.11. Are grassroots legal service workers aware of business secrets or personal privacy in their practice activities?
8.4.2.12. Do grassroots legal service workers accept the property of the other party or interested party or collude with them maliciously in agency activities, thus harming the legitimate rights and interests of the client?
8.4.2.13. Do grassroots legal service workers meet with relevant judicial, arbitration or administrative law enforcement personnel in violation of regulations, or treat them with gifts for the purpose of influencing the outcome of case trial, arbitration and administrative ruling?
8.4.2.14. Do grassroots legal service workers violate the relevant regulations on judicial, arbitration and administrative law enforcement, interfere with or hinder the normal conduct of judicial, arbitration and administrative law enforcement?
8.4.2.15. Do grassroots legal service workers forge, conceal or destroy evidence or intentionally assist clients to forge, conceal or destroy evidence?
8.4.2.16. Do grassroots legal service workers pay bribes or introduce bribes to relevant judicial personnel, arbitrators or administrative law enforcement personnel, or instigate or induce clients to pay bribes to them?
8.4.2.17. Do grassroots legal service workers disclose state secrets they know in their practice?
8.4.2.18. Do grassroots legal service workers refuse to perform their legal aid obligations without justifiable reasons?
8.4.2.19. Do grassroots legal service workers refuse, delay or terminate the implementation of legal aid without justifiable reasons?
8.4.2.20. Do grassroots legal service workers collect property from recipients or seek other illegitimate interests?
8.4.2.21. Do grassroots legal service workers fail to inform the recipients of the progress of legal aid in time?
9. Administrative inspection of judicial authentication institutions
9.1. Inspection object
Judicial expertise institution
9.2. Inspection method
On-site inspection, license inspection, on-site inquiry, information access, off-site inspection, and other means.
9.3. Inspection frequency
In principle, according to the annual law enforcement inspection plan (website publicity).
9.4. Inspection contents and standards
9.4.1. Operating qualification of judicial authentication institutions
9.4.1.1. Is the publicity and custody of the Judicial Appraisal License standardized?
A. The judicial authentication institution hangs the Certificate of Judicial Authentication License (Original) in a prominent position in the practice place (on-site inspection);
B in the process of supervision and inspection by the judicial administrative organ, the judicial authentication institution can produce the original certificate of Judicial Authentication License (copy) (on-site inspection);
C. The actual name, actual residence, business scope, legal representative or the name of the person in charge of the judicial authentication institution are consistent with the information stated in the original and duplicate of the Judicial Authentication License (on-site inspection, on-site comparison with the practice license information through information such as web pages, agreements and brochures);
D. The original and duplicate copies of the Judicial Appraisal License are not obviously damaged or defiled, and there is no trace of artificial alteration of the information specified (on-site inspection);
E. The judicial authentication institution under inspection is in normal practice; If the registration is cancelled or the practice is stopped, the original and copy of the Judicial Appraisal License have been returned to the judicial administrative organ (checked off-site by the management information system of the judicial administrative organ).
9.4.1.2. Does the alteration, extension and cancellation of the Judicial Appraisal License conform to the provisions?
A. The service period of the Judicial Appraisal License is five years, counting from the date of issuance. The judicial authentication license held by the judicial authentication institution has not exceeded the service period (on-site inspection of the original and duplicate of the judicial authentication license);
B the registered items after the change of the judicial authentication institution have been marked by the judicial administrative organ on the copy of the judicial authentication license (on-site inspection of the copy of the judicial authentication license);
C. If the service period of the Judicial Appraisal License expires less than 30 days, and the judicial appraisal institution needs to continue, it has applied to the judicial administrative organ for extension (on-site inspection of the original and duplicate of the Judicial Appraisal License, off-site verification through the administrative examination and approval system).
9.4.1.3. Does the practice place meet the appraisal purpose and whether the regional division is reasonable?
A. The practice place of the judicial authentication institution meets the requirements of laboratory configuration related to judicial authentication (on-site inspection);
B. According to the requirements of business scope and practice category, the practice place shall reasonably divide areas (on-site inspection) such as receiving appraisal entrustment, keeping appraisal materials, carrying out appraisal activities and storing appraisal files.
9.4.1.4. Does the functional area configuration of the laboratory in the practice place meet the requirements?
According to the business scope of the judicial authentication institution, its place setting shall meet the requirements of the laboratory functional areas listed in the following professional fields (on-site inspection and check with the laboratory configuration requirements table of the four types of judicial authentication institutions):
A. Forensic medicine
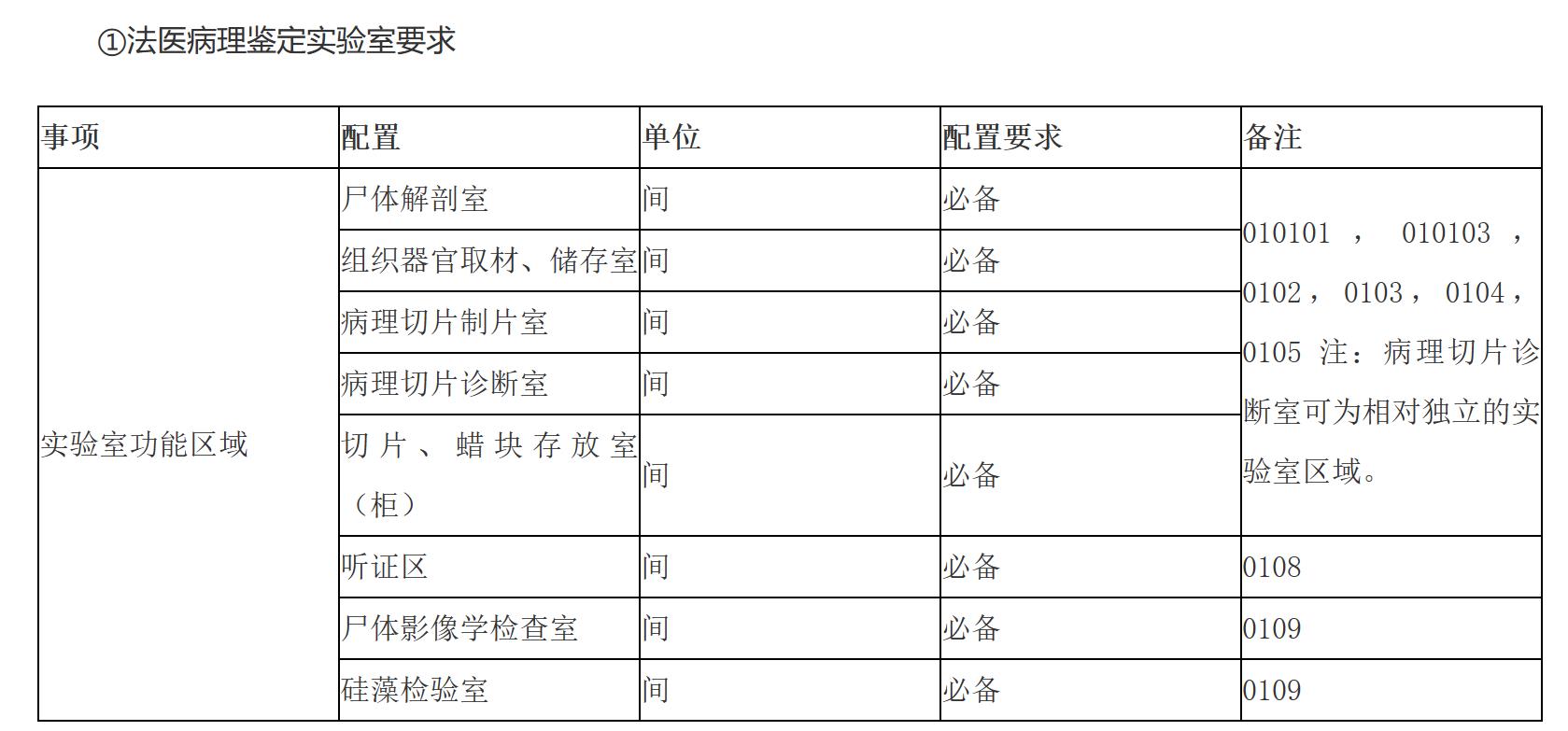
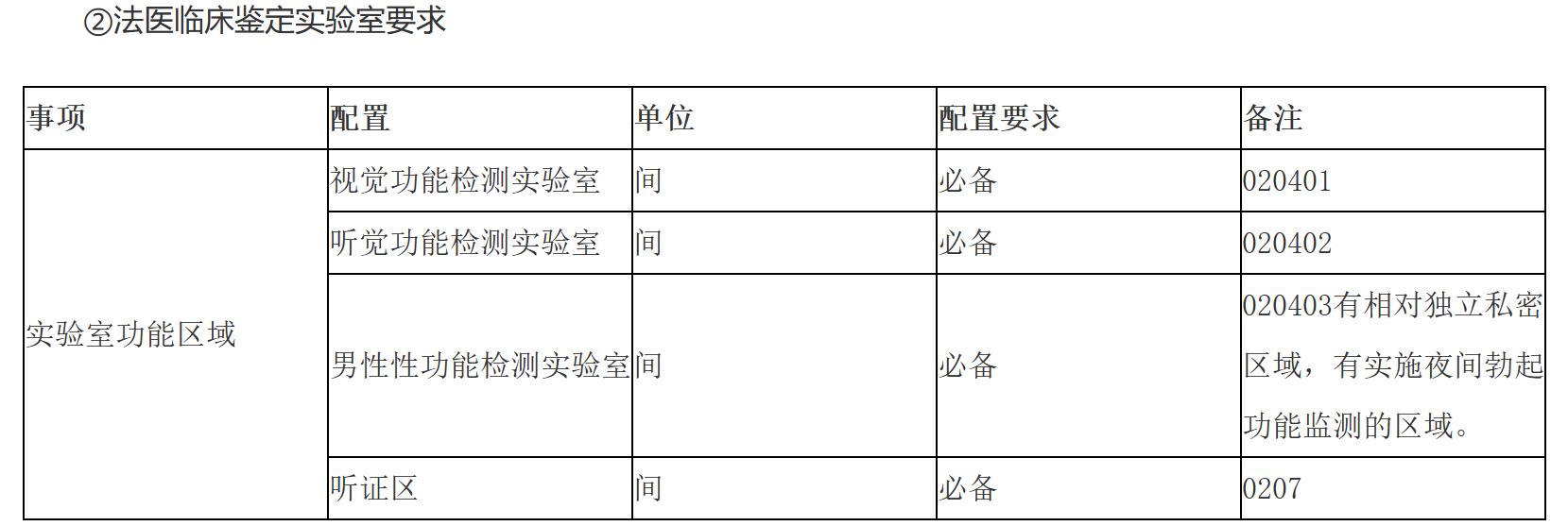
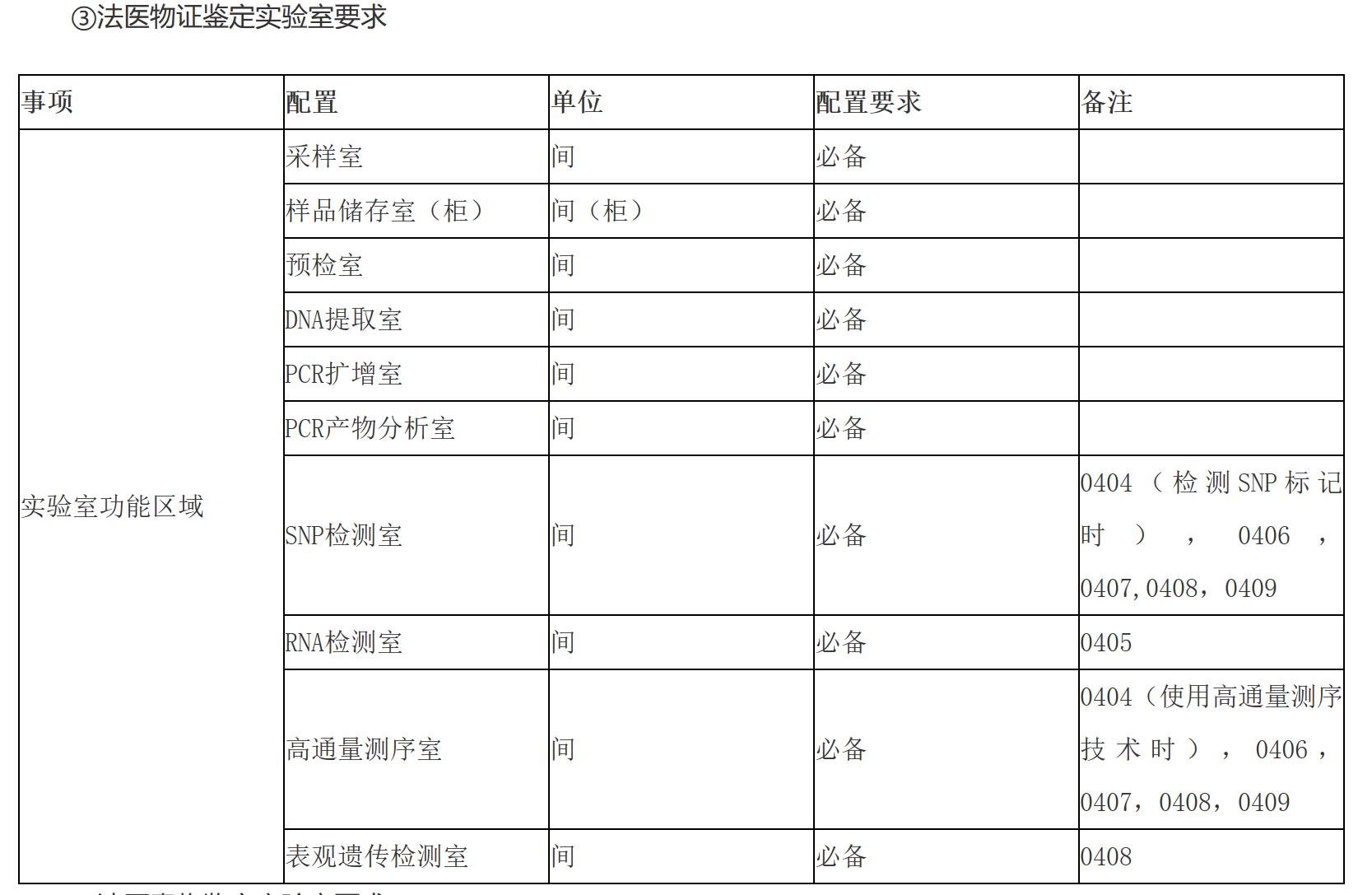
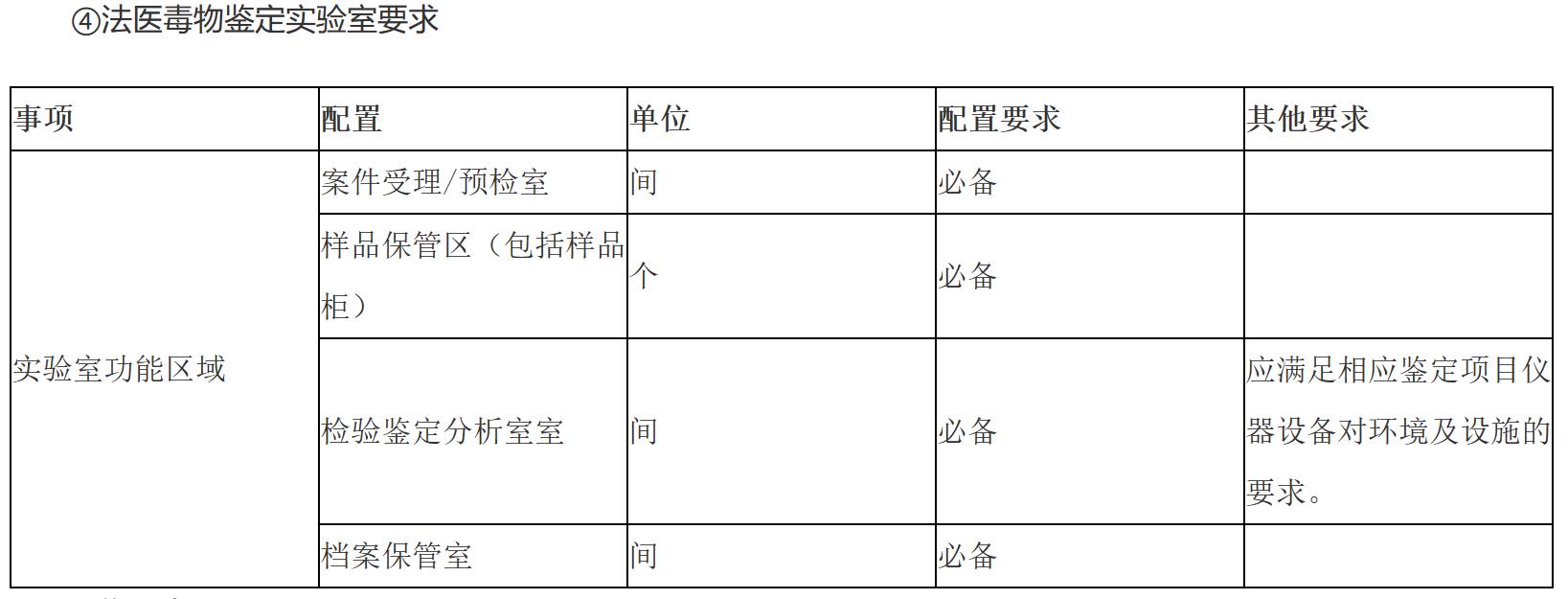
B. Physical evidence
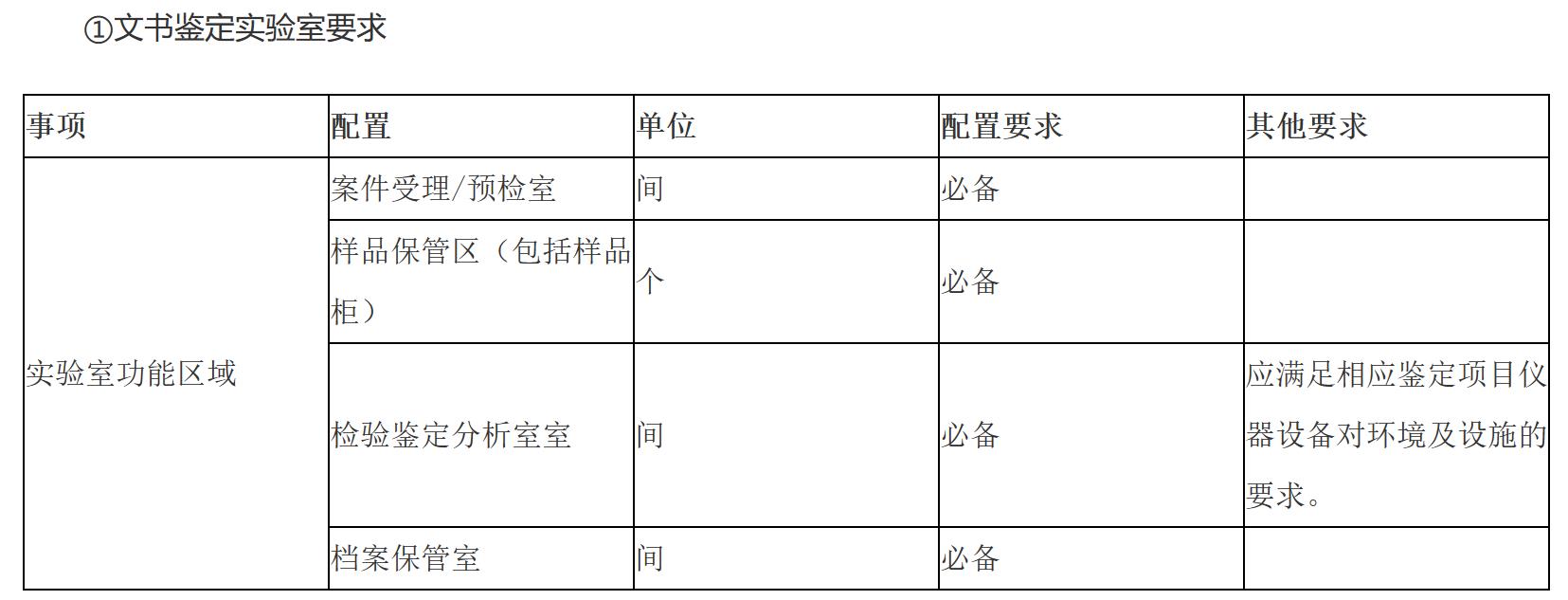
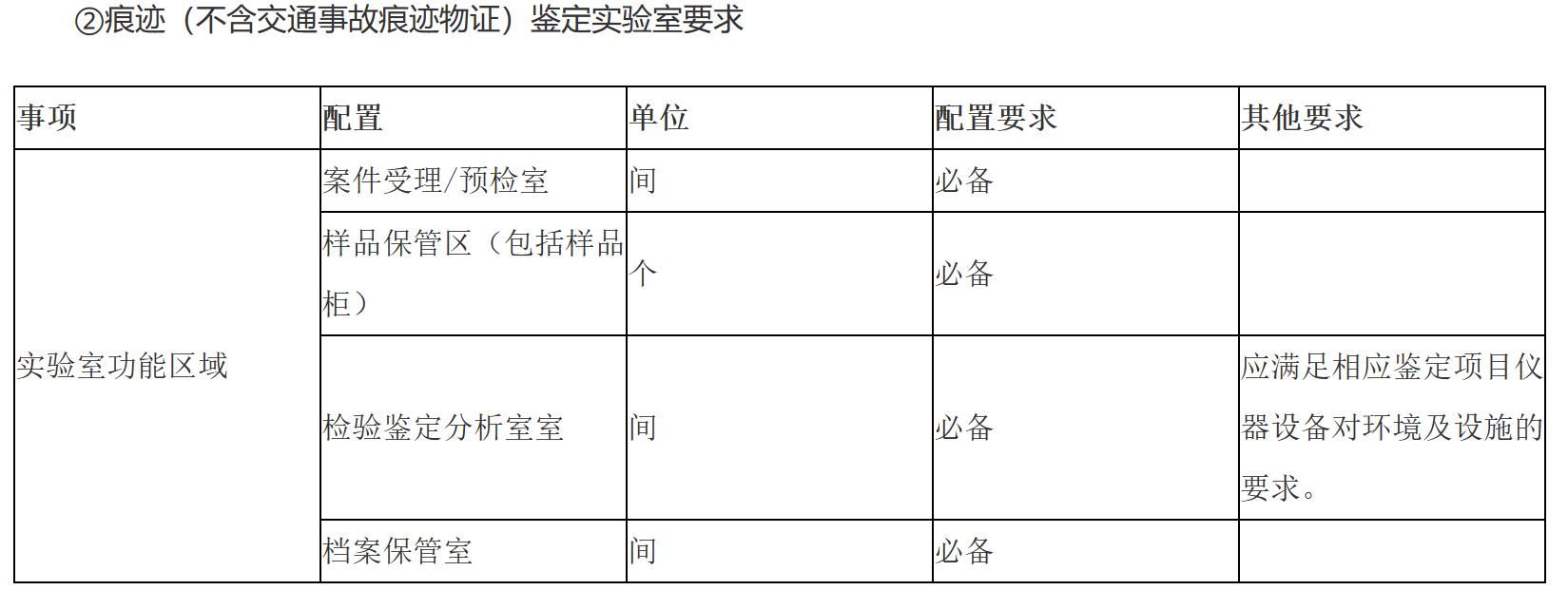
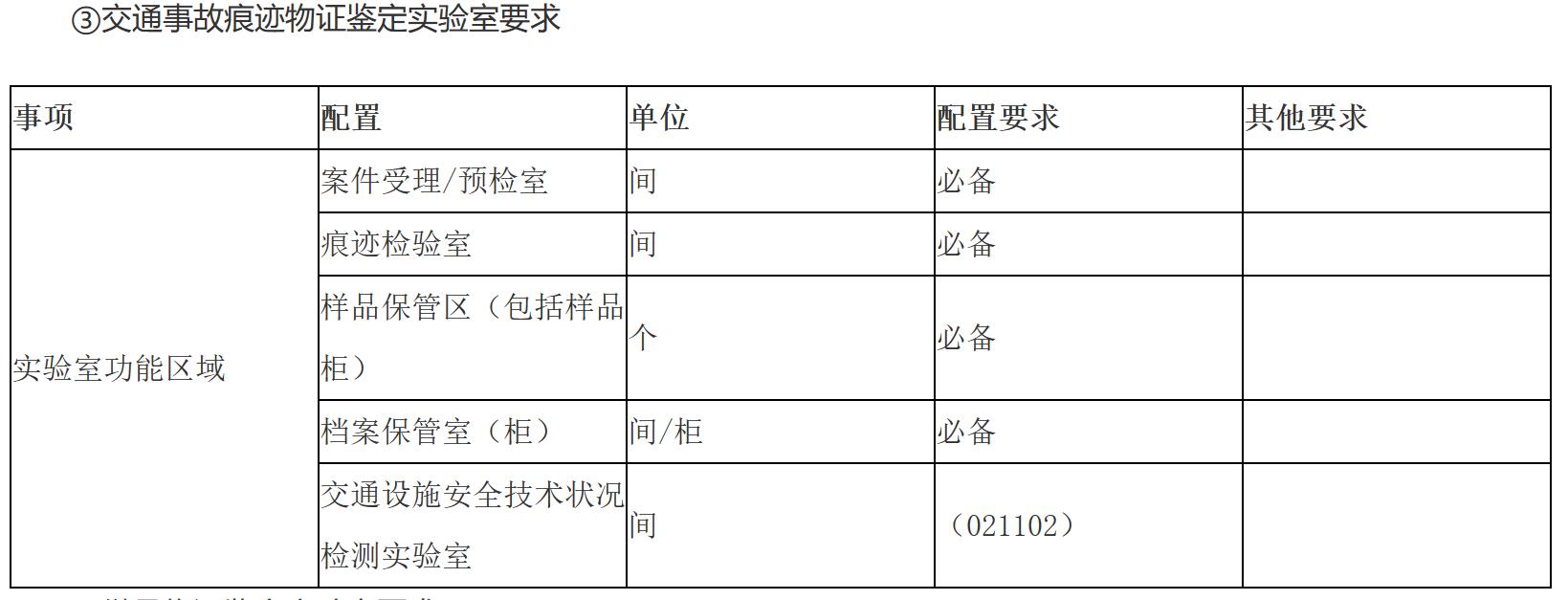
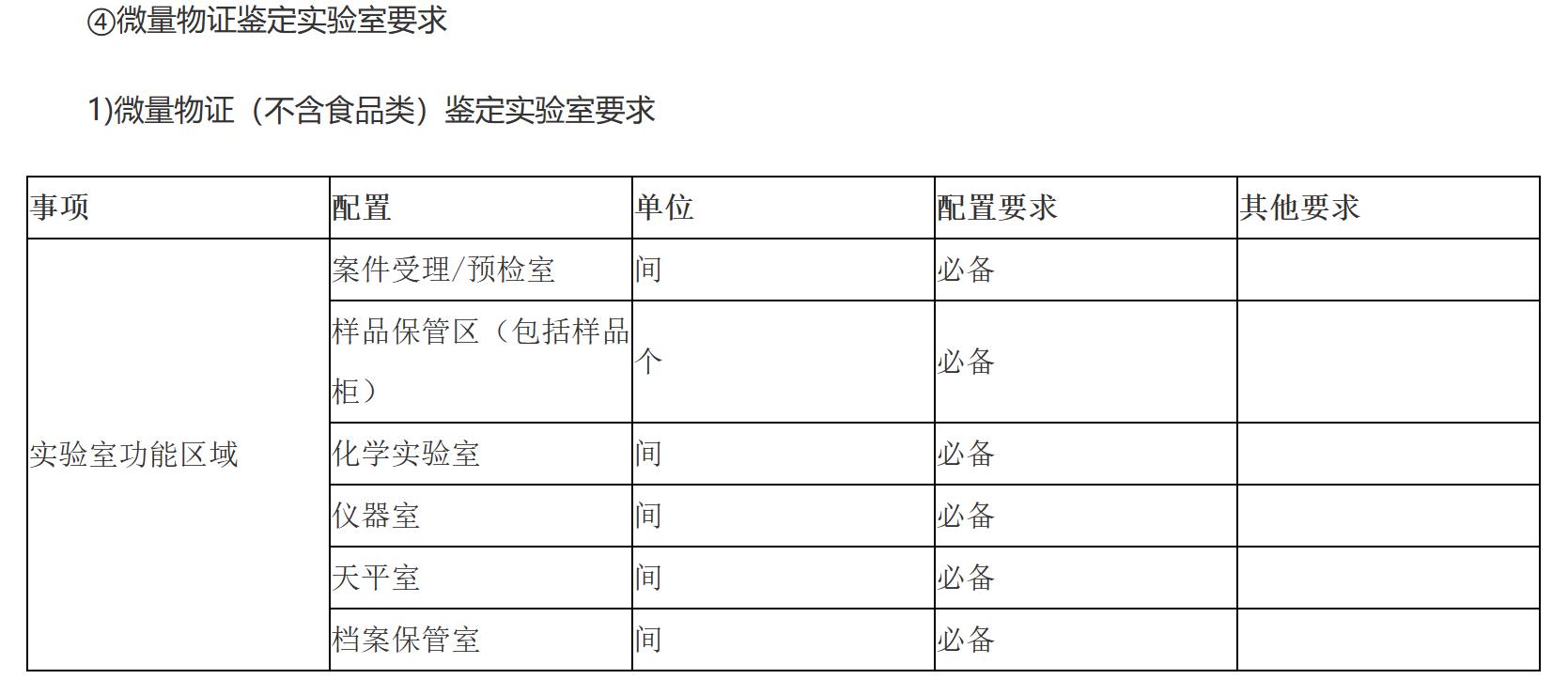
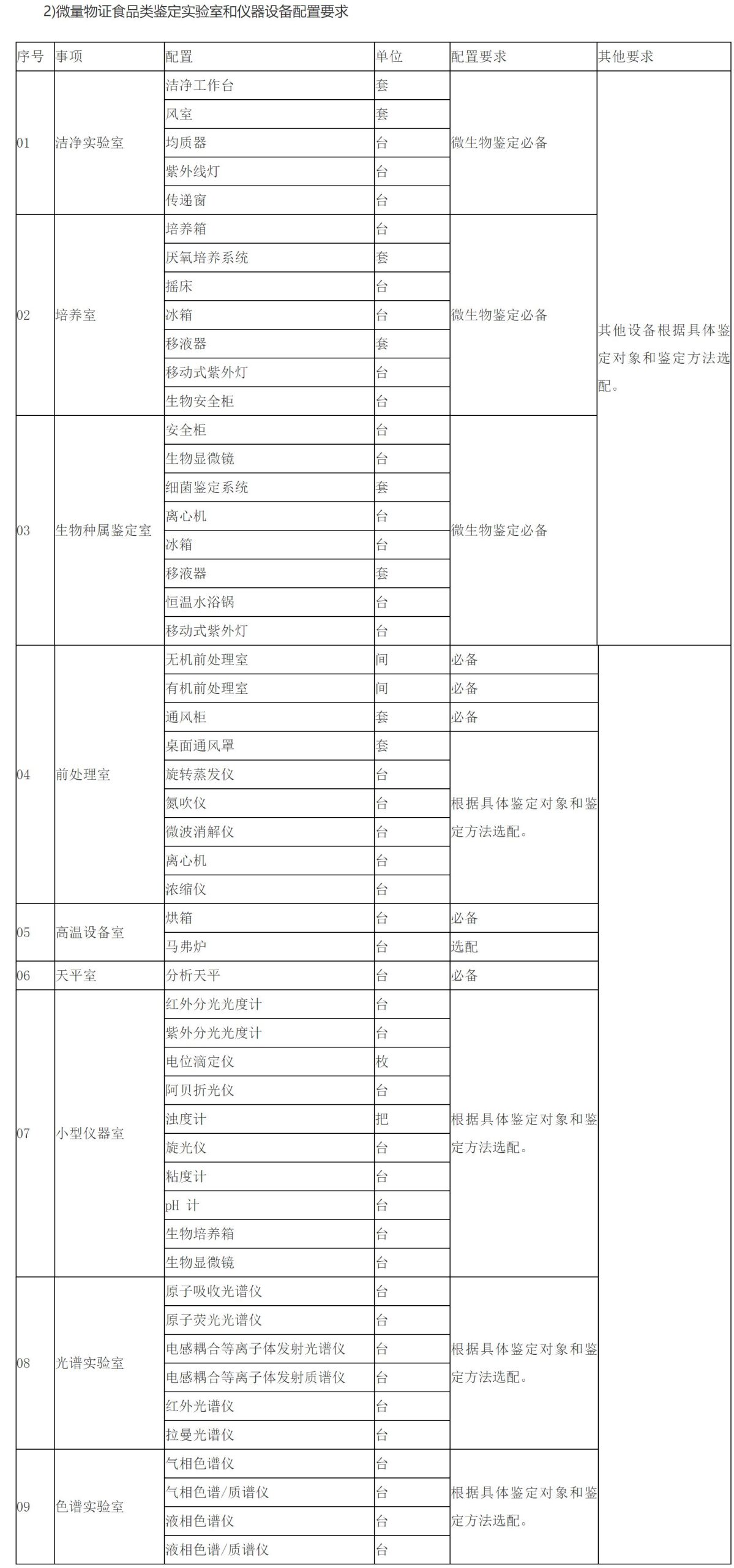
C. Audio-visual materials
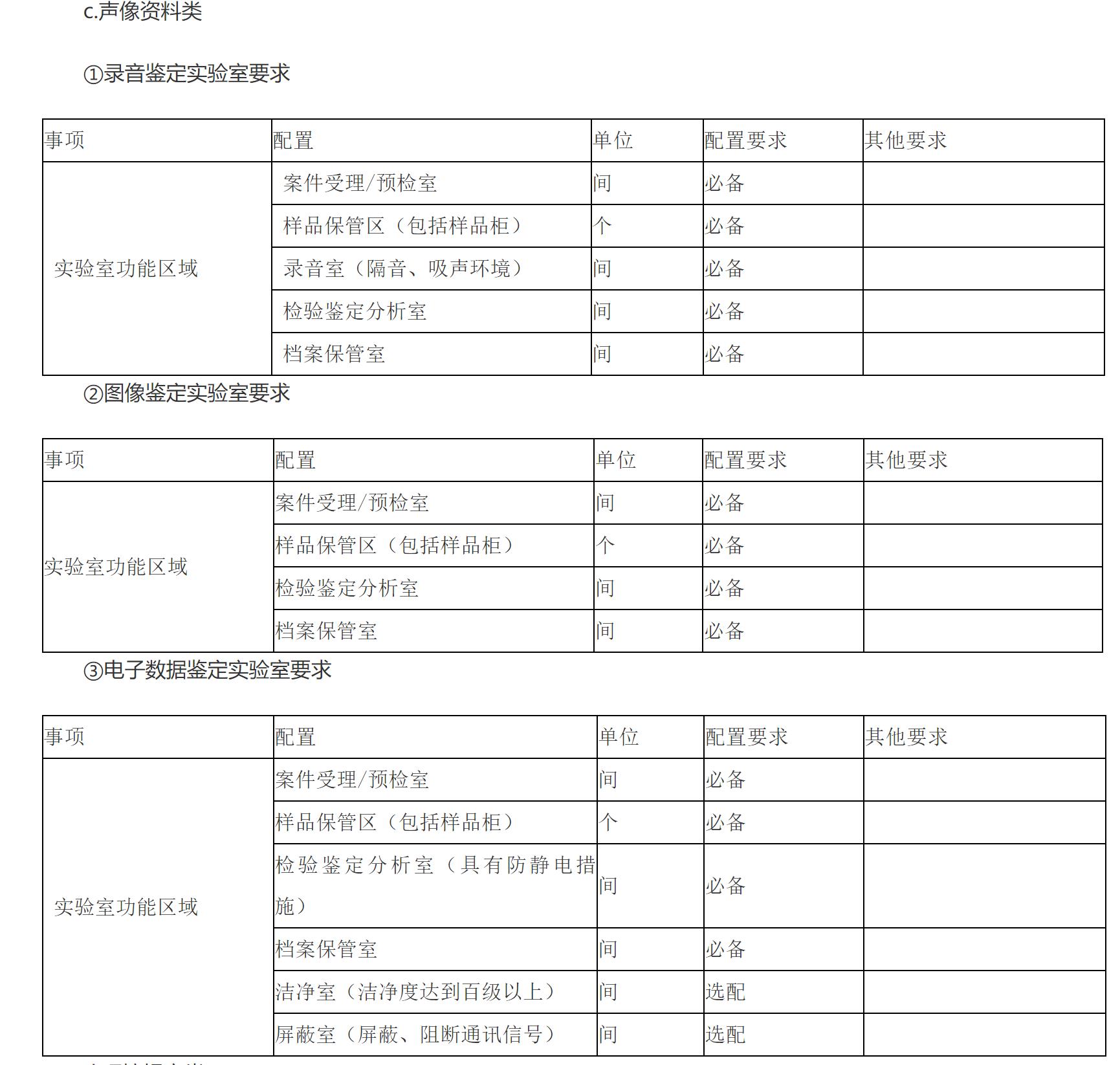
D. Environmental damage category
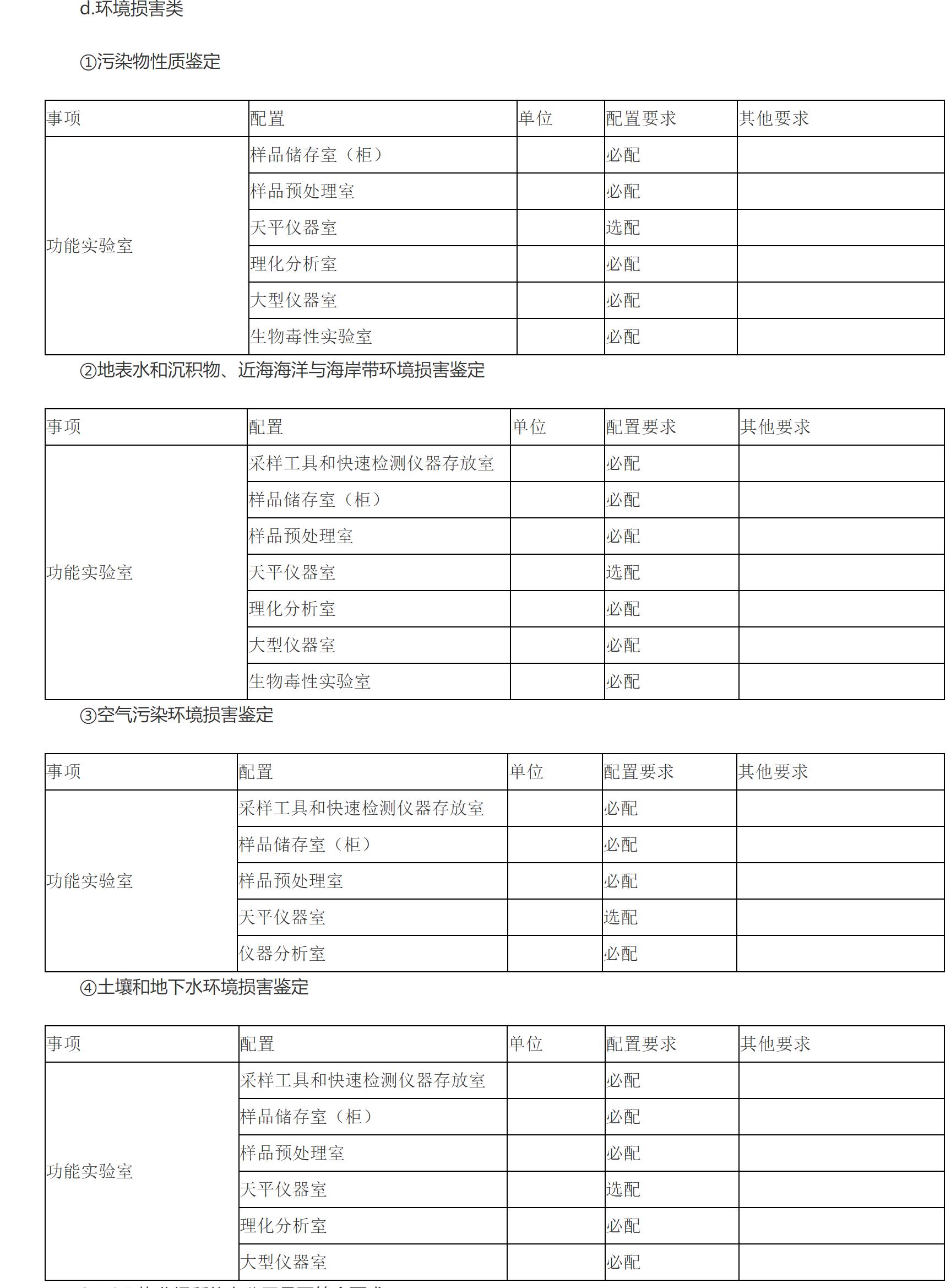
9.4.1.5. Does the information publicity of the practice place meet the requirements?
A. The business scope of the judicial authentication institution and the Certificate of Judicial Authentication License (Original);
B the name, professional title, practice category and practice certificate number of the judicial appraiser;
C. Entrustment, acceptance and appraisal process;
D. charging items and standards for judicial expertise;
E. professional ethics and practice discipline;
F. professional commitment and risk notification;
G. Complaint supervision telephone number and contact name;
H. other contents that need to be publicized.
9.4.1.6. Does the equipment configuration meet the requirements?
According to the business scope of judicial authentication institutions, the equipment configuration shall meet the following requirements, and the equipment can be used normally, and the performance and software function of the equipment can meet the corresponding standards and methods and the actual needs of inspection and appraisal (on-site inspection and verification with the laboratory configuration requirements table of four types of judicial authentication institutions, expert review):
A. Forensic medicine
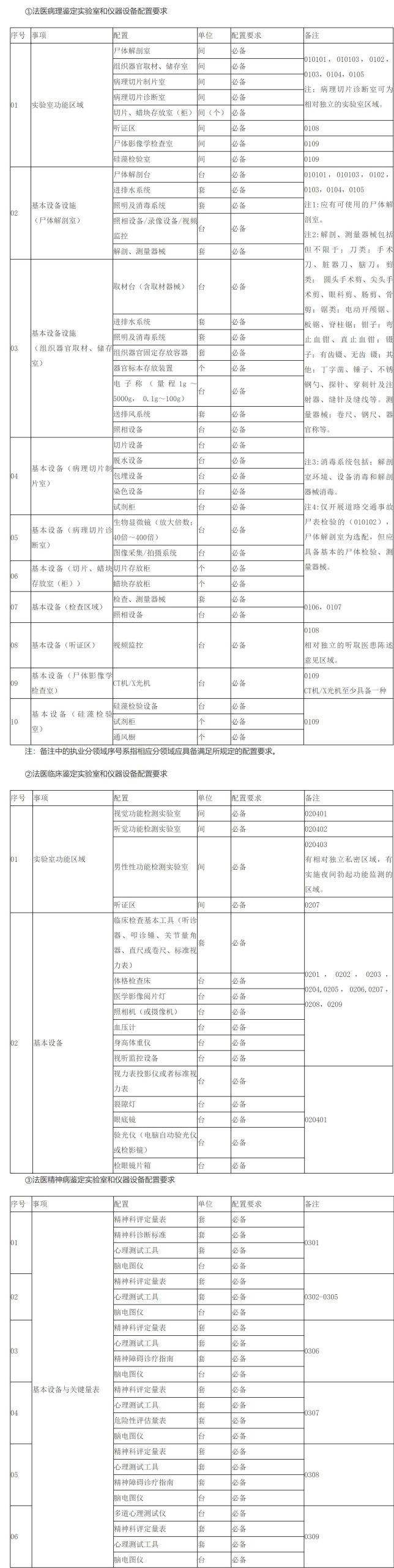
Note 1: The serial number of practicing sub-field in the remarks means that the corresponding sub-field should meet the specified configuration requirements.
Note 2: Psychiatric rating scales include but are not limited to: Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS), Brief Mental Status Test (MMSE), Positive and Negative Mental Symptoms Rating Scale (PANSS), Hamilton Anxiety Scale (HAMA), Hamilton Depression Scale (HAMD), Social Disability Screening Scale (SDSS), and Activity of Daily Living Rating Scale (ADL).
Note 3: Psychological testing tools include but are not limited to: Wechsler Adult Memory Test (WMS), Wechsler Adult Intelligence Test (WAIS), Wechsler Children Intelligence Test (WISC), Raven Standard Reasoning Test (SPM), Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Test (MMPI), etc.
Note 4: The guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of mental disorders include, but are not limited to, Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Mental Disorders, Clinical Diagnostic Guidelines for Psychiatry (Chinese Medical Association), Clinical Technical Operating Guidelines for Psychiatry (Chinese Medical Association) and guidelines for the prevention and treatment of various mental diseases.
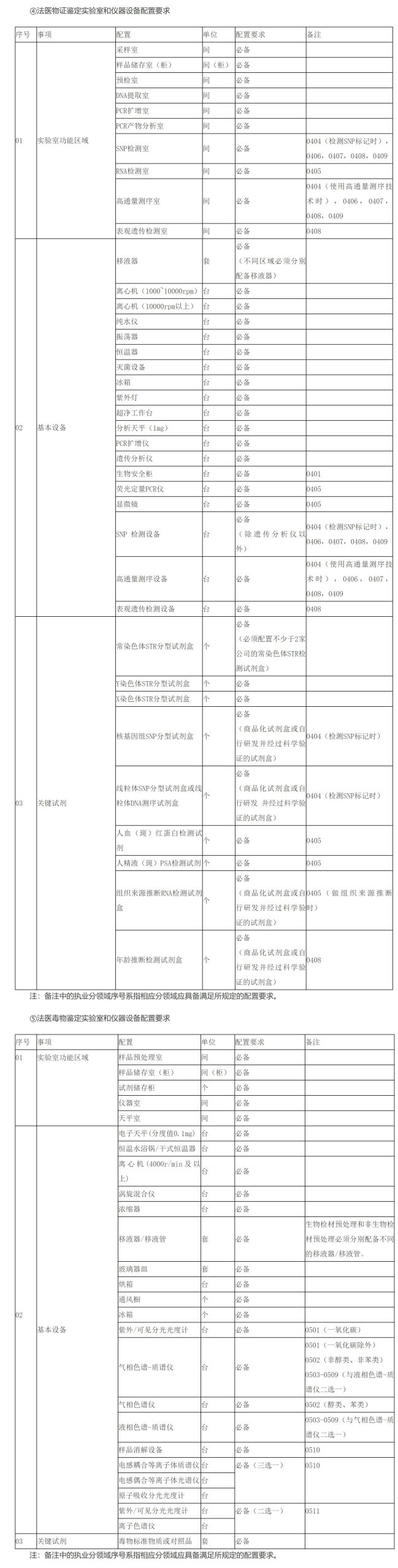
B. Physical evidence
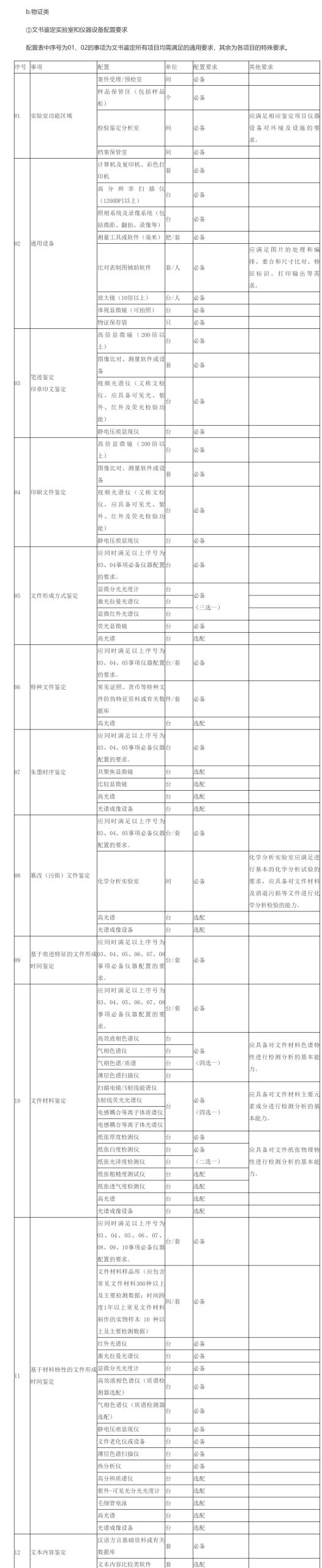
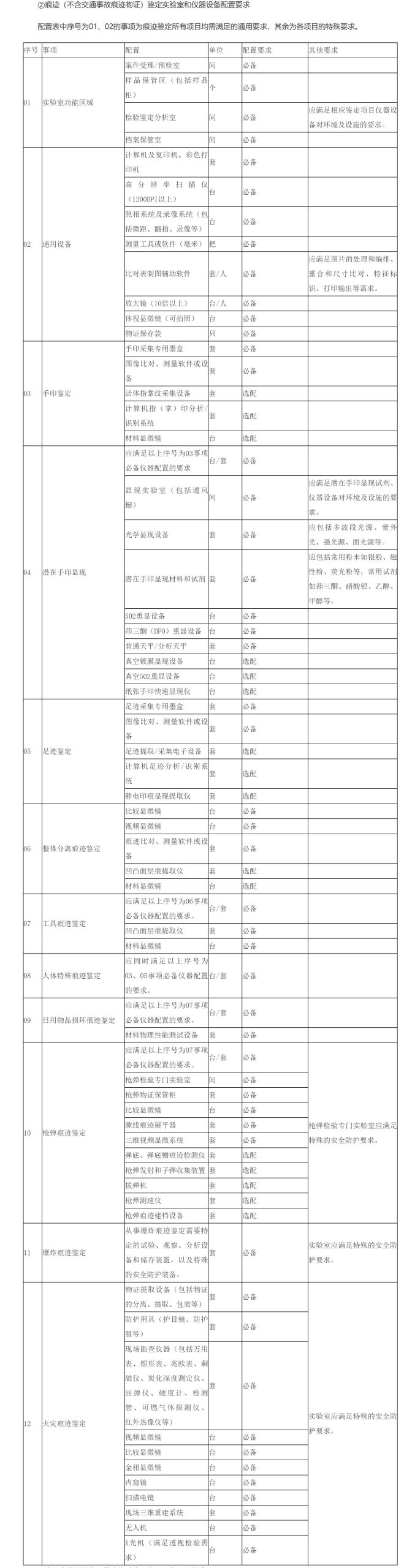
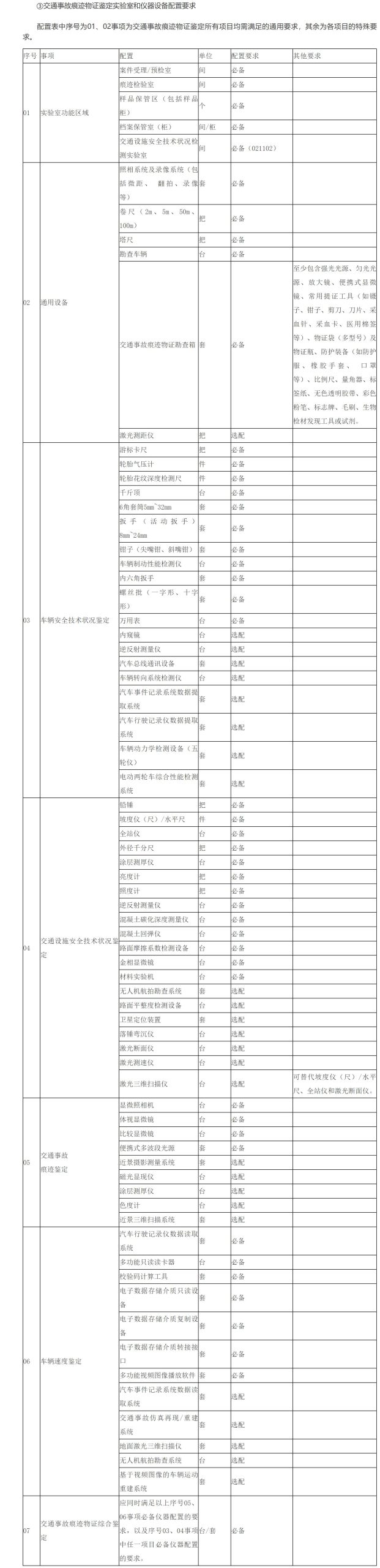
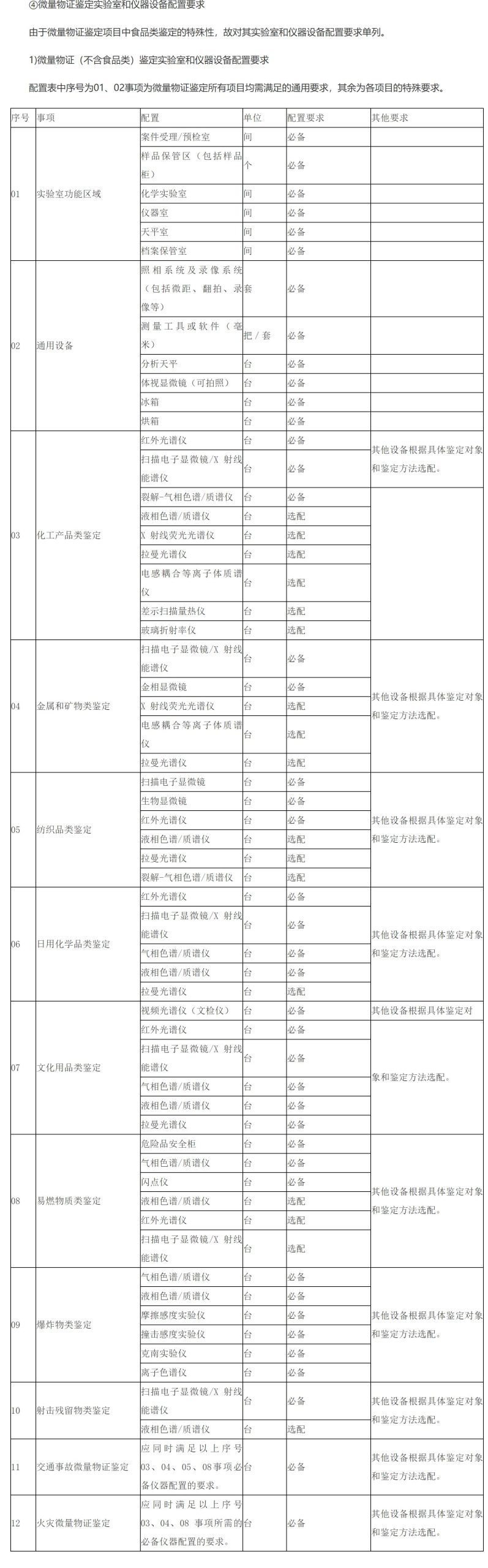
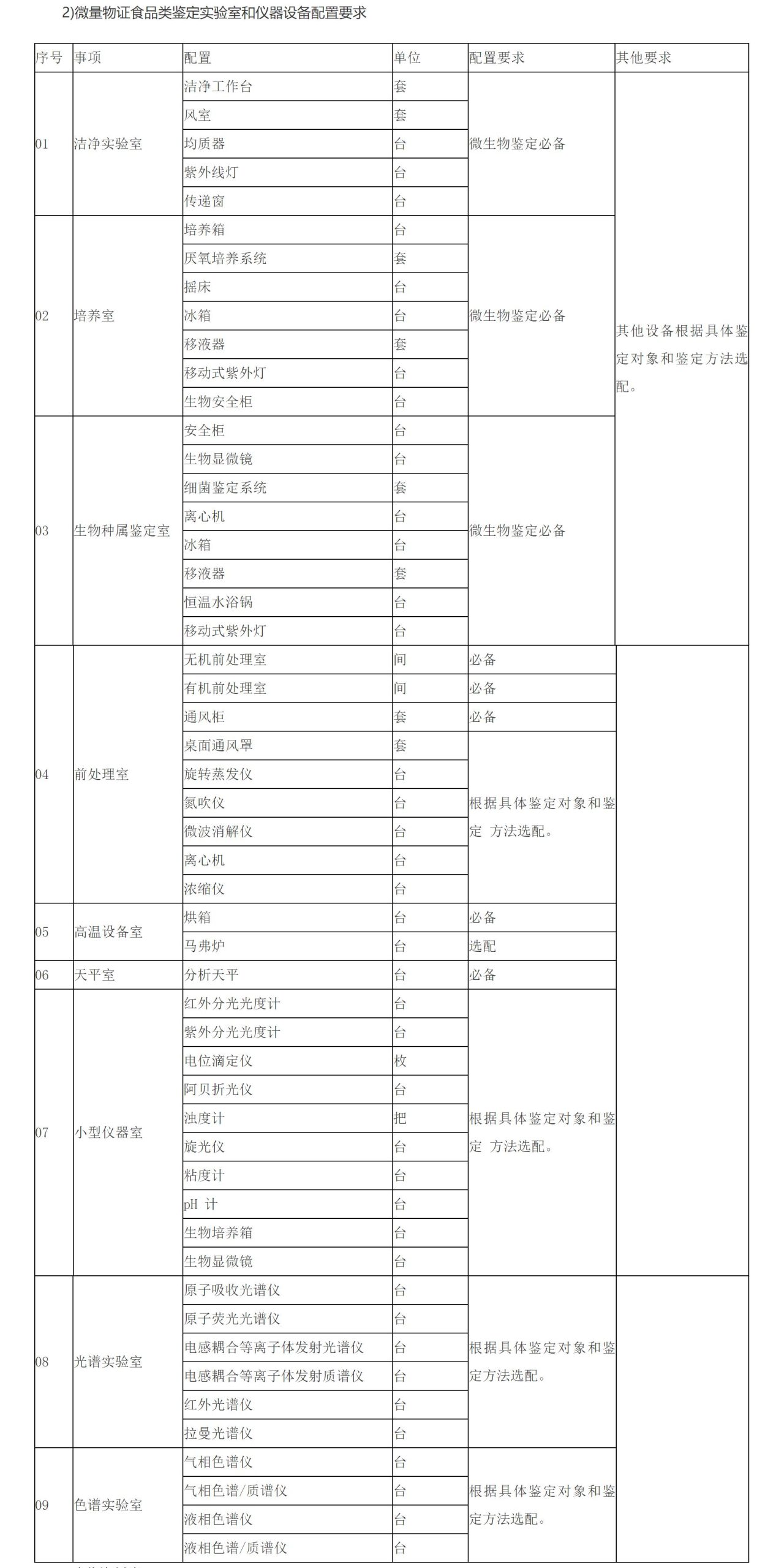
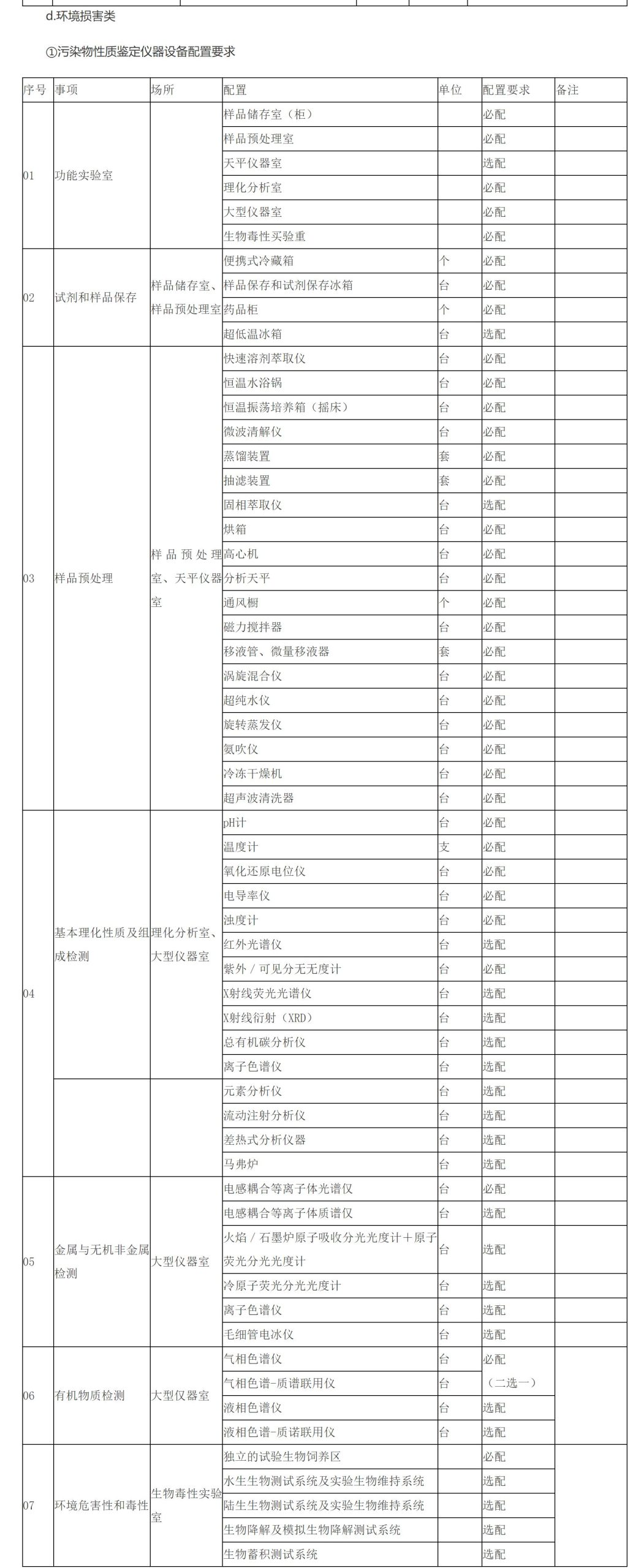
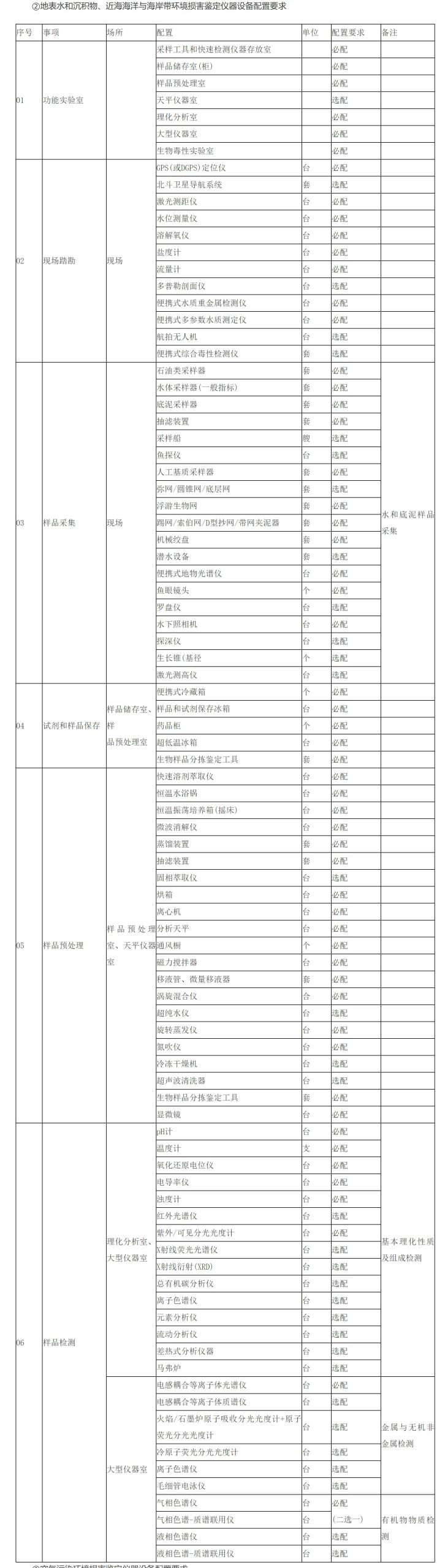
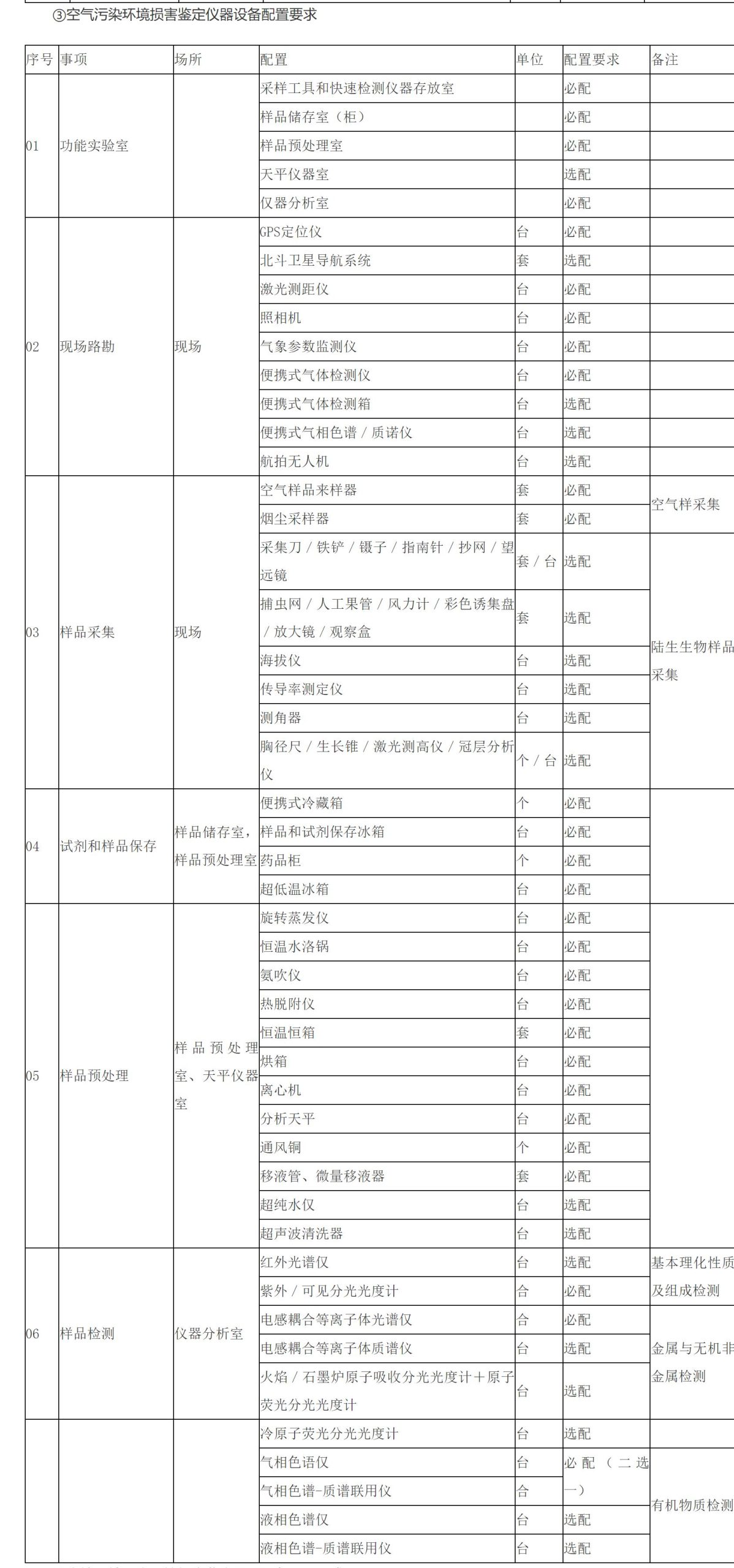
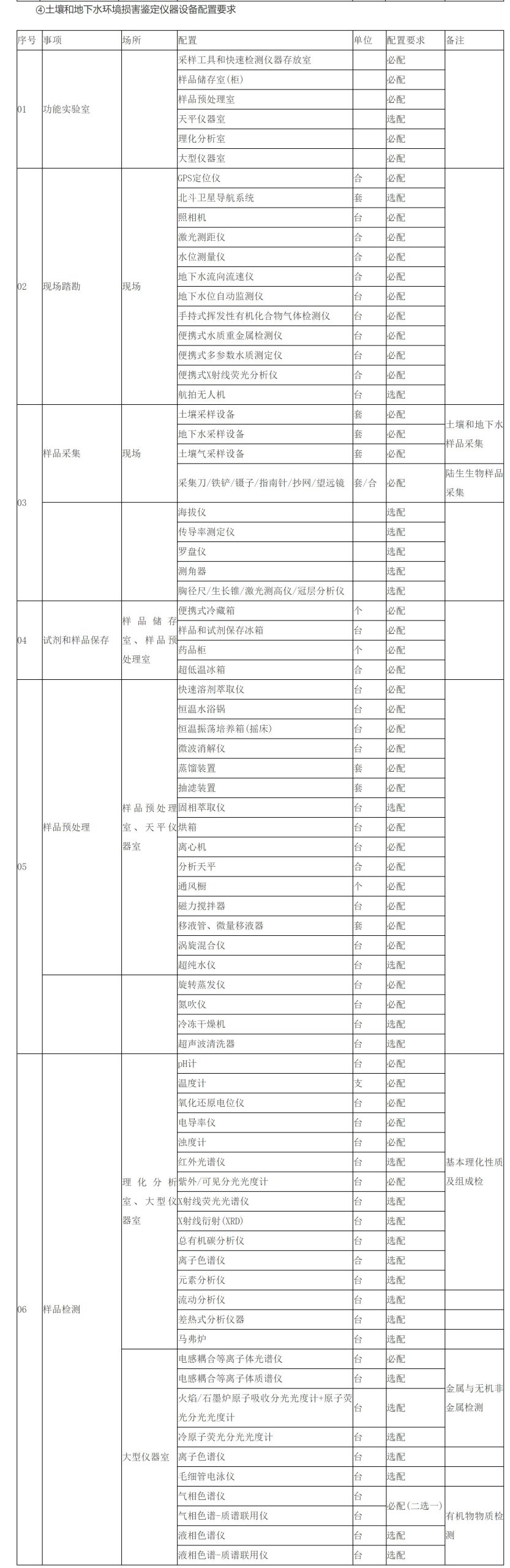
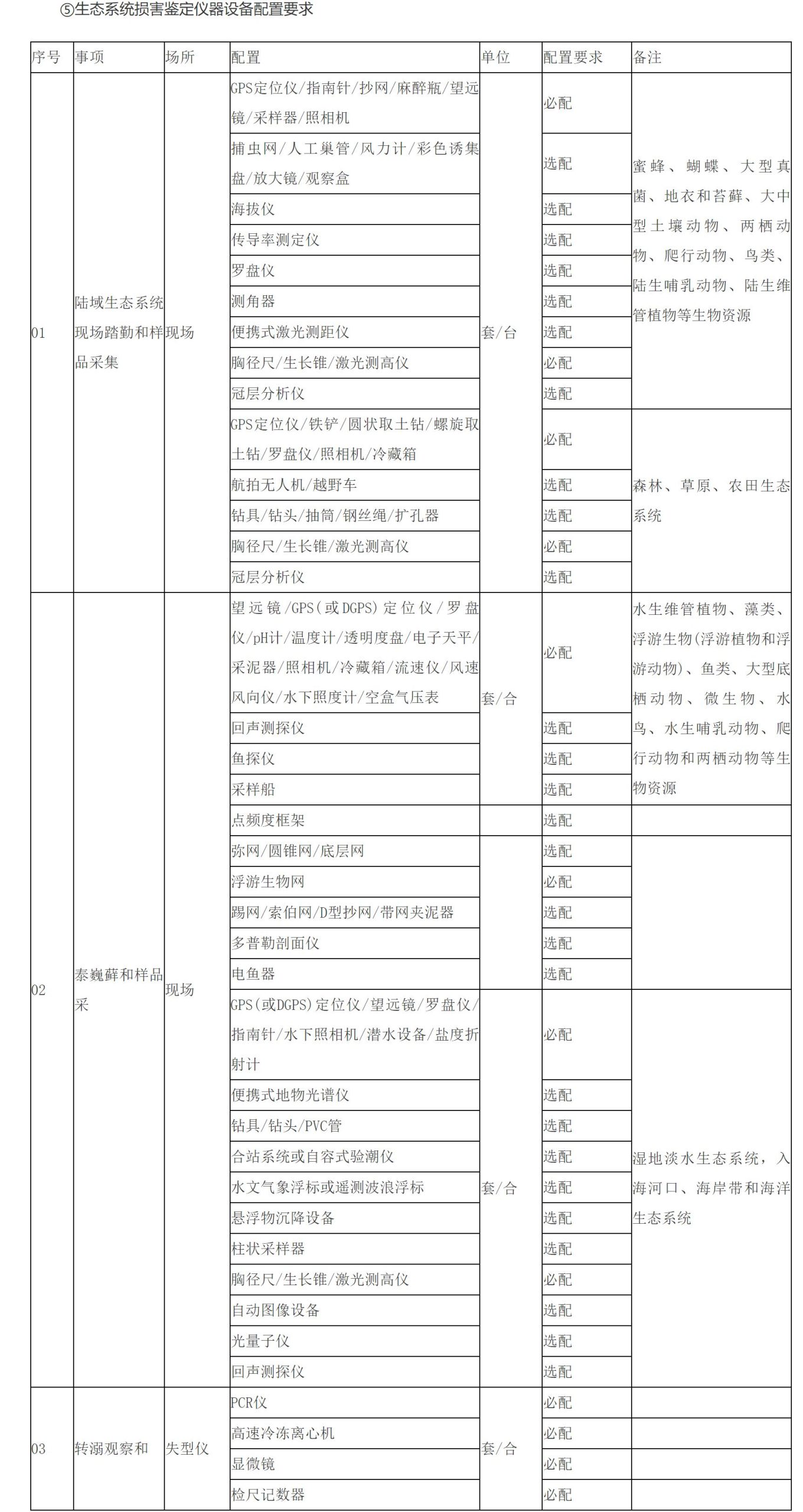
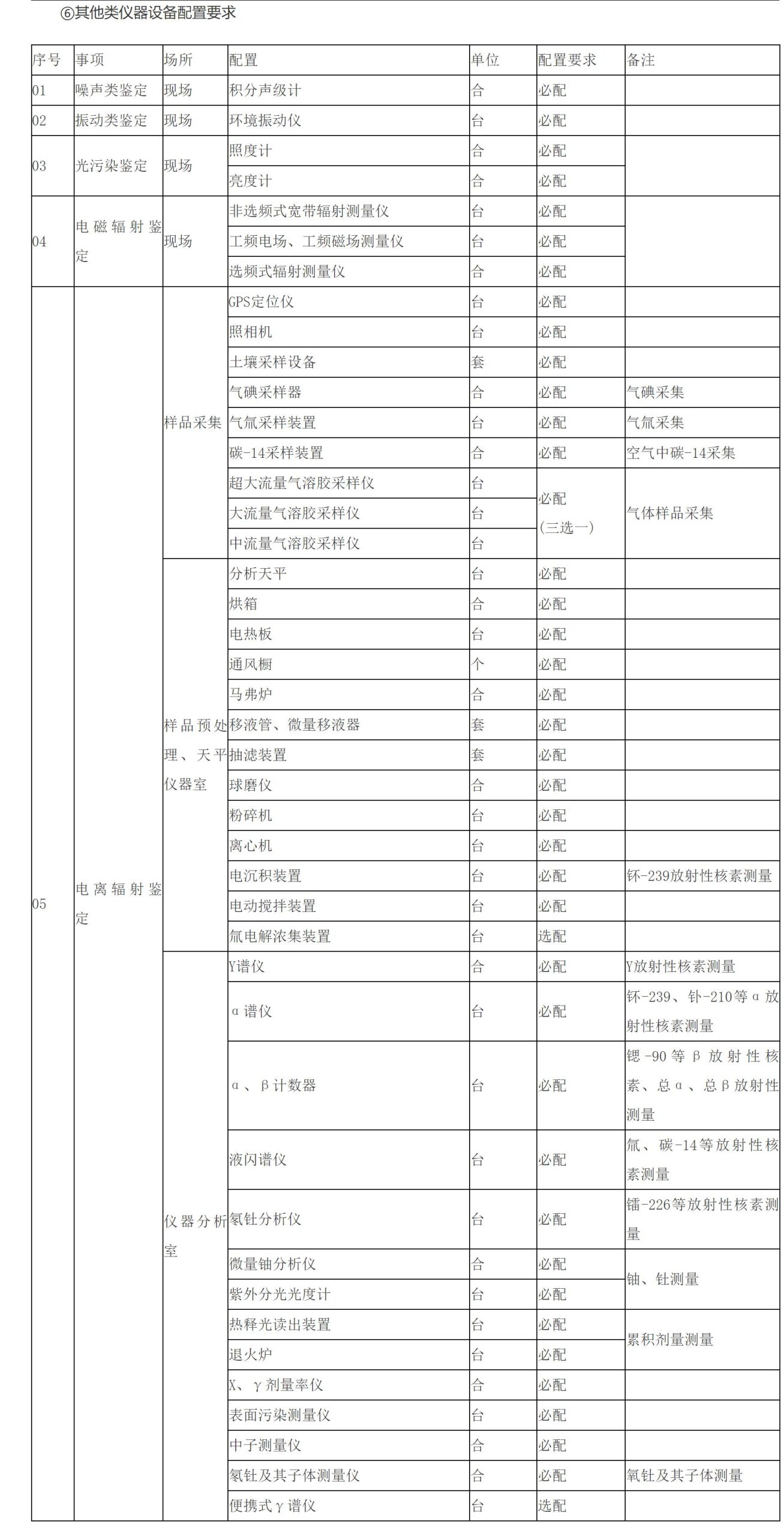
9.4.1.7. Is the maintenance and use of instruments and equipment standardized?
A the use, maintenance and management of instruments and equipment are standardized and in good condition, which can meet the actual needs of inspection and appraisal (on-site inspection of the use status of instruments and equipment);
B there are regular maintenance and verification records of instruments and equipment (on-site inspection, maintenance and verification records).
9.4.1.8. Whether the judicial authentication institution with legal person qualification has formulated the articles of association, and whether the contents specified in the articles of association are sound and perfect.
A. A judicial authentication institution with legal personality can present its articles of association on site (on-site inspection);
B the articles of association shall include the following contents (on-site inspection):
1) the name, domicile and registered capital of the judicial authentication institution;
2) The purpose and organizational form of the judicial authentication institution;
3) The business scope of the judicial authentication institution;
4) The creation and change of the procedures and responsibilities of the person in charge of the judicial authentication institution;
5) Rights and obligations of judicial appraisers and their related employees;
6) Establishment and responsibilities of relevant functional departments within the judicial authentication institution;
7) Alteration and revision of the articles of association of the judicial authentication institution;
8) forms of internal practice management and quality management of judicial authentication institutions;
9) Sources of assets, financial management and forms of use and distribution of judicial authentication institutions;
10) Termination procedures and asset disposal of judicial authentication institutions after cancellation or revocation;
11) Other matters that need to be specified.
C the actual name, domicile and business scope of the judicial authentication institution are consistent with the articles of association, and the contents of the articles of association are not in conflict with laws, regulations and rules (on-site inspection).
9.4.1.9. Is it standard to establish and implement business management system?
A the judicial authentication institution has established a business management system (text of on-site inspection system);
B the business management system shall specify the following contents (on-site inspection system text):
1) Unified acceptance of appraisal entrustment;
2) Sign the entrustment agreement in a unified way;
3) Assign appraisers uniformly;
4) collect appraisal fees uniformly;
5) Establish a unified system for the examination, receipt, storage, use, return and archiving of appraisal materials.
C the judicial authentication institution has records on the implementation of the business management system (on-site inspection records).
9.4.1.10. Is the quality management system standardized and implemented?
A. The judicial authentication institution has established a quality management system, with relevant quality management systems (text of on-site inspection system);
B the quality management system shall specify the following contents (text of on-site inspection system):
1) quality organization;
2) management system;
3) Internal operation procedures.
C the judicial authentication institution has records on the implementation of the quality management system (on-site inspection records).
9.4.1.11. Is it standard to establish and implement financial management system?
A. The judicial authentication institution has established a financial management system (text of on-site inspection system) and set up separate account books;
B. The judicial authentication institution collects fees such as authentication in a unified way, and issues bills according to law (on-site inspection fee voucher);
C. Judicial authentication institutions shall pay according to work internally and reasonably determine the distribution form (text of on-site inspection system);
D gradually establish education and training funds, professional liability insurance funds and institutional development funds (on-site inspection of various fund books);
E. The judicial authentication institution has records on the implementation of the financial management system (on-site inspection records).
9.4.1.12. Is it standard to establish and implement external information management system?
A. The judicial authentication institution has established and improved the external information management system (on-site inspection system text);
B the use of external information shall be checked and verified according to the procedures (on-site inspection of external information use verification records);
C. If external experts are needed due to professional and technical problems, it shall be implemented in accordance with relevant regulations (on-site inspection of external experts agreement, etc.);
D. The external information, opinions and signatures of external experts on the basis of judicial authentication shall be stored in the same authentication business file and filed for future reference (on-site inspection and authentication file).
9.4.1.13. Is it standard to establish and implement internal discussion and review system?
A. The judicial authentication institution has established and improved the internal discussion and review system (on-site inspection system text);
B. For the identification of major difficult and complicated problems or controversial cases, appraisers shall be organized to study and discuss, and written records shall be made (refer to the collective discussion records on site).
9.4.1.14. Is it standardized to establish and implement the seal and certificate management system?
A the judicial authentication institution has established a seal and certificate management system (on-site inspection system text);
B. The red seal, special seal for judicial authentication, special seal for financial authentication and judicial authentication license of judicial authentication institutions shall be managed by designated personnel and used according to regulations (on-site inspection of seal use records), except for publicity.
9.4.1.15. Number and qualification of judicial appraisers
A. A judicial authentication institution shall have more than three judicial authenticators for each judicial authentication business (on-site inspection, off-site verification through the management information system of the judicial administrative organ);
B. The judicial appraiser holds the Judicial Appraiser’s Practice Certificate issued by the Beijing Municipal Bureau of Justice, which has not exceeded the service period and has not been altered (on-site inspection);
C the actual practice institution of the judicial appraiser is consistent with the registered information of the Judicial Appraiser’s Practice Certificate (on-site inspection);
D. The judicial appraiser did not practice during the period when he stopped practicing or continued to practice after his registration was revoked (on-site inspection of the Judicial Appraiser’s Practice Certificate and on-site inquiry of the person in charge of the judicial authentication institution and the judicial appraiser);
E. After the judicial appraiser is sentenced to administrative punishment of stopping practicing or deregistered, he has immediately stopped handling the unfinished judicial appraisal business, and reported it to the judicial appraisal institution in time, which will inform the parties (on-site inspection of the business situation of the judicial appraiser who has stopped practicing or deregistered, and the records informed by the judicial appraisal institution).
9.4.2. Business behavior of judicial authentication institutions
9.4.2.1. Is there any act of judicial authentication institutions carrying out judicial authentication activities beyond the registered scope of judicial authentication business?
A. The judicial authentication business actually carried out by the judicial authentication institution is consistent with the public information of the practice place and website and the information stated in the Judicial Authentication License (on-site inspection of the business development, on-site inspection of the authentication files, on-site inspection of the public information and the Judicial Authentication License);
B. If the business scope of the judicial authentication institution changes, the Municipal Bureau of Justice has gone through the registration formalities for the change, and indicated on the copy of the Judicial Authentication License (on-site inspection of the copy of the Judicial Authentication License).
9.4.2.2. Is there any act of judicial authentication institutions setting up branches without legal registration?
A. The judicial authentication institution has branches within the administrative area of this Municipality, which have been examined and registered by the Beijing Municipal Bureau of Justice (on-site inspection of the Judicial Authentication Permit and off-site verification by the administrative licensing system of the judicial administrative organ);
B. The judicial authentication institution has branches in provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities directly under the Central Government outside this Municipality, which have been examined and registered by the provincial judicial administrative organ in the administrative region where the branch is located, and have been reported to the Beijing Municipal Bureau of Justice for approval (ask the person in charge of the authentication institution on the spot, and check the application materials submitted by the judicial authentication institution to the Beijing Municipal Bureau of Justice off-site).
9.4.2.3. Is there any act that the judicial authentication institution fails to handle the change registration according to law?
A the name, domicile, legal representative or person-in-charge of the judicial authentication institution, business scope and other registered items have changed, and the Beijing Municipal Bureau of Justice has gone through the registration formalities for the change; Or has submitted an application for registration of change and related materials to the Beijing Municipal Bureau of Justice, and is in the process of handling the registration of change (on-site inspection of the application for registration of change submitted by the judicial authentication institution to the judicial administrative organ);
B. The registered items after the change of the judicial authentication institution have been marked on the copy of the Judicial Authentication License and the actual situation is consistent (the copy of the Judicial Authentication License is inspected on site).
9.4.2.4. Is there any act that the judicial authentication institution alters, transfers, rents or lends the Judicial Authentication License?
A. The judicial authentication institution hangs the original of the Judicial Authentication License in a prominent position in the practice place, and can produce the original copy of the Judicial Authentication License in the process of supervision and inspection by the judicial administrative organ, and there is no trace of alteration on the original and copy (on-site inspection of the original and copy of the license certificate);
B. The judicial authentication institution fails to hang the original of the Judicial Authentication License in a prominent position in its practice place, or it is unable to produce the original copy of the Judicial Authentication License during the supervision and inspection by the judicial administrative organ, but it is damaged or lost, and has applied to the Beijing Municipal Bureau of Justice for renewal or replacement of the license, and the lost one has published a loss notice on the institution’s website (on-site inspection of the judicial authentication institution’s application for replacement or replacement of materials, on-site inspection of the website loss notice, and on-site inquiry of the person in charge of the judicial authentication institution).
9.4.2.5. Is there any act of judicial authentication institutions organizing persons who have not obtained the Practice Certificate of Judicial Appraisers to engage in judicial authentication business?
A. After accepting the entrustment of appraisal, the judicial authentication institution shall designate a judicial appraiser with the qualification for the appraisal (on-site inspection of the designated personnel’s Judicial Appraiser’s Practice Certificate);
B. The persons who have signed the real-time records (such as notes, audio recordings, videos, photos, etc.) and the opinions of judicial appraisal have the qualification of judicial appraisal and obtained the Judicial Appraiser’s Practice Certificate (refer to the appraisal files on site and check the Judicial Appraiser’s Practice Certificate on site);
C. The judicial appraisers affiliated to the judicial authentication institutions did not continue to engage in the judicial authentication business during the period when they were given administrative punishment to stop practicing or after their registration was cancelled (off-site inquiry about the penalty publicity information of Beijing Platform for Credit, on-site inquiry about the person in charge of the judicial authentication institutions, and on-site inquiry about notarized files).
9.4.2.6. Is there any act of fraudulent registration by judicial authentication institutions by providing false documents or by other fraudulent means?
A. The following application materials submitted by a legal person or other organization to the judicial administrative organ for engaging in judicial authentication business are true, complete and reliable (the application materials submitted by the legal person or other organization for off-site inspection):
1) application form;
2) Relevant documents proving the identity of the applicant;
3) proof of residence and funds;
4) Relevant industry qualifications and qualification certificates;
5) Instrument and equipment description and ownership certificate;
6) Testing laboratory related data;
7) Relevant materials of the judicial appraiser’s application for practice;
8) Relevant internal management system materials;
9) Other materials that should be submitted.
B the actual domicile, funds, instruments, equipment, laboratories, number of appraisers and qualifications of the judicial authentication institution are all in conformity with the application materials submitted to the judicial administrative organ when applying for registration (on-site inspection).
9.4.2.7. Is there any improper behavior such as judicial authentication institutions paying kickbacks, referral fees and making false propaganda?
A. The judicial authentication institution has no unfair competition behaviors such as paying kickbacks and referral fees (on-site questioning the person in charge of the authentication institution, judicial appraisers and other relevant personnel, on-site inspection of charging vouchers, and on-site telephone call back to the parties):
1) In order to undertake business, the judicial authentication institution repays a certain percentage of the service fee to the client as a "kickback", which leads to the fact that it is not clearly and truthfully recorded in the legally established financial accounts reflecting its production and business activities in accordance with the provisions of the financial accounting system, including not recording it in the financial accounts, transferring it to other financial accounts or making false accounts.
2) In order to undertake business, the judicial authentication institution pays additional fees in the name of "introduction fee", "benefit fee", "cooperation fee", "contact fee" and "information fee" to the units or individuals that help it undertake business.
B. The judicial authentication institution has not made false or misleading commercial propaganda on its business qualification, business status, business performance, user evaluation, and previous honors, or deceived or misled consumers (on-site questioning the person in charge of the authentication institution, judicial appraisers and other relevant personnel, and on-site inspection of websites, posters and brochures).
9.4.2.8. Is there any act that the judicial authentication institution refuses to accept the supervision and inspection of the judicial administrative organ or provides false materials to it?
A. In the process of supervision and inspection by judicial administrative organs on the following matters, judicial authentication institutions can provide convenience for judicial administrative organs to access information and understand the situation, and can truthfully provide relevant information and materials (on-site inspection):
1) Compliance with laws, regulations and rules;
2) Compliance with judicial authentication procedures, technical standards and technical operation specifications;
3) The practice of the judicial appraiser;
4) Other matters stipulated by laws, regulations and rules.
B. Judicial authentication institutions can actively cooperate with judicial administrative organs in the investigation of complaints and clues, and truthfully provide relevant information and materials (on-site inspection).
9.4.2.9. Is there any act of judicial authentication institutions violating the measures for the administration of judicial authentication fees?
Judicial authentication institutions can collect judicial authentication fees in accordance with relevant regulations and standards such as Administrative Measures of Beijing Municipality on Judicial Authentication Fees, Beijing Judicial Authentication Fees Standard (for Trial Implementation), and Beijing Municipal Bureau of Justice’s Accreditation Standard for Judicial Authentication Services with Difficult Problems and Significant Social Impact (on-site inspection of charging vouchers, on-site inquiry of the person in charge of authentication institutions and judicial appraisers, and on-site telephone call back to the parties).
9.4.2.10. Is there any act of judicial authentication institutions that caused great losses to the legitimate rights and interests of the parties due to serious irresponsibility?
The daily management of judicial authentication institutions is standardized and orderly, and the business management system and quality management system are sound and perfect, without any of the following circumstances (on-site inspection system text and implementation records, on-site inquiry of the person in charge and appraiser of authentication institutions, on-site telephone call back to the parties):
A. Due to negligence and chaotic management, the judicial authentication institutions have lost, polluted, delayed and wrongly authenticated the samples;
B. Due to the loss, pollution, delayed identification, wrong identification and other reasons, the parties can’t sue, can’t respond to the lawsuit, seriously damage the interests of their litigation entities or even lose the case, and their legitimate rights and interests are greatly lost.
9.4.2.11. Is there any act that the judicial authentication institution refuses to accept the judicial authentication entrusted by the case-handling organ without justifiable reasons?
A. Except for the entrustment of authentication under any of the following circumstances, the judicial authentication institution shall accept the entrusted authentication matters that belong to its judicial authentication business scope, have legal authentication purposes and provide authentication materials that can meet the needs of authentication (on-site inspection of the power of attorney for judicial authentication, on-site inquiry of the person in charge of the authentication institution, and on-site telephone call back to the client).
1) Entrusting matters beyond the scope of judicial expertise of this institution;
2) It is found that the appraisal materials are untrue, incomplete, insufficient or obtained in an illegal way;
3) The appraisal purpose is illegal or violates social morality;
4) The appraisal requirements do not conform to the practice rules of judicial appraisal or relevant technical specifications for appraisal;
5) The appraisal requirements exceed the technical conditions or appraisal ability of the institution;
6) The client entrusts other judicial authentication institutions to authenticate the same authentication matter at the same time;
7) Other circumstances that do not conform to the provisions of laws, regulations and rules.
B. If the judicial authentication institution decides not to accept the entrustment of authentication, it shall explain the reasons to the client and return the authentication materials (on-site inspection of the notice of inadmissibility, return of the catalogue of authentication materials, delivery certificate, on-site inquiry of the person in charge of the authentication institution, and on-site telephone call back to the client).
9.4.2.12. Do you abide by laws and regulations, professional ethics and discipline, respect science, and technical operation specifications?
A. The judicial authentication institutions shall strictly abide by the laws and regulations related to the judicial authentication business (on-site inspection, on-site questioning of the person in charge of the authentication institutions and the appraisers);
B. The judicial authentication institution strictly abides by the Basic Code of Professional Ethics of Judicial Authentication, and there are no cases such as "personal authentication", "relationship authentication" and false authentication (on-site inspection, on-site questioning of the person in charge of the authentication institution and the appraiser);
C. Judicial authentication institutions respect science when engaging in judicial authentication business, and do not rely on subjective assumptions or take it for granted, or succumb to the intervention of individual leaders or departments to damage the scientificity and objectivity of authentication work (on-site inspection, on-site questioning of the person in charge of authentication institutions and appraisers);
D. The judicial authentication institution strictly abides by the technical operation specifications of judicial authentication when engaging in the business of judicial authentication, and there is no case that the people’s court refuses to adopt the expert opinions due to violation of the technical operation specifications (on-site inspection, on-site questioning of the person in charge of the authentication institution and the appraiser).
10. Administrative inspection of judicial appraisers
10.1. Inspection object
Judicial appraiser
10.2. Inspection method
On-site inspection, license inspection, on-site inquiry, information access, off-site inspection, and other means.
10.3. Inspection frequency
In principle, according to the annual law enforcement inspection plan (website publicity).
10.4. Inspection contents and standards
10.4.1. Professional qualification of judicial appraisers
10.4.1.1. Have you obtained the Practice Certificate of Judicial Appraiser?
10.4.1.2. Is the Judicial Appraiser’s Practice Certificate within the validity period?
10.4.1.3. Whether the practice institution and practice category are consistent with the registration information of the Judicial Appraiser’s Practice Certificate?
10.4.2. Practice of judicial appraisers
10.4.2.1. Is it due to negligence and other reasons that the inspection materials are lost, contaminated, delayed identification, wrong identification, etc.
10.4.2.2. Is it because of the loss, contamination, delayed identification, wrong identification and other reasons that the parties can’t sue, can’t respond to the lawsuit, seriously damage the interests of their litigation entities or even lose the case, and their legitimate rights and interests are greatly lost?
10.4.2.3. Whether to accept the entrustment of judicial expertise privately?
10.4.2.4. Are unregistered personnel engaged in the judicial authentication business that has been included in the adjustment scope of the Measures for the Administration of Registration of Judicial Appraisers?
10.4.2.5. Are you practicing in two or more judicial authentication institutions at the same time?
10.4.2.6. Is there any practice beyond the registered practice category?
10.4.2.7. Whether to provide false certification documents or take other fraudulent means to defraud registration?
10.4.2.8. Whether to make false identification intentionally?
10.4.2.9. Whether the people’s court has been notified according to law to refuse to testify in court?
10.4.2.10. Whether to refuse to accept the supervision and inspection of the judicial administrative organ or provide false materials to it?
10.4.2.11. Whether to divulge state secrets in the course of practicing?
10.4.2.12. Whether to disclose business secrets and personal privacy during the practice?
10.4.2.13. Does it violate the withdrawal regulations?
10.4.2.14. Compliance with laws and regulations
10.4.2.15. Whether to abide by professional ethics and professional discipline?
10.4.2.16. Do you respect science?
10.4.2.17. Do you comply with the technical operation specifications?
11. Administrative inspection of notarization institutions
11.1. Inspection object
Notary institution
11.2. Inspection method
On-site inspection, license inspection, on-site inquiry, information access, off-site inspection, and other means.
11.3. Inspection frequency
In principle, according to the annual law enforcement inspection plan (website publicity).
11.4. Inspection contents and standards
11.4.1. Qualification of notarization institutions
11.4.1.1. Is the publicity and custody of the original and duplicate of the practice license standardized?
A. The notary office hangs the original of the public practice license in an obvious position in the office (on-site inspection);
B in the process of supervision and inspection by the judicial administrative organ, the notary office can produce the original copy of the practice license (on-site inspection);
C the name actually used by the notary public, the actual office space and the name of the person in charge are consistent with the information stated in the original and duplicate of the practice license, and the practice certificate of the person in charge has not been cancelled or revoked (on-site inspection, on-site comparison with the practice license information through web pages, agreements, brochures and other information);
D. The original and duplicate copies of the practicing license of the notarization institution are not obviously damaged or defiled, and there is no trace of artificial alteration of the information stated (on-site inspection);
E. The inspected notary office is in normal practice; If the practice certificate has been revoked or the practice is stopped, the original and duplicate of the practice license have been returned to the judicial administrative organ (checked off-site by the management information system of the judicial administrative organ).
11.4.1.2, whether to participate in the annual assessment of notarization institutions in accordance with the prescribed time limit and requirements.
A. The notarization institution has submitted its annual work report (annual work report submitted by off-site inspection notarization institution) to the judicial administrative organ at the district level before February 1st of that year;
B. The annual work report shall truly and comprehensively reflect the notarization business, notarization quality monitoring, notary’s compliance with professional ethics and practice discipline, notarization fees, financial management, internal system construction, etc. of the notary office in the previous year (the annual work report submitted by the notary office after off-site inspection):
1) Organization construction. Including the construction and activities of the party organization of notarization institutions; The notarization institution meets the statutory conditions for establishment and the nature, system and operation of the institution; The selection, performance and adjustment of the person in charge of the notarization institution; Changes in the number and quality structure of notaries; To carry out the education of professional ethics and practice discipline of notaries and the study and training of notarial business knowledge and skills; Other staffing and management; Office facilities and office environment construction, etc.
2) Practice activities. Including the notary public and its notaries abide by laws, regulations, rules, normative documents and industry norms in their practice activities, and abide by the professional ethics and practice discipline of notarization; Complete the task of notarization business and expand the field of notarization business; The establishment and implementation of the accountability system for the fault of notarization practice; Accept the supervision of judicial administrative organs and notary associations, as well as the supervision of the parties and the society, and promptly investigate and correct the problems existing in practice.
3) The quality of notarization. Including the self-inspection and evaluation of notarization quality; The establishment and implementation of relevant systems and mechanisms such as self-supervision, control, review and error correction of notarization quality; The establishment and implementation of the collective discussion system for major and complicated notarization matters; Accepting complaints, review and fault compensation of notarization business, etc.
4) Annual assessment of notaries’ practice. Including the organization and implementation of the annual assessment of notaries’ practice in accordance with the regulations and the assessment results.
5) Management of notarized archives. Including the implementation of the relevant provisions on the management of notarial archives by notarization institutions; The establishment and implementation of the notarization archives management system within this institution, etc.
6) Notarization fees and financial management. Including the annual notarization fees of notarization institutions; The implementation of the relevant provisions of the state on the administration of notarization fees; Annual financial revenue and expenditure, distribution and implementation of relevant financial management systems; The establishment and implementation of the internal financial management system of the institution; Paying taxes according to law and paying the membership fees, notarization compensation funds and other insurance benefits and funds according to regulations; Accept the inspection and supervision of tax, price, audit and other departments.
7) Construction of internal management system. Including the overall situation, implementation and effect of the establishment and improvement of various internal management systems by notarization institutions in accordance with the relevant provisions of the Notary Law and the Measures for the Administration of Practice of Notary Institutions.
8) Other assessment items that need to be added by the Ministry of Justice or the municipal judicial administrative organ.
C. Notary agencies, notaries and other staff members can truthfully explain the relevant information and provide relevant materials in the implementation of the annual assessment work by the judicial administrative organs, and there are no false reports, concealment, forgery or destruction of relevant materials (on-site inspection, on-site questioning of notary agencies, notaries and other staff members, on-site access to relevant materials and notarial files, and on-site investigation and verification of the situation with relevant units and personnel).
11.4.1.3. Is the actual office space consistent with the address approved by the judicial administrative organ?
A. The actual office space of the notary public is consistent with the information stated in the original and duplicate of the practicing license (on-site inspection, comparison of information between the site and the practicing license);
B. If the office space is changed, it has been audited by the judicial administrative organ at the district level and approved by the judicial administrative organ at the municipal level (on-site inspection, on-site comparison with the practice license information).
11.4.1.4. Does the practice place meet the purpose of practice and whether the practice environment is suitable for notaries to practice?
A. The office space is only used for purposes related to notarization business, not for other production and business activities, and is not mixed with other companies, enterprises or institutions (on-site inspection);
B. Signboards should be hung at the door or entrance of the office, indicating the standardized name and house number of the notary office (on-site inspection);
C. The office space shall be provided with reasonable functional partitions, including offices, conference rooms (reception rooms), accounting rooms, archives rooms, etc. The office area shall be clean and tidy, with complete functional settings and orderly items (on-site inspection);
D. A bulletin board should be posted at a prominent position in the office, which includes the following contents: information of notaries with photos, charging standards for notarization services, service commitments, complaint supervision telephone numbers, etc. (on-site inspection);
E. The archives room is equipped with special filing cabinets and fire-proof, insect-proof and moisture-proof facilities, and the room is kept clean, tidy and ventilated; The completed notarized case files and related materials are stored in the archives (on-site inspection);
F the reception room is equipped with seats, drinking fountains, paper cups, pens and other necessary items (on-site inspection);
G. The office space shall be equipped with necessary office equipment (on-site inspection), including office telephone, copier, fax machine and printer.
11.4.1.5. Is it standard to establish and implement business management system?
A. The notarization institution has established a business management system (text of on-site inspection system);
B whether the business management system is complete includes the following contents (text of on-site inspection system):
1) The notarization institution has established a sound system of notarization business application, acceptance, examination, approval and certification;
2) The notarization institution has established a mechanism to supervise and examine the practice of notaries;
3) The notarization institution shall establish a collective discussion system for major and complicated notarization matters;
4) The notarization institution has established a notarization complaint, review and fault compensation handling mechanism;
5) The notarization institution has established a system of investigating the fault of practice, which clearly stipulates that the contractor notary and approver shall bear the fault liability for wrong certificates and false certificates, and stipulate specific punishment standards for different fault liabilities in accordance with the notarization law, and clarify the responsibility scope of the contractor and approver, which plays a guiding, standardizing and warning role.
C the notarization institution has records on the implementation of the business management system (on-site inspection).
11.4.1.6. Is it standard to establish and implement financial management system?
A the notarization institution has established a financial management system (text of on-site inspection system);
B whether the financial management system is complete includes the following contents (text of on-site inspection system):
1) The financial management system of notarization institutions should abide by financial discipline and financial discipline, strictly implement the prescribed charging standards, abide by the prescribed expenditure distribution principles, and establish a sound financial planning, approval and implementation system;
2) The financial management system of notarization institutions can reduce costs and expenses, increase accumulation and achieve balance of payments through effective financial system arrangement;
3) Establish and improve the internal accounting system in accordance with state regulations, and strengthen fund management and cost control;
4) Establish internal wage management system and social insurance systems such as development fund, welfare fund, reward fund, risk compensation fund, employee pension and medical care.
C the notarization institution has records on the implementation of the financial management system (on-site inspection).
11.4.1.7. Is it standard to establish and implement the file management system?
A. Notary institutions shall do a good job in filing and managing notarial documents in accordance with the Measures for Filing and Filing of Notary Documents and the Measures for the Administration of Notary Archives issued by the Ministry of Justice and the National Archives Bureau (on-site inspection of notarial archives, asking the person in charge of notary institutions and file management personnel);
B. A notarization institution may formulate a notarization file management system (on-site inspection system text) according to the Measures for Filing and Filing of Notary Documents and the Measures for the Management of Notary Files, combined with the actual work of the institution.
11.4.1.8. Number and qualification of practicing notaries
A. The notarization institution shall have at least two notaries (on-site inspection, off-site verification through the management information system of the judicial administrative organ);
B. The notary holds the notarial practice certificate issued by Beijing Municipal Bureau of Justice, and there is no alteration, mortgage, loan or transfer (on-site inspection);
C. The actual practice of the notary public is consistent with the registration information of the practice certificate (on-site inspection);
D. Notaries did not practice during the period when they stopped practicing, or continued to practice after their practice certificates were revoked (on-site inspection of notarization files, on-site inquiry to relevant parties, off-site verification through the management information system of judicial administrative organs);
E. After being punished by administrative punishment of stopping practicing or revoking the practicing certificate, the notary has immediately stopped handling the unfinished notarization business, and reported it to the notary office in time, and the notary office will inform the parties (on-site inspection of the notarization business handled by the personnel who have stopped practicing or revoked the practicing certificate, and the notification records of the notary office, etc.).
11.4.2. Business Behavior of Notary Public Institutions
11.4.2.1. Do you try to win notarization business by slandering other notarization institutions and notaries or paying kickbacks or commissions?
A. Notary institutions do not damage the commercial reputation and reputation of other notaries and notaries by means of unfair competition such as fabricating and disseminating false information or misleading information (on-site questioning the person in charge of notary institutions, notaries, assistant notaries and other relevant personnel, on-site inspection of web pages and publicity materials, and on-site telephone call back to the parties).
B. The notarization institution has no following behaviors of undertaking business by paying kickbacks, commissions and other improper means (on-site questioning the person in charge of the notarization institution, notaries, notaries’ assistants and other relevant personnel, on-site inspection of charging vouchers, and on-site telephone call back to the parties):
1) In order to undertake business, the notary office refunded a certain percentage of the fees charged to the payer as a "rebate", which was not clearly and truthfully recorded in the legally established financial accounts reflecting its production and business activities in accordance with the provisions of the financial accounting system, including not being recorded in the financial accounts, being transferred to other financial accounts or making false accounts.
2) Notary agencies pay kickbacks to units or individuals that help them undertake notarization business, or fees and other benefits with kickbacks in the name of notarization matters such as introduction fee, co-sponsorship fee, liaison fee and information fee.
11.4.2.2. Does it charge notarization fees in violation of the prescribed charging standards?
A. The notarization institution has made or adjusted the charging standard and independently made or adjusted the service charging standard with market-regulated price within the scope stipulated by the government guidance price, which has been announced to the public 30 days in advance, and has informed the Municipal Bureau of Justice and the Municipal Development and Reform Commission in writing (on-site inspection of publicity, off-site inspection of written notification materials submitted by the notarization institution);
B. The notarization institution shall collect the fees for the notarization services with government-guided prices in accordance with the Catalogue and Fees Standards of Notarial Services with Government-guided prices in Beijing, and the actual fees shall not exceed the fees standards set by the government. However, since November 30, 2021, the service items for proving economic contracts, agreements and proving property inheritance, gift and bequest will be charged according to the following adjusted standards of this Municipality (on-site verification of charging vouchers and on-site return visits to the parties):
1) The highest charging standard for the notarization service project of "certifying economic contracts and agreements": 0.24% will be charged for the part with a target amount of less than 1 million yuan (if it is less than 200 yuan in proportion, it will be charged in 200 yuan); 1 million yuan to 4 million yuan (inclusive), 0.16%; 0.024% will be charged for the part above 4 million yuan. The maximum cost of a single notarization business shall not exceed 10,000 yuan.
2) The highest charging standard for the inheritance, gift and bequest of real estate in the notarization service project of "Proof of property inheritance, gift and bequest": 80 yuan per square meter of building according to the area of benefit share. Proof of unilateral gift or donation, half of the charge. The total cost of handling the above notarization matters for a single residential property shall not exceed 10,000 yuan. The finished product price and preferential price (subject to the ownership certificate) are calculated according to the area of benefit share, with 40 yuan per square meter of bungalow and 60 yuan per square meter of building.
C. Old people who have reached the age of 70 when applying for notarization of wills shall not be charged notarization fees, and notarized wills shall be handled for them free of charge. Guaranteed personnel, severely disabled people without a fixed source of income apply for notarization, and apply for notarization matters such as relief funds, subsistence allowances, alimony and alimony, and are exempted from notarization fees (on-site verification of charging vouchers, on-site verification of the identification materials of the parties, on-site inspection of the types of notarization matters, and on-site return visits to the parties);
D. The fees charged by notarization institutions for notarization services with market-regulated prices (fees charged for notarization services other than the Catalogue and Fees Standards of Notarization Services with Government-guided Prices in Beijing and fees charged for other services other than notarization services in the process of providing notarization services for the parties, as entrusted or requested by the parties) are consistent with the fees charged for publicity to the society and submitted to the Municipal Development and Reform Commission and the Municipal Bureau of Justice, and a Confirmation Letter on Negotiation Fees for Notarization Services is signed with the parties (on-site verification of fee vouchers and on-site inspection of the confirmation letter)
E. Notary institutions strictly implement the relevant provisions of clearly marked prices, and have set up special columns in prominent positions of service places and the homepage of their websites (webpages) to publicize all information such as charging items, charging basis, charging standards, service contents, industry supervision and price complaint reporting telephone numbers, and take the initiative to accept social supervision, and at the same time do a good job in publicizing and explaining the charging policy of notarization services (on-site inspection of the publicity of office places and websites, and on-site return visits to the parties);
F. Notary institutions should establish a dynamic management mechanism for notarization service charges, strengthen statistical analysis and report filing of policy implementation, and report the development of notarization business in the previous year and the annual income and expenditure after legal audit to the Municipal Bureau of Justice and the Municipal Development and Reform Commission before the end of May each year, and submit them in writing (the written materials submitted by the off-site inspection notary institutions) if there are new service items or adjustment of charging standards;
G. Notary institutions can improve their own behavior norms, self-discipline and fair competition in the course of operation, without adding unnecessary certification items and increasing prices through circular certification and bundled services, without "charging fees" such as arbitrarily increasing charging items and adjusting charging standards, and without using the old and new charging standards as an opportunity to increase prices in disguise, shirk and refuse to certify, and make things difficult for the masses (on-site inspection of the actual operation behavior of notary institutions, on-site inquiry of the responsible persons and notaries of notarization institutions, and on-site visit to the parties).
11.4.2.3. Is a notarial certificate issued for untrue and illegal matters?
A. The notarization institution has an internal examination and approval system for notarization services, and defines the examination and approval authority, examination and approval categories, examination and approval procedures, examination and approval responsibilities, etc. (text of on-site inspection system);
B. After accepting the application for notarization, the notarization institution shall examine the following matters respectively according to the accreditation rules for different notarization matters (on-site inspection of notarization review opinions):
1) The number, identity, qualification to apply for the notarization and corresponding rights of the parties;
2) Whether the parties’ expression of will is true;
3) Whether the contents of the document applying for notarization are complete, whether the meaning is clear, and whether the signature and seal are complete;
4) Whether the certification materials provided are true, lawful and sufficient;
5) Whether the matters applied for notarization are true and legal.
C. In accordance with the Rules of Notarization Procedure (Revised in 2020), the notary office strictly performs the following review duties (on-site inspection of the explanatory materials or supplementary certification materials of the parties, transcripts of inquiry, transcripts of inspection, entrusted verification materials, collective discussion records of the notary office, work records, etc.):
1) If there are doubts about the authenticity and legality of the matters to be notarized, and the explanations of the parties or the supporting materials provided are considered insufficient, incomplete or doubtful, the parties may be required to make explanations or supplement supporting materials;
2) If the identity of the parties, the matters to be notarized and the certification materials provided by the parties need to be verified in accordance with the relevant accreditation rules or have doubts about it, it shall be verified, or a notary office in a different place shall be entrusted to verify it. When examining the identity of natural persons, we should use identification verification equipment and record the attached files.
3) During the examination, the notary office shall ask the parties concerned about the situation, explain the legal risks, put forward legal opinions and suggestions, and answer the questions of the parties; If it is found that there are major and complicated situations, it shall be discussed collectively by the notary public;
4) In the course of examination, the notarization institution considers that the contents of the documents applying for notarization are incomplete and inaccurate, and shall instruct the parties to make corrections or amendments. If a party refuses to make corrections or amendments, it shall indicate it in the work record.
D. For notarization matters that meet the requirements stipulated in the Notarization Law, Notarization Procedure Rules (Revised in 2020) and relevant accreditation rules, the undertaking notary shall prepare a notarial certificate, together with the documents to be certified, the certification materials provided by the parties, the materials for verification and the notarization examination opinions, and submit it to the person in charge of the notarization institution or the notary appointed by it for examination and approval, except for notarization matters that do not need to be examined and approved according to regulations:
1) Whether the matters and documents applied for notarization are true and legal;
2) Whether the certification materials of notarization matters are true, lawful and sufficient;
3) Whether the accreditation procedure complies with the provisions of the Notary Law, these rules and relevant accreditation rules;
4) Whether the content, expression and format of the notarial certificate to be issued comply with relevant regulations.
The person in charge of a notarization institution or a notary designated to be responsible for examination and approval shall not examine and approve the notarization matters undertaken by himself. The examination and approval of major and complicated notarization matters shall be submitted to the notarization institution for collective discussion before examination and approval; The discussion and the opinions formed shall be recorded and filed.
E. After receiving the application for reexamination put forward by the parties or interested parties, the notary office shall appoint a notary other than the original notary to conduct reexamination. Review conclusions and handling opinions shall be reported to the person in charge of the notarization institution for approval. When conducting a review, a notary office shall examine and verify the mistakes and reasons of the notarial certificate put forward by the applicant, and deal with them according to the following provisions (on-site inspection and review application, review conclusion and approval form for handling opinions, announcement of revocation of notarial certificate, review decision and notarial certificate after handling, on-site inspection of information input in the national notarization management system):
1) If the contents of the notarial certificate are legal and correct, and the handling procedures are correct, make a decision to maintain the notarial certificate;
2) If the contents of the notarial certificate are legal and correct, and only the testimony is expressed or the format is improper, the notarial certificate shall be withdrawn, corrected and reissued to the parties; If it cannot be recovered, a notarial certificate of correction shall be issued separately;
3) If the basic contents of the notarial certificate are illegal or inconsistent with the facts, a decision shall be made to revoke the notarial certificate;
4) If part of the notarial certificate is illegal or inconsistent with the facts, a supplementary notarial certificate may be issued to revoke the contents of the certificate for the illegal or inconsistent part; You can also withdraw the notarial certificate, delete and correct the illegal or inconsistent parts, and then reissue them to the parties;
5) The contents of the notarial certificate are legal and correct, but in case of violation of procedural provisions and lack of necessary procedures in the process of handling, the missing procedures and procedures shall be supplemented; If the notarization procedure cannot be completed or seriously violated, the notarization certificate shall be revoked. The revoked notarial certificate shall be withdrawn and announced, and the notarial certificate shall be invalid from the beginning. Where a notary office revokes a notarial certificate or issues a notarial certificate with corrections, it shall make a decision on revocation or issue a notarial certificate with corrections, and report it to the local notary association for the record and enter it into the national notary management system.
11.4.2.4. Does it damage or tamper with notarized documents or notarized files?
A. The notarial institution shall manage notarial documents and notarial files in strict accordance with the Measures for Filing and Filing of Notary Documents and the Measures for the Administration of Notary Files, and the notarial documents and notarial files shall be kept intact and standardized, without any of the following circumstances (on-the-spot sampling of notarial files shall be conducted to check the materials of notarial documents and the preservation of notarial files, and the person in charge of the notarial institution and the file management personnel shall be asked on the spot):
1) All documents and materials used for notarization, such as certificates, transcripts of conversations and correspondence documents, are in short supply (the page number of the case file is interrupted, inconsistent with the contents in the volume, etc.) or have been altered, added, deleted, defaced or replaced;
2) The original and auxiliary volumes of notarial documents are unpacked, the volumes, boxes, directories and reference tables in the volumes are altered, deleted and defiled, the notarial physical files and audio-visual archives are damaged and destroyed, and the information described in the attached words such as physical evidence photos, CDs, audio tapes and videos is altered, deleted and so on.
B. Archivists can regularly check and count files, take timely preventive measures for files that are damaged, moth-eaten, bitten by rats, deteriorated and faded, and repair and copy them (on-site access to records of file inspection and list work, on-site inspection of file repair, and on-site questioning of the person in charge of notary public institutions and file managers).
C. After the notarization file is filed, if the notarization institution finds that there are errors in the notarial certificate, it will make corrections or amendments according to the procedure, and there is no case of alteration, addition or deletion on the original notarial certificate that has been filed (refer to the supplementary certificate or amendment materials on site).
11.4.2.5. Whether to disclose state secrets, business secrets or personal privacy that you know in your practice?
A. The notarization institution has a management system (text of on-site inspection system) to prevent the disclosure of state secrets, commercial secrets or personal privacy of the parties;
B the publicity web pages and publicity materials of the notary public have no contents involving state secrets, commercial secrets of the parties or personal privacy (on-site inspection of web pages and publicity materials);
C. The notary public and its notaries have not disclosed state secrets, business secrets or personal privacy known in their practice activities through the Internet, WeChat, SMS, etc. (ask the person in charge of the notary public and the notary on the spot);
D. Other staff members of the notarization institution and relevant personnel exposed to the notarization business have not disclosed the state secrets, business secrets or personal privacy they have learned in participating in the notarization business (ask other staff members of the notarization institution and relevant personnel exposed to the notarization business on the spot);
E. Notary institutions can keep notarized matters involving state secrets and wills as secret files (on-site inspection of the storage of secret files).
12. Administrative inspection of notaries
12.1. Inspection object
greffier
12.2. Inspection method
On-site inspection, license inspection, on-site inquiry, information access, off-site inspection, and other means.
12.3. Inspection frequency
In principle, according to the annual law enforcement inspection plan (website publicity).
12.4. Inspection contents and standards
12.4.1. Professional qualification of notaries
12.4.1.1. Have you obtained a notarial practice certificate?
12.4.1.2. Is the registration information of the practice institution and the notary public’s practice certificate consistent?
12.4.2. Practice of Notaries
12.4.2.1. Do you try to win notarization business by slandering other notarization institutions and notaries or paying kickbacks or commissions?
12.4.2.2. Do you practice in two or more notary offices at the same time?
12.4.2.3. Are you engaged in other paid occupations?
12.4.2.4. Do you handle notarization for yourself and your close relatives, or notarization with interests of yourself and your close relatives?
12.4.2.5. Whether to issue a notarial certificate privately?
12.4.2.6. Is a notarial certificate issued for untrue and illegal matters?
12.4.2.7. Are there any signs of damage or tampering in notarized documents or files?
12.4.2.8. Whether to disclose state secrets, business secrets or personal privacy that you know in your practice?
12.4.2.9. Whether to seize or misappropriate notarization fees or seize or steal special notarization articles?
12.4.2.10. Have you ever been subjected to criminal punishment for intentional crime or dereliction of duty?
Three, the administrative confirmation discretion benchmark
1. Public lawyers management institutions for the record.
1.1. Implementation subject
Subordinate units: accepted by the District Judicial Bureau and finalized by the Municipal Judicial Bureau.
Municipal units and units stationed in the central government: accepted and finalized by the Municipal Bureau of Justice.
1.2. Handling basis
Opinions on Implementing the Legal Adviser System and the Lawyer System of Public Lawyer Companies (No.30 [2016] of the Central Office);
Implementation Plan for Implementing the Lawyer System of Public Lawyer Companies (Beijing Office Zi [2017] No.8);
Measures for the Administration of Practice Certificates of Lawyers and Law Firms (revised in 2019);
Measures for the Administration of Public Lawyers (Si Fa Tong [2018] No.131).
1.3. Application materials
A. application for filing by the public lawyer management institution;
B. The approval document for the establishment of this unit, that is, the certification material for confirming the nature of this unit (the vertical management of the central organ and the agency shall provide the management attribute materials with the superior unit);
C. unified social credit code certificate;
D. seal of management organization.
1.4. Processing time limit
The legal time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
1.5. Processing results
The application materials are complete, the contents are true and effective, and the filing results will be informed by telephone.
1.6. Charges
No charge.
1.7. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
2. Issuance of work permit for public lawyers
2.1. Implementation subject
Subordinate units: accepted by the District Judicial Bureau and finalized by the Municipal Judicial Bureau.
Municipal units and units stationed in the central government: accepted and finalized by the Municipal Bureau of Justice.
2.2. Handling basis
Opinions on Implementing the Legal Adviser System and the Lawyer System of Public Lawyer Companies (No.30 [2016] of the Central Office);
Implementation Plan for Implementing the Lawyer System of Public Lawyer Companies (Beijing Office Zi [2017] No.8);
Measures for the Administration of Practice Certificates of Lawyers and Law Firms (revised in 2019);
Measures for the Administration of Public Lawyers (Si Fa Tong [2018] No.131).
2.3 Application materials
A. the identity card of the people’s Republic of China;
B. Legal professional qualification certificate or lawyer qualification certificate;
C. The unit’s review opinions on the applicants of public lawyers and corporate lawyers (those who have had lawyer practice experience (including social lawyers and public lawyers) shall fill in the "time of first practice" in the application information, which shall be clearly indicated in the practice experience;
D. Other materials (if you have had professional experience as a judge, prosecutor or lawyer, please provide relevant supporting materials, such as approval documents, copies of work permits, screenshots of information published on the Internet by the former industry (unit), etc.).
Note: Before filing, make sure that the unit has handled the business of "filing with public lawyer management agency". After the filing of the institution is completed, the business application for "issuance of public lawyer’s work permit" can be filed in the name of the unit.
2.4. Processing time limit
The legal time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
2.5. Processing results
After passing the examination, a lawyer’s work permit will be issued, which will be mailed directly by the municipal unit and mailed to the District Judicial Bureau by the district judicial bureau, which will notify the applicant.
2.6. Charges
No charge.
2.7. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
3. Cancellation of work permit of public lawyer
3.1. Implementation subject
Subordinate units: accepted by the District Judicial Bureau and finalized by the Municipal Judicial Bureau.
Municipal units and units stationed in the central government: accepted and finalized by the Municipal Bureau of Justice.
3.2. Handling basis
Opinions on Implementing the Legal Adviser System and the Lawyer System of Public Lawyer Companies (No.30 [2016] of the Central Office);
Implementation Plan for Implementing the Lawyer System of Public Lawyer Companies (Beijing Office Zi [2017] No.8);
Measures for the Administration of Practice Certificates of Lawyers and Law Firms (revised in 2019);
Measures for the Administration of Public Lawyers (Si Fa Tong [2018] No.131).
3.3. Application materials
A. Cancellation materials of company (public office) lawyers (review opinions of the unit on the cancellation of public office lawyers);
B lawyer’s work permit (the original lawyer’s work permit should be sent back when submitting the application. If the certificate is lost, a statement should be published in the newspaper, and the contents of the header and statement should be cut out and pasted on A4 paper.
3.4. Processing time limit
The legal time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
3.5. Processing results
The application materials are complete, the contents are true and valid, and the cancellation is approved.
3.6. Charges
No charge.
3.7. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
4. The company’s lawyer management organization for the record.
4.1. Implementation subject
District-owned enterprises: accepted by the District Judicial Bureau and finalized by the Municipal Judicial Bureau.
The establishment of enterprises and municipal enterprises by the central government in Beijing: accepted and finalized by the Municipal Bureau of Justice.
4.2. Handling basis
Opinions on Implementing the Legal Adviser System and the Lawyer System of Public Lawyer Companies (No.30 [2016] of the Central Office);
Implementation Plan for Implementing the Lawyer System of Public Lawyer Companies (Beijing Office Zi [2017] No.8);
Measures for the Administration of Practice Certificates of Lawyers and Law Firms (revised in 2019);
Measures for the Administration of Corporate Lawyers (Sfa Tong [2018] No.131).
4.3 Application materials
A. the filing application of the company’s lawyer management institution;
B. Materials of this unit nature;
The first category: state-owned enterprises at all levels.
1) If the applicant is a first-class central enterprise in Kyoko (branch), it shall submit the attribute certificate of the first-class central enterprise: the directory of the State Council State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission, the approval documents of the central ministries and commissions (and units at the same level) on the establishment of the central enterprise or other supporting materials (choose one, please mark the central enterprise in the directory of SASAC);
2) If the applicant is a city (district) owned by a state-owned enterprise, submit the list of SASAC of the city (district), the approval document for establishment or other supporting materials (choose one, please indicate the enterprise in the list of SASAC). City (District) is a subsidiary (branch) of state-owned enterprises at all levels can apply separately, but also by the city (District) is a unified declaration of state-owned enterprises, unified management. If a subsidiary (branch) company declares separately, it shall submit the certificate that the city (district) is a state-owned enterprise.
3) Enterprises established by other state-level and central-level units are incorporated in Kyoko (branches), and other state-owned enterprises established in Beijing and District shall refer to the preceding two paragraphs. If the nature of the unit is unknown, submit the asset registration certificate or other documents to prove the state contribution.
The second category: pilot private enterprises in Beijing
1) Materials of unit nature (including foreign investment, it shall be accompanied by an explanation and the enterprise registration information of the applicant (business license, enterprise report of the national enterprise credit information publicity system or screenshot of the website);
2) Top 100 list of private enterprises selected by Beijing Federation of Industry and Commerce in 2)XX (screenshot of documents or website of the Federation of Industry and Commerce, and the enterprise shall be marked if a screenshot is provided);
3) Briefing on the operation of the unit (outlining the business, operating income, employees, copies of relevant qualification documents, operation of the legal department, etc.);
4) Commitment letter for private enterprises to participate in the pilot work of corporate lawyers.
C. unified social credit code certificate;
D. seal of management organization.
4.4. Processing time limit
The legal time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
4.5. Processing results
The application materials are complete, the contents are true and effective, and the filing results will be informed by telephone.
4.6. Charges
No charge.
4.7. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
5. Issuance of company lawyer’s work permit
5.1. Implementation subject
District-owned enterprises: accepted by the District Judicial Bureau and finalized by the Municipal Judicial Bureau.
The establishment of enterprises and municipal enterprises by the central government in Beijing: accepted and finalized by the Municipal Bureau of Justice.
5.2. Handling basis
Opinions on Implementing the Legal Adviser System and the Lawyer System of Public Lawyer Companies (No.30 [2016] of the Central Office);
Implementation Plan for Implementing the Lawyer System of Public Lawyer Companies (Beijing Office Zi [2017] No.8);
Measures for the Administration of Practice Certificates of Lawyers and Law Firms (revised in 2019);
Measures for the Administration of Corporate Lawyers (Sfa Tong [2018] No.131).
5.3 Application materials
A. the identity card of the people’s Republic of China;
B. legal professional qualification certificate;
C. The unit’s review opinions on the applicants of public lawyers and corporate lawyers (those who have had lawyer practice experience (including social lawyers and public lawyers) shall fill in the "time of first practice" in the application information, which shall be clearly indicated in the practice experience;
D. Other materials (if you have had professional experience as a judge, prosecutor or lawyer, please provide relevant supporting materials, such as approval documents, copies of work permits, screenshots of information published on the Internet by the former industry (unit), etc.).
5.4. Processing time limit
The legal time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
5.5. Processing results
Pass the examination and issue a lawyer’s work permit. The municipal units directly mail it, and the district units mail it to the District Judicial Bureau, which will notify the applicant.
5.6. Charges
No charge.
5.7. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
6. Cancellation of company lawyer’s work permit
6.1. Implementation subject
District-owned enterprises: accepted by the District Judicial Bureau and finalized by the Municipal Judicial Bureau.
The establishment of enterprises and municipal enterprises by the central government in Beijing: accepted and finalized by the Municipal Bureau of Justice.
6.2. Basis for handling
Opinions on Implementing the Legal Adviser System and the Lawyer System of Public Lawyer Companies (No.30 [2016] of the Central Office);
Implementation Plan for Implementing the Lawyer System of Public Lawyer Companies (Beijing Office Zi [2017] No.8);
Measures for the Administration of Practice Certificates of Lawyers and Law Firms (revised in 2019);
Measures for the Administration of Public Lawyers (Si Fa Tong [2018] No.131).
6.3 Application materials
A. Cancellation materials of company (public office) lawyers (the unit’s review opinions on the cancellation of company lawyers);
B lawyer’s work permit (the original lawyer’s work permit should be sent back when submitting the application. If the certificate is lost, a statement should be published in the newspaper, and the contents of the header and statement should be cut out and pasted on A4 paper.
6.4. Processing time limit
The legal time limit is 30 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
6.5. Processing results
The application materials are complete, the contents are true and valid, and the cancellation is approved.
6.6. Charges
No charge.
6.7. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
7. A certificate issued by a lawyer who applies to change his practice institution that does not meet the requirements of Article 21 of the Measures for the Administration of Lawyers’ Practice.
7.1. Implementation subject
District justice bureau.
7.2. Handling basis
Articles 20 and 21 of the Administrative Measures on Lawyers’ Practice (revised in 2016).
7.3 Application materials
A. materials on the termination of employment relationship between the applicant and the original practice institution;
B. Handling the letter of commitment to inform the lawyer that he does not have the evidence in Article 21 of the Measures for the Administration of Lawyers’ Practice.
7.4. Processing time limit
The legal time limit is 5 working days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
7.5. Processing results
The application materials are complete and the contents meet the requirements, and a certificate that the applicant does not have the prescribed circumstances is issued.
7.6. Charges
No charge.
7.7. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
Four, the administrative payment discretion benchmark
1. Examination and approval of citizens’ applications for legal aid
1.1. Implementation subject
Municipal Bureau of Justice and District Bureau of Justice.
1.2. Handling basis
People’s Republic of China (PRC) Legal Aid Law (2021)
Legal Aid Ordinance (2003)
Regulations of Beijing Municipality on Legal Aid (2008)
Procedures for Handling Legal Aid Cases (revised in 2023)
Opinions on Implementing the Informing Commitment System of Legal Aid in Beijing (Trial) (J.S.F. [2022] No.33)
1.3. Application materials
A resident identity card or other valid identification certificate, and the certificate of power of attorney shall be submitted if the application is made on behalf of the applicant;
B. Statement of family members and financial difficulties of legal aid applicants;
C. Letter of commitment to inform the legal aid application;
D. authorization letter for verification of legal aid applicant’s notification commitment
E. case materials for applying for legal aid.
1.4. Processing time limit
The legal time limit is 7 days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
1.5. Processing results
A. If the application materials submitted by the applicant meet the requirements, it shall be accepted, and a written certificate of receipt of the application materials shall be issued to the applicant, indicating the name, quantity and date of receipt of the application materials; If the application materials submitted by the applicant are incomplete, it shall inform the applicant of all the contents that need to be supplemented at one time, or require the applicant to make necessary explanations. If the applicant fails to supplement the materials or make explanations as required, it shall be deemed to have withdrawn the application; If the application matters do not fall within the scope of acceptance of this legal aid institution, the applicant shall be informed to apply to the legal aid institution with jurisdiction or to the relevant department for handling.
B review the application for legal aid within seven days from the date of receiving it, and make a decision on whether to grant legal aid. The time required for the applicant to supplement the materials and make explanations, and the time for the legal aid institution to request the cooperation and verification of the legal aid institution in different places shall not be included in the review period.
C. Upon examination, those who meet the conditions for legal aid shall be decided to give legal aid, and a written decision on granting legal aid shall be made; Those who do not meet the conditions for legal aid shall decide not to grant legal aid, and make a decision on not granting legal aid. The decision not to grant legal aid shall specify the reasons for not granting legal aid and the ways and means for the applicant to raise objections.
1.6. Charges
No charge.
1.7. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
2. Payment of legal aid subsidies
2.1. Implementation subject
Municipal Bureau of Justice and District Bureau of Justice.
2.2. Handling basis
People’s Republic of China (PRC) Legal Aid Law (2021)
Legal Aid Ordinance (2003)
Regulations of Beijing Municipality on Legal Aid (2008)
Procedures for Handling Legal Aid Cases (revised in 2023)
Measures of Beijing Municipality on Subsidies for Legal Aid (J.S.F. [2018] No.86)
Notice of Beijing Municipal Bureau of Justice and Beijing Municipal Bureau of Finance on Relevant Matters Concerning the Adjustment of the Payment of Legal Aid Subsidies (No.27 [2023] of the Secretary for Justice)
2.3 Application materials
A. notice of assignment of legal aid;
B. agency/defense agreement;
C. power of attorney;
D. notification of the rights, obligations and risks of the recipient;
E. transcript of conversation;
F. marking transcripts;
G. marking materials;
H. transcripts of court hearings;
I. proxy words and cross-examination opinions;
J. adjudicative documents or staged work descriptions;
K. Notification/report records of legal aid cases;
L. legal aid case closing report form.
2.4. Processing time limit
The legal time limit is 30 days. (The commitment time limit shall be subject to the publicity on the website or service hall)
2.5. Processing results
If the filing materials for closing the case are complete and standardized, legal aid subsidies shall be paid to legal aid personnel in a timely manner. (Confirmation Form of Subsidies for Cases Closed by Legal Aid Center and Confirmation Form of Subsidies for Cases Closed by Notifying Defenders)
2.6. Charges
No charge.
2.7. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
3. The people’s mediators subsidies
3.1. Implementation subject
In principle, the first trial in Shangjie Township and the final trial at the district level can be adjusted according to the actual work in each district and made public.
3.2. Handling basis
People’s Republic of China (PRC) People’s Mediation Law (2010)
3.3. Application materials
Handle the case file.
3.4. Processing time limit
The legal time limit is 30 days.
3.5. Processing results
The materials are complete, true and effective, filled in completely and clearly, and the payment amount conforms to the subsidy provisions of people’s mediation cases. (Case Subsidy Confirmation Form)
3.6. Charges
No charge.
3.7. Quantitative restrictions
Unlimited
































































































![[Guangming Daily Science and Technology World]](http://www.yijiusc.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/jPOZmwYF.jpg)
![[Guangming Daily Science and Technology World]](http://www.yijiusc.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/5Ut38bB3.jpg)
 Only indicate
Only indicate